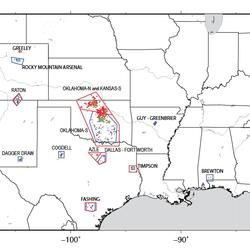
PubTalk 5/2018 — Yes Humans really are causing induced earthquakes
PubTalk 5/2018 — Yes Humans really are causing induced earthquakesTitle: Yes, Humans Really Are Causing Earthquakes! How Energy Industry Practices are Causing Earthquakes in America's Heartland