Seismometers record vibrations from a wide assortment of ground motion events. Each event type has a distinctive ground-motion signal with unique frequency and amplitude—its own seismic signature. Seismologists are trained to identify the source of seismic events seen on a webicorder based on its ‘seismic signature’.
Do earthquakes large enough to collapse buildings and roads accompany volcanic eruptions?
Not usually. Earthquakes associated with eruptions rarely exceed magnitude 5, and these moderate earthquakes are not big enough to destroy buildings and roads.
The largest earthquakes at Mount St. Helens in 1980 were magnitude 5, large enough to sway trees and damage buildings, but not destroy them. During the huge eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991, dozens of light to moderate earthquakes (magnitude 3 to 5) were felt by several hundred thousand people. Many houses collapsed, but not primarily because of the shaking. Heavy ash from the eruption (made heavier by rain from a hurricane) accumulated on roofs and crushed them.
Stronger earthquakes sometimes DO occur near volcanoes as a result of tectonic faulting. For example, four magnitude 6 earthquakes struck Long Valley caldera, California, in 1980, and a magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, in 1975. Both volcanoes were quiet at the time. The Hawaii earthquake triggered a small eruption at the summit of Kilauea. No eruption occurred at Long Valley.
Learn more: Monitoring Volcano Seismicity Provides Insight to Volcanic Structure
Related
Can earthquakes trigger volcanic eruptions? Can earthquakes trigger volcanic eruptions?
Sometimes, yes. A few large regional earthquakes (greater than magnitude 6) are considered to be related to a subsequent eruption or to some type of unrest at a nearby volcano. However, volcanoes can only be triggered into eruption by nearby tectonic earthquakes if they are already poised to erupt. This requires two conditions to be met: Enough "eruptible" magma within the volcanic system...
When will the next large earthquake occur in Yellowstone? When will the next large earthquake occur in Yellowstone?
Earthquakes cannot be predicted yet, but modern surveillance for earthquakes in Yellowstone conducted with seismographs (instruments that measure earthquake locations and magnitudes) and GPS - Global Positioning Systems (instruments that measure slow ground movements) help scientists understand the state of stress in the Earth's crust. Those stresses could trigger earthquakes as well as magma...
Are there earthquakes associated with Mount Hood? Are there earthquakes associated with Mount Hood?
Mount Hood is one of the most seismically active volcanoes in the Washington and Oregon Cascades, and the most seismically active volcano in Oregon. In an average month 1-2 earthquakes are located within 5 km (3 miles) of the summit. Earthquakes large enough to be felt occur on Mount Hood every two years on average. Seismic monitoring, in effect since 1977, indicates a generalized concentration of...
At what magnitude does damage begin to occur in an earthquake? At what magnitude does damage begin to occur in an earthquake?
It isn't that simple. There is not one magnitude above which damage will occur. It depends on other variables, such as the distance from the earthquake, what type of soil you are on, building construction, etc. That being said, damage does not usually occur until the earthquake magnitude reaches somewhere above 4 or 5. Learn more: Glossary of earthquake terms Earthquake Magnitude, Energy Release...
What does an earthquake feel like? What does an earthquake feel like?
The way an earthquake feels depends on where you are, where the earthquake is, and how big the earthquake is: A large earthquake nearby will feel like a sudden large jolt followed quickly by more strong shaking that may last a few seconds or up to a couple of minutes if it's a rare great event. The shaking will feel violent and it will be difficult to stand up. The contents of your house will be a...
What was the most destructive volcanic eruption in the history of the United States? What was the most destructive volcanic eruption in the history of the United States?
The May 18, 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens (Washington) was the most destructive in the history of the United States. Novarupta (Katmai) Volcano in Alaska erupted considerably more material in 1912, but owing to the isolation and sparse population of the region, there were no human deaths and little property damage. In contrast, the eruption of Mount St. Helens caused loss of lives and...
What was the largest volcanic eruption in the 20th century? What was the largest volcanic eruption in the 20th century?
The world's largest eruption of the 20th century occurred in 1912 at Novarupta on the Alaska Peninsula in what is now Katmai National Park and Preserve. An estimated 15 cubic kilometers of magma was explosively erupted during 60 hours beginning on June 6th. This volume is equivalent to 230 years of eruption at Kilauea (Hawaii) or about 30 times the volume erupted by Mount St. Helens (Washington)...
Where do earthquakes occur? Where do earthquakes occur?
Earthquakes can strike any location at any time, but history shows they occur in the same general patterns year after year, principally in three large zones of the earth: The world's greatest earthquake belt, the circum-Pacific seismic belt, is found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean, where about 81 percent of our planet's largest earthquakes occur. It has earned the nickname "Ring of Fire". Why...
