FAQs
Have questions? The answer is probably here!
Can you feel an earthquake if you're in a cave? Is it safer to be in a cave during an earthquake?
There is nothing different about a cave that would make it immune to the shaking from an earthquake. Just as there are safer and less safe places to be on the surface of the earth during an earthquake, there are also various characteristics inside caves that make some cave locations safer or less safe than others. First of all, whether or not you feel an earthquake in a cave depends chiefly upon...
What are earthquake lights?
Phenomena such as sheet lightning, balls of light, streamers, and steady glows, reported in association with earthquakes are called earthquake lights (EQL). Geophysicists differ on the extent to which they think that individual reports of unusual lighting near the time and epicenter of an earthquake actually represent EQL: some doubt that any of the reports constitute solid evidence for EQL...
What are tsunamis?
Tsunamis are ocean waves triggered by: Large earthquakes that occur near or under the ocean Volcanic eruptions Submarine landslides Onshore landslides in which large volumes of debris fall into the water Scientists do not use the term "tidal wave" because these waves are not caused by tides. Tsunami waves are unlike typical ocean waves generated by wind and storms, and most tsunamis do not "break"...
Does fracking cause earthquakes?
Most induced earthquakes are not directly caused by hydraulic fracturing (fracking). The recent increase in earthquakes in the central United States is primarily caused by disposal of waste fluids that are a byproduct of oil production. Wastewater disposal wells typically operate for longer durations and inject much more fluid than is injected during the hydraulic fracturing process, making them...
Do all wastewater disposal wells induce earthquakes?
No. Of more than 150,000 Class II injection wells in the United States, roughly 40,000 are waste fluid disposal wells for oil and gas operations. Only a small fraction of these disposal wells have induced earthquakes that are large enough to be of concern to the public. Learn more: USGS Induced Earthquakes EPA's Underground Injection Control (UIC) program
Is it possible to anticipate whether a planned wastewater disposal activity will trigger earthquakes that are large enough to be of concern?
Currently, there are no methods available to do this in a definitive sense. We have developed methods that use injection information to help us determine whether injection activities might cause induced earthquakes and rule out other injection activities that are unlikely to induce earthquakes, but we cannot say either with certainty. There are a number of conditions that increase the likelihood...
How does the injection of fluid at depth cause earthquakes?
The fluid that is injected at depth is sometimes hydraulically connected to faults. When this happens, fluid pressures increase within the fault, counteracting the frictional forces on faults. This makes earthquakes more likely to occur on them. An analog to this system is an air hockey table. When an air hockey table is off, the puck does not move readily, but when the table is on, the puck...
How large are the earthquakes induced by fluid injection?
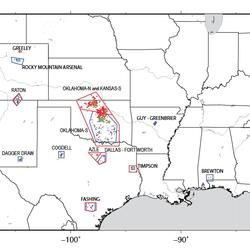
The largest earthquake induced by fluid injection that has been documented in the scientific literature was a magnitude 5.8 earthquake on September 23, 2016 in central Oklahoma. Four magnitude 5+ earthquakes have occurred in Oklahoma, three of which occurred in 2016. In 2011, a magnitude 5.3 earthquake was induced by fluid injection in the Raton Basin, Colorado. Earthquakes with magnitudes between...
Are earthquakes induced by fluid-injection activities always located close to the point of injection?
No. Given enough time, the pressure increase created by injection can migrate substantial horizontal and vertical distances from the injection location. Induced earthquakes can occur 10 or more miles from injection wells. Induced earthquakes can also occur a few miles below injection wells. Learn more: USGS Induced Earthquakes
Is there any possibility that a wastewater injection activity could interact with a nearby fault to trigger a major earthquake that causes extensive damage over a broad region?
So far, there is no documented example linking injection operations to triggering of major earthquakes. However, we cannot eliminate this possibility. Other human activities--for example oil production in Uzbekistan--have induced M7+ earthquakes. Learn more: USGS Induced Earthquakes
Does the production of oil and gas from shales cause earthquakes? If so, how are the earthquakes related to these operations?
To produce oil and gas from shale formations, it is necessary to increase the interconnectedness of the pore space (permeability) of the shale so that the gas can flow through the rock mass and be extracted through production wells. This is usually done by hydraulic fracturing ("fracking"). Fracking intentionally causes small earthquakes (magnitudes smaller than 1) to enhance permeability, but it...
Oklahoma has had a surge of earthquakes since 2009. Are they due to fracking?
Beginning in 2009, Oklahoma experienced a surge in seismicity. This surge was so large that its rate of magnitude 3 and larger earthquakes exceeded California’s from 2014 through 2017. While these earthquakes have been induced by oil and gas related process, few of these earthquakes were induced by fracking. The largest earthquake known to be induced by hydraulic fracturing in Oklahoma was a M3.6...