If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the right block moves toward you and the left block moves away.
What is an earthquake and what causes them to happen?
An earthquake is caused by a sudden slip on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cause the shaking that we feel.
In California there are two plates - the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The Pacific Plate consists of most of the Pacific Ocean floor and the California Coast line. The North American Plate comprises most the North American Continent and parts of the Atlantic Ocean floor. The primary boundary between these two plates is the San Andreas Fault. The San Andreas Fault is more than 650 miles long and extends to depths of at least 10 miles. Many other smaller faults like the Hayward (Northern California) and the San Jacinto (Southern California) branch from and join the San Andreas Fault Zone.
The Pacific Plate grinds northwestward past the North American Plate at a rate of about two inches per year. Parts of the San Andreas Fault system adapt to this movement by constant "creep" resulting in many tiny shocks and a few moderate earth tremors. In other areas where creep is NOT constant, strain can build up for hundreds of years, producing great earthquakes when it finally releases.
Learn More: Glossary of earthquake terms
Related
Foreshocks, aftershocks - what's the difference? Foreshocks, aftershocks - what's the difference?
"Foreshock" and "aftershock" are relative terms. Foreshocks are earthquakes that precede larger earthquakes in the same location. An earthquake cannot be identified as a foreshock until after a larger earthquake in the same area occurs. Aftershocks are smaller earthquakes that occur in the same general area during the days to years following a larger event or "mainshock." They occur within 1-2...
Can the position of the moon or the planets affect seismicity? Are there more earthquakes in the morning/in the evening/at a certain time of the month? Can the position of the moon or the planets affect seismicity? Are there more earthquakes in the morning/in the evening/at a certain time of the month?
Earthquakes are equally as likely to occur in the morning or the evening. Many studies in the past have shown no significant correlations between the rate of earthquake occurrence and the semi-diurnal tides when using large earthquake catalogs. Several recent studies, however, have found a correlation between earth tides (caused by the position of the moon relative to the earth) and some types of...
What is surface faulting or surface rupture in an earthquake? What is surface faulting or surface rupture in an earthquake?
Surface rupture occurs when movement on a fault deep within the earth breaks through to the surface. NOT ALL earthquakes result in surface rupture.
At what depth do earthquakes occur? What is the significance of the depth? At what depth do earthquakes occur? What is the significance of the depth?
Earthquakes occur in the crust or upper mantle, which ranges from the earth's surface to about 800 kilometers deep (about 500 miles). The strength of shaking from an earthquake diminishes with increasing distance from the earthquake's source, so the strength of shaking at the surface from an earthquake that occurs at 500 km deep is considerably less than if the same earthquake had occurred at 20...
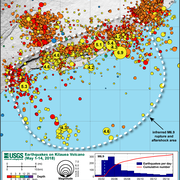
Why are there so many earthquakes in the Geysers area in Northern California? Why are there so many earthquakes in the Geysers area in Northern California?
The Geysers Geothermal Field is located in a tectonically active region of Northern California. The major seismic hazards in the region are from large earthquakes occurring along regional faults that are located miles away from the geothermal field, such as the San Andreas and Healdsburg-Rodgers Creek faults. However, activities associated with the withdrawal of steam for producing electric power...
Do earthquakes occur in Antarctica? Do earthquakes occur in Antarctica?
Earthquakes do occur in Antarctica, but not very often. There have been some big earthquakes--including one magnitude 8.1--in the Balleny Islands (between Antarctica and New Zealand). The boundary between the Scotia Plate and the Antarctic Plate just grazes the north tip of the Antarctic Peninsula (look "northwest" from the Pole toward South America). There is also a hint of a line of seismicity...
Where can I find earthquake educational materials? Where can I find earthquake educational materials?
