File Management
Learn more about uploading, downloading, and managing files in ScienceBase.
Table of Contents
- Upload Files to ScienceBase
- Uploading FGDC-compliant XML metadata files
- Uploading Large Files
- Advanced Usage for Cloud Optimized Files
- Globus to ScienceBase Transfer
- Uploading Spatial Data
- Downloading Files
- Downloading Large Files
Upload Files to ScienceBase
Almost any file type can be uploaded to ScienceBase. Multiple files can be uploaded to a single item, individually or bundled together in a zipped file. The current file size limit for uploads and downloads in ScienceBase is about 30 GB (dependent on users’ local internet connections). The limit for number of individual files per item is 100 (note: please upload fewer files so that users can more easily view the list).
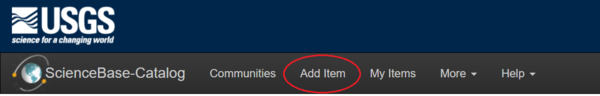
To upload files and enter descriptive information, a user must be logged in and have edit permission to the ScienceBase item. All items in ScienceBase have an edit form with multiple tabs for uploading files and entering descriptive information. To create a new item, click the "Add Item" link in the black title bar or the "Add" drop-down menu in the upper right corner of the folder view.
The Add Item link in the top banner:
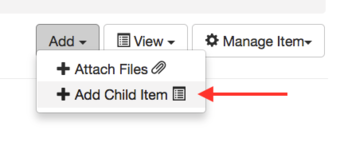
The Add dropdown menu in the upper right corner of the page:
Users can access the edit form of an existing item by clicking on the "Manage Item" dropdown menu and selecting "Edit Item".
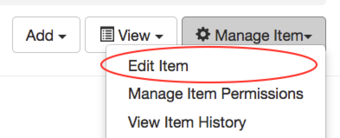
Once in the edit form, select the "Files" tab and click "Add files…" After a file has been uploaded, enter a title into the text box on the right side of the uploaded file. The title will appear below the file name on the item view. While it is useful to add titles in this way, users should also save files with descriptive and meaningful file names prior to uploading them.
Uploading FGDC-compliant XML metadata files
All USGS datasets should have associated metadata that comply with an FGDC-endorsed standard – either Content Standard for Digital Geospatial Metadata (CSDGM) or the ISO metadata standard. Metadata files can be uploaded and stored as resources in ScienceBase items.
Please note: the ScienceBase edit form does not contain all the fields that are required by FGDC endorsed metadata standards. Filling out the edit form is not an alternative to uploading FGDC compliant metadata.
For more information about metadata standards and creation tools, see the USGS Data Management website.
ScienceBase has the capability to recognize and parse FGDC-endorsed Content Standard for Digital Geospatial Metadata (CSDGM) and ISO metadata files that are in XML format. This means that information from these files can be used to populate ScienceBase fields. If a CSDGM or ISO XML file is uploaded, ScienceBase will recognize the format and automatically bring up the following menu:
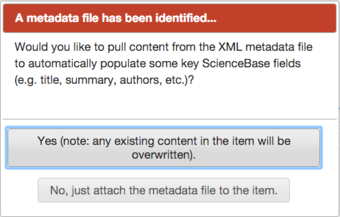
Select "Yes" to automatically populate many of the fields in the ScienceBase edit form. If you have already entered content in the edit form, it will be overwritten. Select "No" if you would like to upload the metadata file without populating any of the fields.
