USGS EcoNews | Fall 2024 - Vol. 5 | Issue 4
The final issue of EcoNews for 2024 highlights several tools that aid natural resource managers with on the ground decisions. From frameworks for effective restoration to accessible data and tools for pragmatic decisions, the USGS strives to provide practical science for our partners.
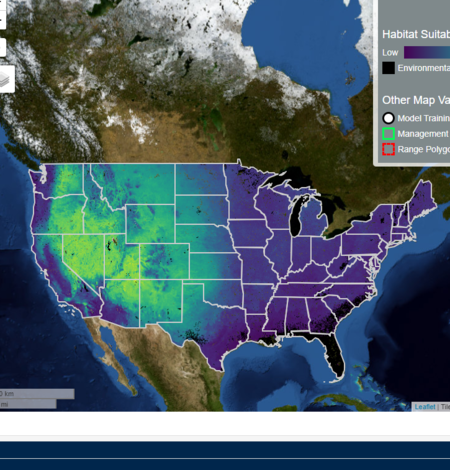
Developing habitat models for rare plants to inform decision making on multiple-use public lands
Public lands provide important habitat for many rare plants. However, public lands often need to accommodate many other uses, including traditional and renewable energy development, in addition to conservation. We are working with the Bureau of Land Management to coproduce ensemble habitat suitability models that can inform agency planning and permitting decisions that may impact rare plants.
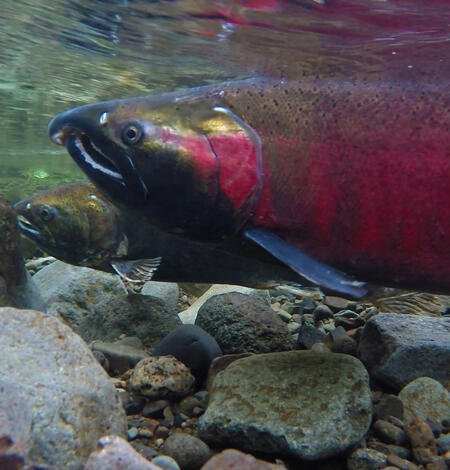
Re-Thinking Salmon Counts: Research Uses Environmental DNA to Fill Monitoring Gaps in Alaskan Salmon Runs
With climate change and extreme weather complicating traditional salmon monitoring efforts, researchers funded by the U.S. Geological Survey are testing environmental DNA (eDNA) sampling techniques to bolster salmon monitoring and management in the Yukon River.
Project ROAM
USGS is identifying, testing, and verifying rapid methods for rangeland assessment and restoration monitoring. Our methods complement existing monitoring frameworks, providing land management agencies with timely information that can be used to determine if restoration investments are successful, and why. Standardization, validation, repeatability, data management, and training are at the core of...
Trees in cities are beyond shady
DENVER — Hotter areas can actually be the biggest winners when it comes to the difference a tree can make when temperatures are sizzling.
INHABIT: A web tool for invasive plant management across the contiguous United States
INHABIT is a desktop-optimized web application and decision support tool with mapped and tabular summaries of habitat suitability models for over two hundred fifty terrestrial invasive plant species of management concern across the contiguous United States. It is the product of a scientist-practitioner partnership and is designed to facilitate enhanced invasive species management actions...
USGS Energy and Wildlife Research Year in Review
Covering studies published October 2023 through September 2024
U.S. Geological Survey climate science plan—Future research directions
Executive Summary Climate is the primary driver of environmental change and is a key consideration in defining science priorities conducted across all mission areas in the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Recognizing the importance of climate change to its future research agenda, the USGS’s Climate Science Steering Committee requested the development of a Climate Science Plan to identify...
Sustaining Horseshoe Crabs and Supporting Migratory Shorebirds in the Delaware Bay
USGS is developing predictive models to inform sustainable harvest of horseshoe crabs (Limulus polyphemus) in Delaware Bay to help managers make decisions to support needs of people and shorebirds including rufa red knot (Calidris canutus rufa).
NASA Partners with the Alaska CASC and Others to Make NASA Climate Data Tools More Accessible to Tribal and Indigenous Communities
NASA released a workshop report on the UNBOUND-FEW workshop series, which was facilitated in part by Tribal Resilience Learning Network staff from the Alaska CASC. The workshop report reveals key recommendations for making data tools more useful for climate adaptation planning.
The Powerhouse of USGS Paleo-research
Unravelling mysteries of the past, and helping project future patterns, by studying paleoclimate.
Statewide Assessment of Iowa Streams Links Landscape Characteristics to Antibiotic Resistance Signatures
U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) scientists conducted the first statewide assessment of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB), and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in streams (water column and bed sediment samples) across Iowa. Results indicated that ARB and ARGs were prevalent, and a combination of watershed characteristics (such as land use, livestock population, and human population)...
A new study predicts grizzly bear habitat use in the Bitterroot Ecosystem of Montana and Idaho
RESTON, Va. — A new study co-authored by scientists from the U.S. Geological Survey and Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks helps to identify where in the Bitterroot Ecosystem grizzly bears could call home through reintroduction or recolonization.
Coastal Wetland Vulnerability to Climate Change and Sea-Level Rise: Understanding Ecological Thresholds and Ecosystem Transformations
Eighteen USGS coastal scientists from all four coasts of the conterminous United States are working together to advance the understanding of climate change and sea-level rise impacts to coastal wetlands.