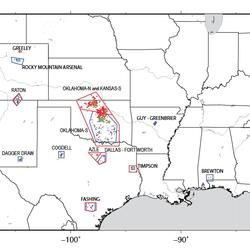
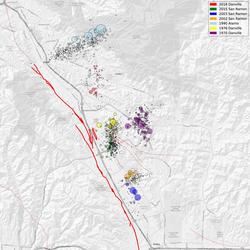
Foreshocks, aftershocks - what's the difference?
"Foreshock" and "aftershock" are relative terms.
Foreshocks are earthquakes that precede larger earthquakes in the same location. An earthquake cannot be identified as a foreshock until after a larger earthquake in the same area occurs.
Aftershocks are smaller earthquakes that occur in the same general area during the days to years following a larger event or "mainshock." They occur within 1-2 fault lengths away and during the period of time before the background seismicity level has resumed. As a general rule, aftershocks represent minor readjustments along the portion of a fault that slipped at the time of the mainshock. The frequency of these aftershocks decreases with time. Historically, deep earthquakes (>30 km) are much less likely to be followed by aftershocks than shallow earthquakes.
Learn More: Glossary of earthquake terms
Related
Where can I find earthquake educational materials? Where can I find earthquake educational materials?
Start with our Earthquake Hazards Education site. That includes: Earthquakes for Kids Cool Earthquake Facts Earthquake Science for Everyone Other good starting points include: State Geological Surveys for states in earthquake-prone regions The Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drills website SAGE (Seismological Facility for the Advancement of Geoscience), which is a non-profit consortium
Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes? Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes?
Earthquakes induced by human activity have been documented at many locations in the United States and in many other countries around the world. Earthquakes can be induced by a wide range of causes including impoundment of reservoirs, surface and underground mining, withdrawal of fluids and gas from the subsurface, and injection of fluids into underground formations. While most induced earthquakes...
What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms? What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms?
Aftershocks are a sequence of earthquakes that happen after a larger mainshock on a fault. Aftershocks occur near the fault zone where the mainshock rupture occurred and are part of the "readjustment process” after the main slip on the fault. Aftershocks become less frequent with time, although they can continue for days, weeks, months, or even years for a very large mainshock. A swarm, on the...
Earthquake hazards: A national threat Earthquake hazards: A national threat
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Program - investing in a safer future The USGS Earthquake Hazards Program - investing in a safer future
Foreshocks and aftershocks of the great 1857 California earthquake Foreshocks and aftershocks of the great 1857 California earthquake
The severity of an earthquake The severity of an earthquake
This dynamic earth: the story of plate tectonics This dynamic earth: the story of plate tectonics
Related
Where can I find earthquake educational materials? Where can I find earthquake educational materials?
Start with our Earthquake Hazards Education site. That includes: Earthquakes for Kids Cool Earthquake Facts Earthquake Science for Everyone Other good starting points include: State Geological Surveys for states in earthquake-prone regions The Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drills website SAGE (Seismological Facility for the Advancement of Geoscience), which is a non-profit consortium
Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes? Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes?
Earthquakes induced by human activity have been documented at many locations in the United States and in many other countries around the world. Earthquakes can be induced by a wide range of causes including impoundment of reservoirs, surface and underground mining, withdrawal of fluids and gas from the subsurface, and injection of fluids into underground formations. While most induced earthquakes...
What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms? What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms?
Aftershocks are a sequence of earthquakes that happen after a larger mainshock on a fault. Aftershocks occur near the fault zone where the mainshock rupture occurred and are part of the "readjustment process” after the main slip on the fault. Aftershocks become less frequent with time, although they can continue for days, weeks, months, or even years for a very large mainshock. A swarm, on the...