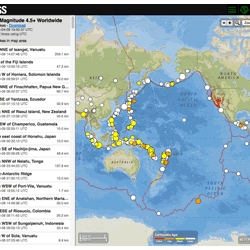
Where can I find current earthquake lists and maps for the world or for a specific area? Where can I find current earthquake lists and maps for the world or for a specific area?
The Earthquake Hazards Program Latest Earthquakes Map displays earthquakes in near-realtime and up to the past 30 days of earthquakes. The interface includes three panels: a list of earthquakes, a map, and a settings/options panel. You can pan and zoom the map to view specific areas. Click on an event on the list or map for additional information and a link to the event page with all the details...
Seismometers record vibrations from a wide assortment of ground motion events. Each event type has a distinctive ground-motion signal with unique frequency and amplitude—its own seismic signature. Seismologists are trained to identify the source of seismic events seen on a webicorder based on its ‘seismic signature’.
This video provides a tutorial for anyone interested in interpreting the seismic records on public webicorder displays.
This video provides a tutorial for anyone interested in interpreting the seismic records on public webicorder displays.
The United States has 169 active volcanoes. More than half of them could erupt explosively, sending ash up to 20,000 or 30,000 feet where commercial air traffic flies. USGS scientists are working to improve our understanding of volcano hazards to help protect communities and reduce the risks.
Video Sections:
The United States has 169 active volcanoes. More than half of them could erupt explosively, sending ash up to 20,000 or 30,000 feet where commercial air traffic flies. USGS scientists are working to improve our understanding of volcano hazards to help protect communities and reduce the risks.
Video Sections:
USGS volcano seismologist, Seth Moran, describes how seismology and seismic networks are used to mitigate volcanic hazards.
USGS volcano seismologist, Seth Moran, describes how seismology and seismic networks are used to mitigate volcanic hazards.
USGS technologist Rick LaHusen describes how the development and deployment of instruments plays a crucial role in mitigating volcanic hazards.
USGS technologist Rick LaHusen describes how the development and deployment of instruments plays a crucial role in mitigating volcanic hazards.
Photo of chimney damage at a house in Louisa County, Virginia. This was a result from a magnitude 5.8 earthquake in Virginia on August 23, 2011.
Photo of chimney damage at a house in Louisa County, Virginia. This was a result from a magnitude 5.8 earthquake in Virginia on August 23, 2011.
Collection of USGS still images taken after the January 17, 1994 Northridge earthquake highlighting the damage to buildings and infrastructure.
Collection of USGS still images taken after the January 17, 1994 Northridge earthquake highlighting the damage to buildings and infrastructure.
A unified catalog of earthquake hypocenters and magnitudes at volcanoes in Alaska—1989 to 2018 A unified catalog of earthquake hypocenters and magnitudes at volcanoes in Alaska—1989 to 2018
California's restless giant: The Long Valley Caldera California's restless giant: The Long Valley Caldera
Mount St. Helens, 1980 to now—what’s going on? Mount St. Helens, 1980 to now—what’s going on?
Mauna Loa--history, hazards and risk of living with the world's largest volcano Mauna Loa--history, hazards and risk of living with the world's largest volcano
Earthquakes in Hawai‘i—an underappreciated but serious hazard Earthquakes in Hawai‘i—an underappreciated but serious hazard
Seismic precursors to volcanic explosions during the 2006 eruption of Augustine Volcano: Chapter 2 in The 2006 eruption of Augustine Volcano, Alaska Seismic precursors to volcanic explosions during the 2006 eruption of Augustine Volcano: Chapter 2 in The 2006 eruption of Augustine Volcano, Alaska
Related
Can earthquakes trigger volcanic eruptions? Can earthquakes trigger volcanic eruptions?
Sometimes, yes. A few large regional earthquakes (greater than magnitude 6) are considered to be related to a subsequent eruption or to some type of unrest at a nearby volcano. However, volcanoes can only be triggered into eruption by nearby tectonic earthquakes if they are already poised to erupt. This requires two conditions to be met: Enough "eruptible" magma within the volcanic system...
When will the next large earthquake occur in Yellowstone? When will the next large earthquake occur in Yellowstone?
Earthquakes cannot be predicted yet, but modern surveillance for earthquakes in Yellowstone conducted with seismographs (instruments that measure earthquake locations and magnitudes) and GPS - Global Positioning Systems (instruments that measure slow ground movements) help scientists understand the state of stress in the Earth's crust. Those stresses could trigger earthquakes as well as magma...
Are there earthquakes associated with Mount Hood? Are there earthquakes associated with Mount Hood?
Mount Hood is one of the most seismically active volcanoes in the Washington and Oregon Cascades, and the most seismically active volcano in Oregon. In an average month 1-2 earthquakes are located within 5 km (3 miles) of the summit. Earthquakes large enough to be felt occur on Mount Hood every two years on average. Seismic monitoring, in effect since 1977, indicates a generalized concentration of...