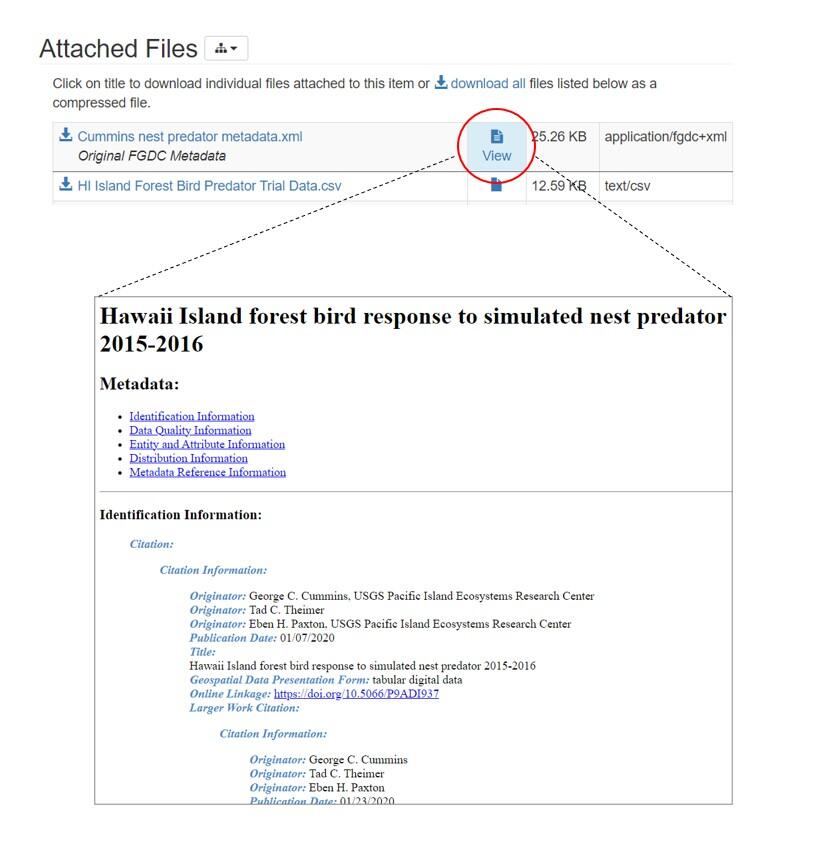
ScienceBase will apply a stylesheet to CSDGM and ISO metadata records so that they can be viewed a more easy-to-read format:
Uploading Large Files
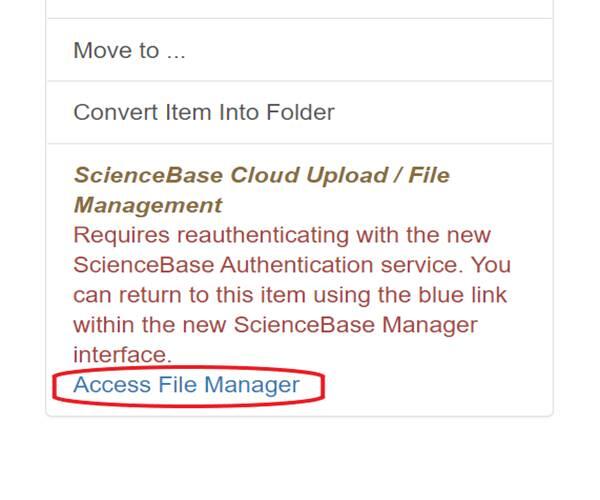
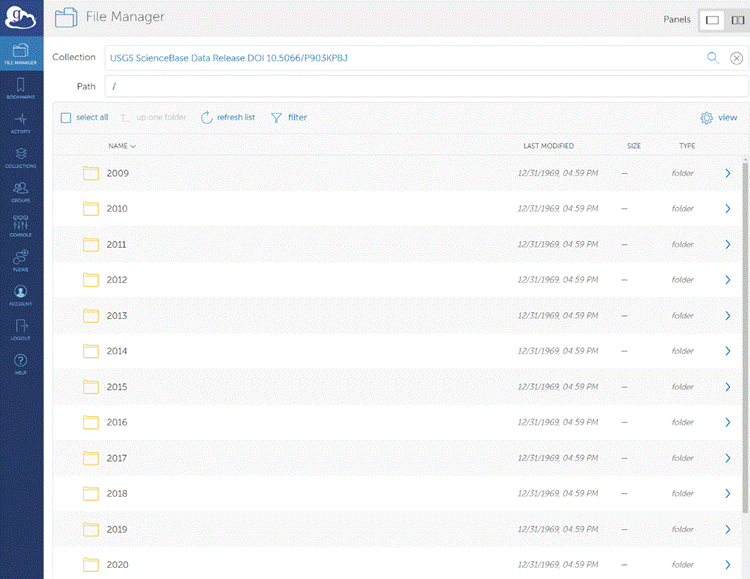
To upload files larger than 1GB, please use the ScienceBase Cloud Upload / File Manager. The upper file size limit is about 30GB. This tool allows users to upload files directly to cloud storage in the USGS Cloud Hosting Solutions (CHS) environment. It can be accessed by logging in and scrolling down to the "Item Actions" section of the ScienceBase item view and selecting "Access File Manager." Users will be prompted through another login step to use the file manager.
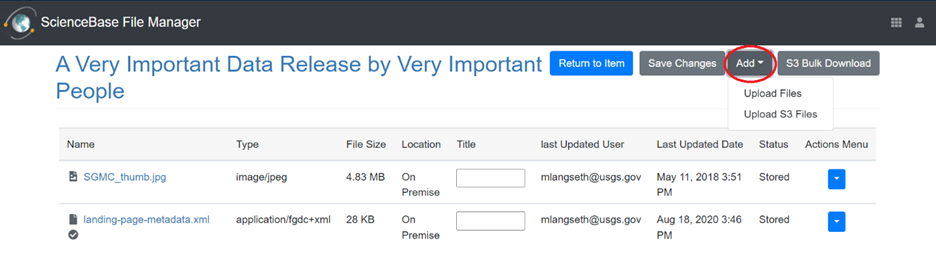
Once in File Manager, users can click the "Add" dropdown menu and choose to upload files from their local computer or from a readable S3 bucket location. While performance will depend on a user's local internet connection, files up to ~30 GB in size can be successfully transferred. Once a file has been uploaded to the cloud, it will be available for download from the ScienceBase item. Users who would like to provide access to their cloud optimized files should refer to the "Advanced Usage for Cloud Optimized Files" section below.