Start with our Earthquake Hazards Education site. That includes: Earthquakes for Kids Cool Earthquake Facts Earthquake Science for Everyone Other good starting points include: State Geological Surveys for states in earthquake-prone regions The Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drills website SAGE (Seismological Facility for the Advancement of Geoscience), which is a non-profit consortium
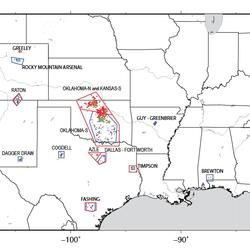
Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes? Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes?
Earthquakes induced by human activity have been documented at many locations in the United States and in many other countries around the world. Earthquakes can be induced by a wide range of causes including impoundment of reservoirs, surface and underground mining, withdrawal of fluids and gas from the subsurface, and injection of fluids into underground formations. While most induced earthquakes...
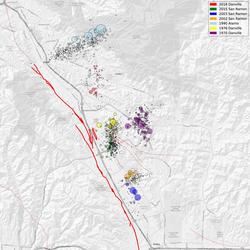
What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms? What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms?
Aftershocks are a sequence of earthquakes that happen after a larger mainshock on a fault. Aftershocks occur near the fault zone where the mainshock rupture occurred and are part of the "readjustment process” after the main slip on the fault. Aftershocks become less frequent with time, although they can continue for days, weeks, months, or even years for a very large mainshock. A swarm, on the...
If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the right block moves toward you and the left block moves away.
Diagram of left-lateral motion on fault. If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the left block moves toward you and the right block moves away. See also right-lateral.
Diagram of left-lateral motion on fault. If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the left block moves toward you and the right block moves away. See also right-lateral.
Horst and graben diagram. A graben is a down-dropped block of the earth's crust resulting from extension, or pulling, of the crust.
Horst and graben diagram. A graben is a down-dropped block of the earth's crust resulting from extension, or pulling, of the crust.
Subduction zone of the Juan de Fuca Plate and North America Plate, creating the Mt. St. Helens and Mt. Hood volcanoes.
Subduction zone of the Juan de Fuca Plate and North America Plate, creating the Mt. St. Helens and Mt. Hood volcanoes.
Building damanged by the February 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand.
Building damanged by the February 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand.
Listen to hear the answer.
What is an earthquake and what causes them to happen?
What is an earthquake and what causes them to happen?Listen to hear the answer.
Listen to hear the answer.
Oblique aerial view of San Andreas Fault (between white arrows) in southeastern Coachella Valley, near Red Canyon; view to the west.
Oblique aerial view of San Andreas Fault (between white arrows) in southeastern Coachella Valley, near Red Canyon; view to the west.
U.S. Geological Survey Earthquake Hazards Program decadal science strategy, 2024–33 U.S. Geological Survey Earthquake Hazards Program decadal science strategy, 2024–33
Natural Hazards Science at the U.S. Geological Survey Natural Hazards Science at the U.S. Geological Survey
Earthquake hazards: A national threat Earthquake hazards: A national threat
Quaternary Fault and Fold Database for the Nation Quaternary Fault and Fold Database for the Nation
The severity of an earthquake The severity of an earthquake
This dynamic earth: the story of plate tectonics This dynamic earth: the story of plate tectonics
The interior of the earth The interior of the earth
Our changing continent Our changing continent
Related
Foreshocks, aftershocks - what's the difference? Foreshocks, aftershocks - what's the difference?
"Foreshock" and "aftershock" are relative terms. Foreshocks are earthquakes that precede larger earthquakes in the same location. An earthquake cannot be identified as a foreshock until after a larger earthquake in the same area occurs. Aftershocks are smaller earthquakes that occur in the same general area during the days to years following a larger event or "mainshock." They occur within 1-2...
Can the position of the moon or the planets affect seismicity? Are there more earthquakes in the morning/in the evening/at a certain time of the month? Can the position of the moon or the planets affect seismicity? Are there more earthquakes in the morning/in the evening/at a certain time of the month?
Earthquakes are equally as likely to occur in the morning or the evening. Many studies in the past have shown no significant correlations between the rate of earthquake occurrence and the semi-diurnal tides when using large earthquake catalogs. Several recent studies, however, have found a correlation between earth tides (caused by the position of the moon relative to the earth) and some types of...