At what magnitude does damage begin to occur in an earthquake? At what magnitude does damage begin to occur in an earthquake?
It isn't that simple. There is not one magnitude above which damage will occur. It depends on other variables, such as the distance from the earthquake, what type of soil you are on, building construction, etc. That being said, damage does not usually occur until the earthquake magnitude reaches somewhere above 4 or 5. Learn more: Glossary of earthquake terms Earthquake Magnitude, Energy Release...
What does an earthquake feel like? What does an earthquake feel like?
The way an earthquake feels depends on where you are, where the earthquake is, and how big the earthquake is: A large earthquake nearby will feel like a sudden large jolt followed quickly by more strong shaking that may last a few seconds or up to a couple of minutes if it's a rare great event. The shaking will feel violent and it will be difficult to stand up. The contents of your house will be a...
What was the most destructive volcanic eruption in the history of the United States? What was the most destructive volcanic eruption in the history of the United States?
The May 18, 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens (Washington) was the most destructive in the history of the United States. Novarupta (Katmai) Volcano in Alaska erupted considerably more material in 1912, but owing to the isolation and sparse population of the region, there were no human deaths and little property damage. In contrast, the eruption of Mount St. Helens caused loss of lives and...
What was the largest volcanic eruption in the 20th century? What was the largest volcanic eruption in the 20th century?
The world's largest eruption of the 20th century occurred in 1912 at Novarupta on the Alaska Peninsula in what is now Katmai National Park and Preserve. An estimated 15 cubic kilometers of magma was explosively erupted during 60 hours beginning on June 6th. This volume is equivalent to 230 years of eruption at Kilauea (Hawaii) or about 30 times the volume erupted by Mount St. Helens (Washington)...
Where do earthquakes occur? Where do earthquakes occur?
Earthquakes can strike any location at any time, but history shows they occur in the same general patterns year after year, principally in three large zones of the earth: The world's greatest earthquake belt, the circum-Pacific seismic belt, is found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean, where about 81 percent of our planet's largest earthquakes occur. It has earned the nickname "Ring of Fire". Why...
Where can I find current earthquake lists and maps for the world or for a specific area? Where can I find current earthquake lists and maps for the world or for a specific area?
The Earthquake Hazards Program Latest Earthquakes Map displays earthquakes in near-realtime and up to the past 30 days of earthquakes. The interface includes three panels: a list of earthquakes, a map, and a settings/options panel. You can pan and zoom the map to view specific areas. Click on an event on the list or map for additional information and a link to the event page with all the details...
Seismometers record vibrations from a wide assortment of ground motion events. Each event type has a distinctive ground-motion signal with unique frequency and amplitude—its own seismic signature. Seismologists are trained to identify the source of seismic events seen on a webicorder based on its ‘seismic signature’.
Seismometers record vibrations from a wide assortment of ground motion events. Each event type has a distinctive ground-motion signal with unique frequency and amplitude—its own seismic signature. Seismologists are trained to identify the source of seismic events seen on a webicorder based on its ‘seismic signature’.
This video provides a tutorial for anyone interested in interpreting the seismic records on public webicorder displays.
This video provides a tutorial for anyone interested in interpreting the seismic records on public webicorder displays.
The United States has 169 active volcanoes. More than half of them could erupt explosively, sending ash up to 20,000 or 30,000 feet where commercial air traffic flies. USGS scientists are working to improve our understanding of volcano hazards to help protect communities and reduce the risks.
Video Sections:
The United States has 169 active volcanoes. More than half of them could erupt explosively, sending ash up to 20,000 or 30,000 feet where commercial air traffic flies. USGS scientists are working to improve our understanding of volcano hazards to help protect communities and reduce the risks.
Video Sections:
USGS volcano seismologist, Seth Moran, describes how seismology and seismic networks are used to mitigate volcanic hazards.
USGS volcano seismologist, Seth Moran, describes how seismology and seismic networks are used to mitigate volcanic hazards.
USGS technologist Rick LaHusen describes how the development and deployment of instruments plays a crucial role in mitigating volcanic hazards.
USGS technologist Rick LaHusen describes how the development and deployment of instruments plays a crucial role in mitigating volcanic hazards.
Photo of chimney damage at a house in Louisa County, Virginia. This was a result from a magnitude 5.8 earthquake in Virginia on August 23, 2011.
Photo of chimney damage at a house in Louisa County, Virginia. This was a result from a magnitude 5.8 earthquake in Virginia on August 23, 2011.
Collection of USGS still images taken after the January 17, 1994 Northridge earthquake highlighting the damage to buildings and infrastructure.
Collection of USGS still images taken after the January 17, 1994 Northridge earthquake highlighting the damage to buildings and infrastructure.