Does the Latest Earthquakes map show non-earthquake seismic events?
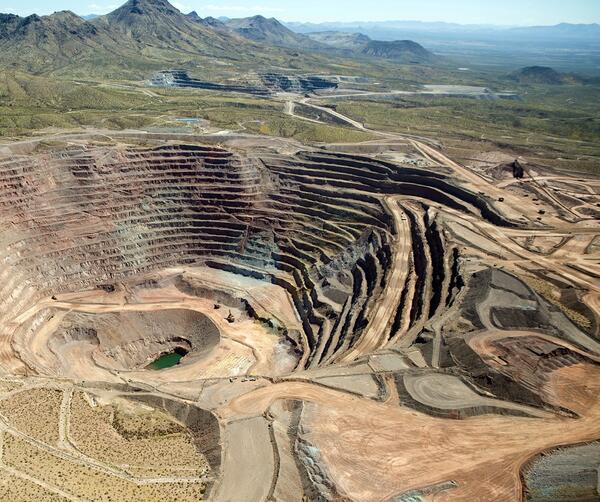
In addition to naturally occurring earthquakes, human activities such as mining and construction blasts can sometimes produce seismic waves large enough to be detected on the USGS national seismic network. These artificially-generated events have a different seismic ‘fingerprint’ from tectonic earthquakes, so they can be discerned by a seismologist when reviewed.
Specifically, small quarry blasts tend to have a shorter surface wave ‘echo’ than natural earthquakes. Seismologists also note if the blast was in an area NOT known for earthquakes and if it was located within 1-2 miles of an active quarrying operation. The USGS no longer does a systematic review of mining seismicity, but these events can sometimes be identified using certain criteria.
If we determine a seismic event to be a mining blast or some other non-earthquake event, we will designate it on our Latest Earthquakes map using a diamond icon. When searching the Earthquake Catalog, users can find non-earthquake events using ‘Advanced Options>Event Type’.
Additionally, IRIS (a USGS research partner) has an Exotic Seismic Events catalog.
Learn more:
Updated Date: February 20, 2025