Please note that no automated scraping or processing will occur for files that are uploaded through the File Manager (e.g., no automatic metadata ingest, no map service generation, etc.). Users who need these features should continue to use the traditional file upload path in the edit form, by selecting "Manage Item" > "Edit Item" > "Files".
Currently, cloud storage and access costs are supported by the USGS Science Analytics and Synthesis Program (SAS) for public data releases in ScienceBase. However, scientists who are interested in using these features for very large datasets (e.g., over 1TB) should reach out to the ScienceBase team for additional details (sciencebase@usgs.gov).
Advanced Usage for Cloud Optimized Files
With the adoption of cloud-based file storage, the scientific and open-source programming communities have made notable advancements in protocols for working with data in specific file formats (https://guide.cloudnativegeo.org/). Cloud optimized datasets provide powerful open-source options for working with certain tabular, geospatial, and gridded datasets (e.g., Parquet files, Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) files, Zarr files, etc.)
ScienceBase can now offer expanded support for some of these file types. Users who have uploaded cloud optimized files may need to take an additional step to make the files available to cloud workflows. To do so, click the "Actions Menu" dropdown arrow next to the cloud optimized file and select "Publish":
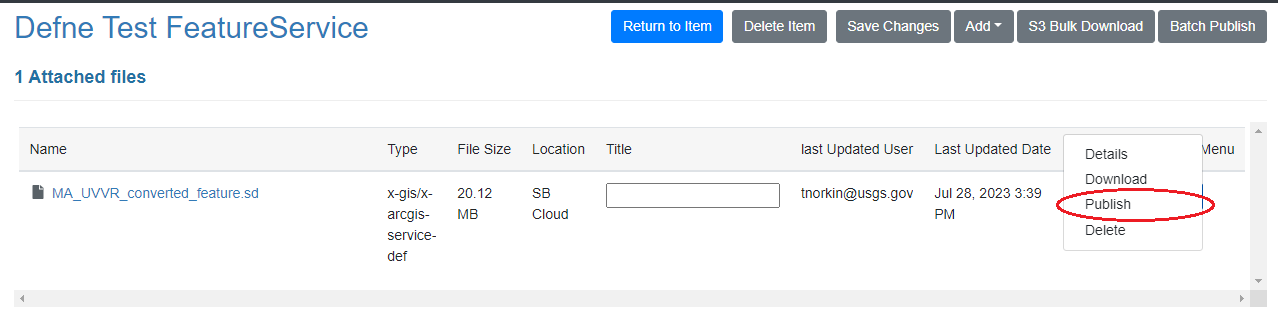
This action will add a copy of the file to the public ScienceBase S3 bucket and will add the public S3 URI to the item JSON, which provides a route from which the file can be consumed using desktop applications and common libraries in programming languages such as R and Python.
It is important for data authors to understand the details of what is possible for different file formats and workflows; pushing files to this dedicated public S3 location in ScienceBase is unnecessary for files that are not internally formatted for this type of access. Please note that making a copy of a file available in the public S3 location is intended only for formally published data (i.e., ScienceBase data release products) and is a different process than making an item publicly available. Please contact the ScienceBase team (sciencebase@usgs.gov) if you are interested in learning more about how to work with cloud optimized files within the system.
Globus to ScienceBase Transfer
Case 1: Globus to ScienceBase Transfer
ScienceBase can now ingest files from Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 buckets with the proper Identity and Access Management (IAM) configuration. This supports the ability to pull files from other USGS Cloud Hosting Solutions (CHS) locations, or research partners, into ScienceBase CHS storage. However, many researchers in USGS still do not work directly with S3 buckets (via console or command line interface), and those who do may find the IAM configuration process challenging. The USGS Science Analytics and Synthesis group has therefore established an AWS S3 bucket with the proper IAM configuration to support ingest into ScienceBase. This eliminates the complexity of working through IAM configurations on a case-by-case basis for buckets. The ScienceBase data release team has developed a process using Globus to help users move their data into this staging location, after which the files can be attached to ScienceBase items and moved into ScienceBase cloud storage via the application’s user interface (or via code).
Who should use this file upload method?
- Users with data that are already available on an existing Globus endpoint.
- Users with data larger than 30 GB.
- Users experiencing timeouts when uploading data through the ScienceBase Cloud Uploader.
