In this video excerpt, we see motion from two video surveillance cameras capturing continuous daytime video data on pupfish spawning, and as seen here, other occurrences. The cameras are positioned approximately four feet above the water surface and one underwater.
What is Devils Hole in Nevada?
Devils Hole is a tectonic cave developed in the discharge zone of a regional aquifer in south-central Nevada. The walls of this predominantly subaqueous (underwater) cavern are coated with dense vein calcite that precipitated from groundwater moving through the cavern. The stable isotopic content of the calcite provides a 500,000-year record of variations in temperature and other climate conditions. The data collected at Devils Hole has been an important contribution to our understanding of the onset and duration of ice ages, and has spurred renewed interest in using cave deposits as archives of paleoclimate.
Related
How can I find the depth to the water table in a specific location? How can I find the depth to the water table in a specific location?
The depth to the water table can change (rise or fall) depending on the time of year. During the late winter and spring when accumulated snow starts to melt and spring rainfall is plentiful, water on the surface infiltrates into the ground and the water table rises. When water-loving plants start to grow again in the spring and precipitation gives way to hot, dry summers, the water table falls...
What is the Ground Water Atlas of the United States? What is the Ground Water Atlas of the United States?
This Ground Water Atlas of the United States is a series of USGS publications that describe the location, the extent, and the geologic and hydrologic characteristics of the important aquifers of the Nation. The series consists of 13 chapters that describe the regional groundwater resources that collectively cover 50 States, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Learn more: Principal Aquifers...
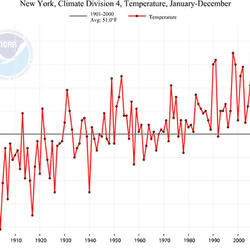
How do we know the climate is changing? How do we know the climate is changing?
The scientific community is certain that the Earth's climate is changing because of the trends that we see in the instrumented climate record and the changes that have been observed in physical and biological systems. The instrumental record of climate change is derived from thousands of temperature and precipitation recording stations around the world. We have very high confidence in these...
What are the long-term effects of climate change? What are the long-term effects of climate change?
Scientists have predicted that long-term effects of climate change will include a decrease in sea ice and an increase in permafrost thawing, an increase in heat waves and heavy precipitation, and decreased water resources in semi-arid regions. Below are some of the regional impacts of global change forecast by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: North America: Decreasing snowpack in the...
What is the difference between global warming and climate change? What is the difference between global warming and climate change?
Although people tend to use these terms interchangeably, global warming is just one aspect of climate change. “Global warming” refers to the rise in global temperatures due mainly to the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. “Climate change” refers to the increasing changes in the measures of climate over a long period of time – including precipitation, temperature, and...
Does the USGS monitor global warming? Does the USGS monitor global warming?
Not specifically. Our charge is to understand characteristics of the Earth, especially the Earth's surface, that affect our Nation's land, water, and biological resources. That includes quite a bit of environmental monitoring. Other agencies, especially NOAA and NASA, are specifically funded to monitor global temperature and atmospheric phenomena such as ozone concentrations. The work through...
In this video excerpt, we see motion from two video surveillance cameras capturing continuous daytime video data on pupfish spawning, and as seen here, other occurrences. The cameras are positioned approximately four feet above the water surface and one underwater.
Listen to hear the answer.
A group of Devils Hole pupfish forage along the edge of the shallow spawning shelf in Devils Hole.
A group of Devils Hole pupfish forage along the edge of the shallow spawning shelf in Devils Hole.
Groundwater characterization and effects of pumping in the Death Valley regional groundwater flow system, Nevada and California, with special reference to Devils Hole Groundwater characterization and effects of pumping in the Death Valley regional groundwater flow system, Nevada and California, with special reference to Devils Hole
Devils Hole, Nevada—A photographic story of a restricted subaqueous environment Devils Hole, Nevada—A photographic story of a restricted subaqueous environment
Devils Hole, Nevada--A Primer Devils Hole, Nevada--A Primer
The chronology for the d18O record from Devils Hole, Nevada, extended into the Mid-Holocene The chronology for the d18O record from Devils Hole, Nevada, extended into the Mid-Holocene
Why Study Paleoclimate? Why Study Paleoclimate?
500,000-year stable carbon isotopic record from Devils Hole, Nevada 500,000-year stable carbon isotopic record from Devils Hole, Nevada
500,000-year temperature record challenges ice age theory 500,000-year temperature record challenges ice age theory
Related
How can I find the depth to the water table in a specific location? How can I find the depth to the water table in a specific location?
The depth to the water table can change (rise or fall) depending on the time of year. During the late winter and spring when accumulated snow starts to melt and spring rainfall is plentiful, water on the surface infiltrates into the ground and the water table rises. When water-loving plants start to grow again in the spring and precipitation gives way to hot, dry summers, the water table falls...
What is the Ground Water Atlas of the United States? What is the Ground Water Atlas of the United States?
This Ground Water Atlas of the United States is a series of USGS publications that describe the location, the extent, and the geologic and hydrologic characteristics of the important aquifers of the Nation. The series consists of 13 chapters that describe the regional groundwater resources that collectively cover 50 States, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Learn more: Principal Aquifers...
How do we know the climate is changing? How do we know the climate is changing?
The scientific community is certain that the Earth's climate is changing because of the trends that we see in the instrumented climate record and the changes that have been observed in physical and biological systems. The instrumental record of climate change is derived from thousands of temperature and precipitation recording stations around the world. We have very high confidence in these...
What are the long-term effects of climate change? What are the long-term effects of climate change?
Scientists have predicted that long-term effects of climate change will include a decrease in sea ice and an increase in permafrost thawing, an increase in heat waves and heavy precipitation, and decreased water resources in semi-arid regions. Below are some of the regional impacts of global change forecast by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: North America: Decreasing snowpack in the...
What is the difference between global warming and climate change? What is the difference between global warming and climate change?
Although people tend to use these terms interchangeably, global warming is just one aspect of climate change. “Global warming” refers to the rise in global temperatures due mainly to the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. “Climate change” refers to the increasing changes in the measures of climate over a long period of time – including precipitation, temperature, and...
Does the USGS monitor global warming? Does the USGS monitor global warming?
Not specifically. Our charge is to understand characteristics of the Earth, especially the Earth's surface, that affect our Nation's land, water, and biological resources. That includes quite a bit of environmental monitoring. Other agencies, especially NOAA and NASA, are specifically funded to monitor global temperature and atmospheric phenomena such as ozone concentrations. The work through...
In this video excerpt, we see motion from two video surveillance cameras capturing continuous daytime video data on pupfish spawning, and as seen here, other occurrences. The cameras are positioned approximately four feet above the water surface and one underwater.
In this video excerpt, we see motion from two video surveillance cameras capturing continuous daytime video data on pupfish spawning, and as seen here, other occurrences. The cameras are positioned approximately four feet above the water surface and one underwater.
Listen to hear the answer.
A group of Devils Hole pupfish forage along the edge of the shallow spawning shelf in Devils Hole.
A group of Devils Hole pupfish forage along the edge of the shallow spawning shelf in Devils Hole.