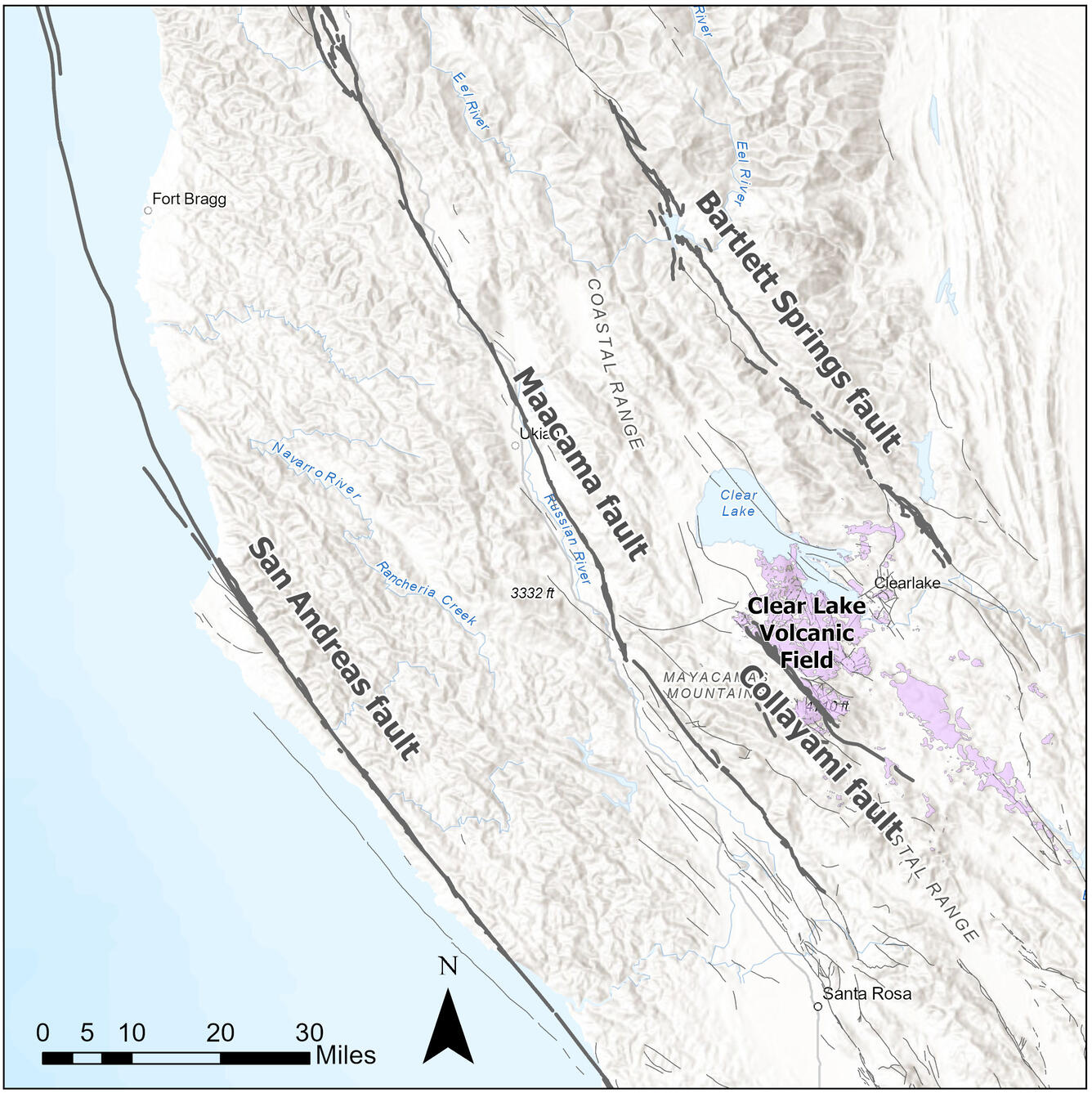
Faults bounding the Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Detailed Description
The Clear Lake volcanic field erupted in association with and within the San Andreas Fault Zone. Although the San Andreas fault is the hallmark fault associated with the transform tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American plates, the “boundary” between plates is more accurately described by a zone of faulting than by a single fault. This zone of dominantly right-lateral transform faults accommodates the differential lateral movement between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates. Bends in these faults can lead to mountain building and basin formation, with the direction of the bend determining which landform is created. The mountains and basins into and onto which the Clear Lake volcanic field erupted are a result of movement along these faults. This figure shows the major transform structures in the region of the Clear Lake volcanic field – the Bartlett Springs and Maacama faults are the major bounding faults of the field. Both are right-lateral transform faults, just like the San Andreas, which can be seen to the west of the volcanic field.
Sources/Usage
Public Domain.