Who should NOT use this file upload method?
- Users whose primary challenge pertains to a large number of unique data files. While the upload of S3 files to ScienceBase items can now be scripted using the Python API wrapper sciencebasepy, ScienceBase still has a limit of 100 files per item. Contact the ScienceBase team at sciencebase@usgs.gov for strategies and options.
Case 2: Globus Deep Storage Data Release
The ScienceBase Data Release team has also recently developed a process for releasing what the team is calling a “Deep Storage” data release. For these data releases, the data remain in a Globus Collection and public users will need a free Globus account to access the data. The ScienceBase landing page and the attached metadata record support the discovery and presentation of the data release, but data file access is accomplished via Globus to navigate through the data release collection and obtain the data. Unlike the temporary Globus Collections used to support the S3 data transfer to ScienceBase (described above), these deep storage collections will persist on USGS on-premise or cloud storage configured as long-term cataloged collection.
Who should use this file upload method?
- Users with large volumes of data files that, when compiled, total multiple TBs of data.
Who should NOT use this file upload method?
- Users that need fast, programmatic access to data file content via web services (e.g., cloud optimized geoTIFFs). For example, web applications cannot be built on top of the data in this deep storage.
Contact the ScienceBase data release team at sciencebase_datarelease@usgs.gov to determine if Globus could be used to support your use case.
Uploading Spatial Data
Certain geospatial file formats (see list below) can be parsed by ScienceBase for display in the preview map and for generating web service URLs.
For more information and instructions on creating geospatial services, please see the ScienceBase Geospatial Services page.
File formats that can be processed by ScienceBase to enable interactive online viewing include the following:
- Shapefiles (.shp) -- shapefiles can be displayed without symbology in the preview map. Keyhole Markup Language, Web Map Services, and Web Feature Services are created.
- GeoTIFFs (.tif) -- GeoTIFFs can be viewed without symbology in the preview map. Keyhole Markup Language, Web Map Services, and Web Coverage Services are created.
- ESRI Service Definition files (.sd) -- Service Definition files allow ScienceBase to display shapefile and GeoTIFF symbology in the preview map. Keyhole Markup Language, Web Map Services, and ArcGIS Mapping Services are created.
The current file size limit for file uploads and downloads in ScienceBase is about 30GB; however, there are additional limits if files are used to create web services. Files must be uploaded through the edit form (not the ScienceBase Cloud Uploader) in order to create web services.
- Shapefiles -- ScienceBase can process shapefiles up to 500MB.
- GeoTIFFs -- ScienceBase can process GeoTIFFs with overviews (internal or external) up to 1GB. A GeoTIFF without an overview must be less than 250MB.
- ESRI Service Definition files -- Single file uploads should not exceed 1-2GB. ScienceBase can process uploaded .sd files if the unzipped content does not exceed 4GB.
Downloading Files
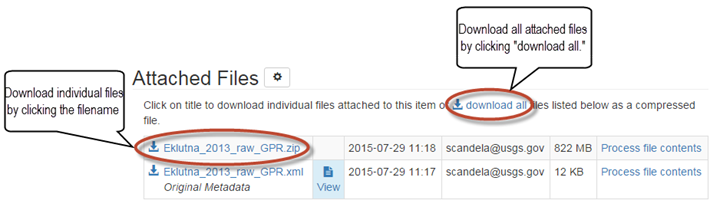
If a ScienceBase item has files attached to it, they will be listed in the "Attached Files" section which appears toward the bottom of a record, just below the "Contacts" section. Files can be downloaded to a local system individually or together as a zipped file. Click on the filename to download individual files or click the "download all" link. Note: the "download all" link is only available when the aggregated file size of attached files is under 10GB.
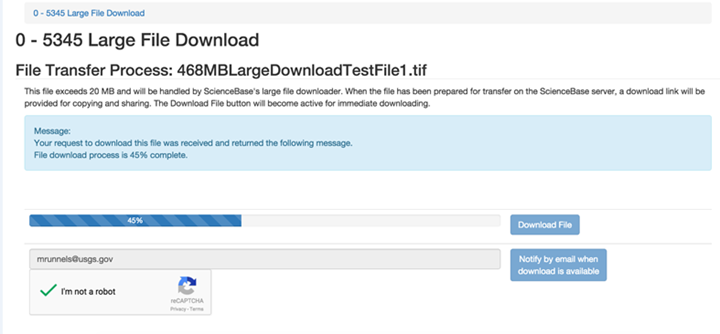
Downloading Large Files
For downloads of files exceeding 1GB, ScienceBase employs a temporary Amazon S3 download location, from which a user can acquire the file. There is an option to select "Notify by email when download is available." Follow the link in your email and select "Download File" to initiate the download.
Screenshot of large file downloader with a file transfer in progress: