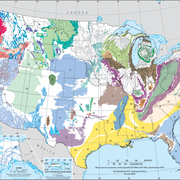
The study area for the Lake Michigan Basin groundwater-flow model encompasses the entire Michigan Structural Basin centered in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan and extending into parts of Illinois, Wisconsin, Indiana, Ohio, and Ontario, Canada.
Within the Michigan Structural Basin, Precambrian crystalline rocks and the Precambrian Jacobsville Sandstone are overlain by approximately 14,000 feet of younger Paleozoic and Mesozoic Era sedimentary rocks. The Paleozoic Era rocks are made up of Cambrian Period sandstones and dolomites, Ordovician Period sandstones and limestones overlain by shale, Silurian and Devonian Period limestones and dolomites, and Mississippian Period limestones and shales. The Mesozoic Era rocks are made up of Pennsylvanian Period sandstones and shales and Jurassic Period sandstones. These rocks are overlain by glacial deposits from Wisconsinan age and earlier glaciations and unconsolidated sediment of recent age. All of the glacial and unconsolidated sediments and sedimentary rocks located within the boundary of the study area are included within the Lake Michigan Basin model. The sedimentary rocks within the boundary of the simulation were divided into 15 hydrogeologic units. The 15 units were then subdivided into a total of 20 model layers (L1 through L20 below) for use within the simulation. The Silurian-Devonian and Mount Simon hydrogeologic units were subdivided into three and two model layers, respectively. Both the hydrogeologic units and model layers were identified by evaluating the major lithology of the geologic formation and its relative importance as a water-bearing formation within the simulation area.

The data below are supplemental to Hydrogeologic framework of bedrock units and initial salinity distribution for a simulation of groundwater flow for the Lake Michigan basin (USGS Scientific Investiations Report 2009-5060). The report includes a description of methods used to derive the data.
Click on the links below to download files for this aquifer. For information about the available file types, see Aquifer data: Explanation of spatial data formats.
Hydrogeologic Unit Surfaces: Metadata Shapefile Text File
- Land surface (LSD) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Quaternary unit (L1_3) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Jurassic unit (L4) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Upper Pennsylvanian unit (L5) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Lower Pennsylvanian unit (L6) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Michigan Formation unit (L7) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Marshall Formation unit (L8) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Devonian-Mississippian unit (L9) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Silurian-Devonian unit (L10_12) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Maquoketa Formation unit (L13) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Sinnipee Formation unit (L14) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- St. Peter Formation (L15) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Prairie du Chien-Franconia unit (L16) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Ironton-Galesville unit (L17) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Eau Claire unit (L18) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Mt. Simon Formaton unit (L19_20) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
Below are other webpages associated with this aquifer.
Principal Aquifers of the United States
Regional Groundwater Availability Studies
Below are publications associated with this aquifer.
Hydrogeologic Framework of Bedrock Units and Initial Salinity Distribution for a Simulation of Groundwater Flow for the Lake Michigan Basin Hydrogeologic Framework of Bedrock Units and Initial Salinity Distribution for a Simulation of Groundwater Flow for the Lake Michigan Basin
Ground Water Atlas of the United States Ground Water Atlas of the United States
Principal aquifers [of the United States] Principal aquifers [of the United States]
The study area for the Lake Michigan Basin groundwater-flow model encompasses the entire Michigan Structural Basin centered in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan and extending into parts of Illinois, Wisconsin, Indiana, Ohio, and Ontario, Canada.
Within the Michigan Structural Basin, Precambrian crystalline rocks and the Precambrian Jacobsville Sandstone are overlain by approximately 14,000 feet of younger Paleozoic and Mesozoic Era sedimentary rocks. The Paleozoic Era rocks are made up of Cambrian Period sandstones and dolomites, Ordovician Period sandstones and limestones overlain by shale, Silurian and Devonian Period limestones and dolomites, and Mississippian Period limestones and shales. The Mesozoic Era rocks are made up of Pennsylvanian Period sandstones and shales and Jurassic Period sandstones. These rocks are overlain by glacial deposits from Wisconsinan age and earlier glaciations and unconsolidated sediment of recent age. All of the glacial and unconsolidated sediments and sedimentary rocks located within the boundary of the study area are included within the Lake Michigan Basin model. The sedimentary rocks within the boundary of the simulation were divided into 15 hydrogeologic units. The 15 units were then subdivided into a total of 20 model layers (L1 through L20 below) for use within the simulation. The Silurian-Devonian and Mount Simon hydrogeologic units were subdivided into three and two model layers, respectively. Both the hydrogeologic units and model layers were identified by evaluating the major lithology of the geologic formation and its relative importance as a water-bearing formation within the simulation area.

The data below are supplemental to Hydrogeologic framework of bedrock units and initial salinity distribution for a simulation of groundwater flow for the Lake Michigan basin (USGS Scientific Investiations Report 2009-5060). The report includes a description of methods used to derive the data.
Click on the links below to download files for this aquifer. For information about the available file types, see Aquifer data: Explanation of spatial data formats.
Hydrogeologic Unit Surfaces: Metadata Shapefile Text File
- Land surface (LSD) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Quaternary unit (L1_3) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Jurassic unit (L4) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Upper Pennsylvanian unit (L5) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Lower Pennsylvanian unit (L6) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Michigan Formation unit (L7) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Marshall Formation unit (L8) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Devonian-Mississippian unit (L9) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Silurian-Devonian unit (L10_12) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Maquoketa Formation unit (L13) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Sinnipee Formation unit (L14) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- St. Peter Formation (L15) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Prairie du Chien-Franconia unit (L16) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Ironton-Galesville unit (L17) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Eau Claire unit (L18) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
- Mt. Simon Formaton unit (L19_20) ASCII grid (Model Resolution)
Below are other webpages associated with this aquifer.
Principal Aquifers of the United States
Regional Groundwater Availability Studies
Below are publications associated with this aquifer.