"Lake Mead — Clear and Vital" is a thirteen minute documentary relating the crucial role of science in maintaining high water quality in Lake Mead. The program was produced coincident with release of the Lakes Mead and Mohave Circular a USGS publication covering past and on-going research in the lakes and tributaries of the Lake Mead National Recreation Area.
Near-Continuous Depth-Dependent Water-Quality Data from Automatic Profiling Systems and Meteorological Data, Lakes Mead and Mohave, Arizona and Nevada, USA
The Colorado River is one of the most intensely used rivers in the western United States, providing recreational watercraft activities and domestic drinking, industrial, and irrigation water for over 22 million users in the desert southwest. The quality of this water must be maintained to guarantee a reliable and safe resource for its many uses. The Colorado River provides an estimated 97 percent of the inflow into Lake Mead. Lake Mohave is downstream of Lake Mead (separated by the Hoover Dam) and is part of the Lower Colorado River system.

The USGS Nevada Water Science Center, in cooperation with its partners, collected near-continuous depth-dependent water-quality profile data from October 2000 through September 2016 at monitoring stations located throughout Lake Mead National Recreation Area (LAKE). In addition, hourly-averaged meteorological data were also collected from October 2004 through March 2017 at selected stations. The data were collected as part of a multi-agency monitoring network maintained to provide resource managers with baseline water-quality data and to gain a better understanding of the hydrodynamics of the waters of LAKE.
Data Collection
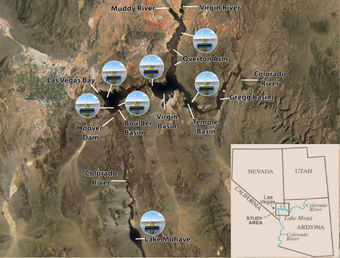
The water-quality stations were as follows: Temple Basin near the Temple Bar Marina; Overton Arm Basin near the confluence of the Muddy and Virgin Rivers; Virgin Basin, near the Narrows, which separates the Virgin and Boulder Basins; Las Vegas Bay (Sites 1-4), near the confluence of the Las Vegas Wash; near Sentinel Island, Boulder Basin; Boulder Basin, approximately 2.5 miles upstream of Hoover Dam; and Lake Mohave, south southwest of the lake. Meteorological data were collected at the following stations: Temple Basin, Overton Arm Basin, Virgin Basin, Las Vegas Bay Site 4, Sentinel Island, and Boulder Basin.
The following water-quality data were collected using a multiparameter sonde as part of an automated profiling system:
- depth,
- water temperature,
- specific conductivity,
- pH,
- dissolved oxygen, and
- turbidity
In addition, the following meteorological data were collected:
- air temperature,
- relative humidity,
- barometric pressure,
- solar radiation, and
- wind speed and direction
Below are multimedia items associated with this project.
"Lake Mead — Clear and Vital" is a thirteen minute documentary relating the crucial role of science in maintaining high water quality in Lake Mead. The program was produced coincident with release of the Lakes Mead and Mohave Circular a USGS publication covering past and on-going research in the lakes and tributaries of the Lake Mead National Recreation Area.
Below are publications associated with this project.
Lake Mead--clear and vital Lake Mead--clear and vital
Evaluating lake stratification and temporal trends by using near-continuous water-quality data from automated profiling systems for water years 2005-09, Lake Mead, Arizona and Nevada Evaluating lake stratification and temporal trends by using near-continuous water-quality data from automated profiling systems for water years 2005-09, Lake Mead, Arizona and Nevada
A synthesis of aquatic science for management of Lakes Mead and Mohave A synthesis of aquatic science for management of Lakes Mead and Mohave
Physical and Chemical Water-Quality Data from Automatic Profiling Systems, Boulder Basin, Lake Mead, Arizona and Nevada, Water Years 2001-04 Physical and Chemical Water-Quality Data from Automatic Profiling Systems, Boulder Basin, Lake Mead, Arizona and Nevada, Water Years 2001-04
The Colorado River is one of the most intensely used rivers in the western United States, providing recreational watercraft activities and domestic drinking, industrial, and irrigation water for over 22 million users in the desert southwest. The quality of this water must be maintained to guarantee a reliable and safe resource for its many uses. The Colorado River provides an estimated 97 percent of the inflow into Lake Mead. Lake Mohave is downstream of Lake Mead (separated by the Hoover Dam) and is part of the Lower Colorado River system.

The USGS Nevada Water Science Center, in cooperation with its partners, collected near-continuous depth-dependent water-quality profile data from October 2000 through September 2016 at monitoring stations located throughout Lake Mead National Recreation Area (LAKE). In addition, hourly-averaged meteorological data were also collected from October 2004 through March 2017 at selected stations. The data were collected as part of a multi-agency monitoring network maintained to provide resource managers with baseline water-quality data and to gain a better understanding of the hydrodynamics of the waters of LAKE.
Data Collection
The water-quality stations were as follows: Temple Basin near the Temple Bar Marina; Overton Arm Basin near the confluence of the Muddy and Virgin Rivers; Virgin Basin, near the Narrows, which separates the Virgin and Boulder Basins; Las Vegas Bay (Sites 1-4), near the confluence of the Las Vegas Wash; near Sentinel Island, Boulder Basin; Boulder Basin, approximately 2.5 miles upstream of Hoover Dam; and Lake Mohave, south southwest of the lake. Meteorological data were collected at the following stations: Temple Basin, Overton Arm Basin, Virgin Basin, Las Vegas Bay Site 4, Sentinel Island, and Boulder Basin.

The following water-quality data were collected using a multiparameter sonde as part of an automated profiling system:
- depth,
- water temperature,
- specific conductivity,
- pH,
- dissolved oxygen, and
- turbidity
In addition, the following meteorological data were collected:
- air temperature,
- relative humidity,
- barometric pressure,
- solar radiation, and
- wind speed and direction
Below are multimedia items associated with this project.
"Lake Mead — Clear and Vital" is a thirteen minute documentary relating the crucial role of science in maintaining high water quality in Lake Mead. The program was produced coincident with release of the Lakes Mead and Mohave Circular a USGS publication covering past and on-going research in the lakes and tributaries of the Lake Mead National Recreation Area.
"Lake Mead — Clear and Vital" is a thirteen minute documentary relating the crucial role of science in maintaining high water quality in Lake Mead. The program was produced coincident with release of the Lakes Mead and Mohave Circular a USGS publication covering past and on-going research in the lakes and tributaries of the Lake Mead National Recreation Area.
Below are publications associated with this project.