What is surface faulting or surface rupture in an earthquake? What is surface faulting or surface rupture in an earthquake?
Surface rupture occurs when movement on a fault deep within the earth breaks through to the surface. NOT ALL earthquakes result in surface rupture.
At what depth do earthquakes occur? What is the significance of the depth? At what depth do earthquakes occur? What is the significance of the depth?
Earthquakes occur in the crust or upper mantle, which ranges from the earth's surface to about 800 kilometers deep (about 500 miles). The strength of shaking from an earthquake diminishes with increasing distance from the earthquake's source, so the strength of shaking at the surface from an earthquake that occurs at 500 km deep is considerably less than if the same earthquake had occurred at 20...
Why are there so many earthquakes in the Geysers area in Northern California? Why are there so many earthquakes in the Geysers area in Northern California?
The Geysers Geothermal Field is located in a tectonically active region of Northern California. The major seismic hazards in the region are from large earthquakes occurring along regional faults that are located miles away from the geothermal field, such as the San Andreas and Healdsburg-Rodgers Creek faults. However, activities associated with the withdrawal of steam for producing electric power...
Do earthquakes occur in Antarctica? Do earthquakes occur in Antarctica?
Earthquakes do occur in Antarctica, but not very often. There have been some big earthquakes--including one magnitude 8.1--in the Balleny Islands (between Antarctica and New Zealand). The boundary between the Scotia Plate and the Antarctic Plate just grazes the north tip of the Antarctic Peninsula (look "northwest" from the Pole toward South America). There is also a hint of a line of seismicity...
Where can I find earthquake educational materials? Where can I find earthquake educational materials?
Start with our Earthquake Hazards Education site. That includes: Earthquakes for Kids Cool Earthquake Facts Earthquake Science for Everyone Other good starting points include: State Geological Surveys for states in earthquake-prone regions The Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drills website SAGE (Seismological Facility for the Advancement of Geoscience), which is a non-profit consortium
Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes? Can we cause earthquakes? Is there any way to prevent earthquakes?
Earthquakes induced by human activity have been documented at many locations in the United States and in many other countries around the world. Earthquakes can be induced by a wide range of causes including impoundment of reservoirs, surface and underground mining, withdrawal of fluids and gas from the subsurface, and injection of fluids into underground formations. While most induced earthquakes...
What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms? What is the difference between aftershocks and swarms?
Aftershocks are a sequence of earthquakes that happen after a larger mainshock on a fault. Aftershocks occur near the fault zone where the mainshock rupture occurred and are part of the "readjustment process” after the main slip on the fault. Aftershocks become less frequent with time, although they can continue for days, weeks, months, or even years for a very large mainshock. A swarm, on the...
If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the right block moves toward you and the left block moves away.
If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the right block moves toward you and the left block moves away.
Diagram of left-lateral motion on fault. If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the left block moves toward you and the right block moves away. See also right-lateral.
Diagram of left-lateral motion on fault. If you were to stand on the fault and look along its length, this is a type of strike-slip fault where the left block moves toward you and the right block moves away. See also right-lateral.
Horst and graben diagram. A graben is a down-dropped block of the earth's crust resulting from extension, or pulling, of the crust.
Horst and graben diagram. A graben is a down-dropped block of the earth's crust resulting from extension, or pulling, of the crust.
Subduction zone of the Juan de Fuca Plate and North America Plate, creating the Mt. St. Helens and Mt. Hood volcanoes.
Subduction zone of the Juan de Fuca Plate and North America Plate, creating the Mt. St. Helens and Mt. Hood volcanoes.
Building damanged by the February 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand.
Building damanged by the February 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, New Zealand.
Listen to hear the answer.
What is an earthquake and what causes them to happen?
What is an earthquake and what causes them to happen?Listen to hear the answer.
Listen to hear the answer.
Oblique aerial view of San Andreas Fault (between white arrows) in southeastern Coachella Valley, near Red Canyon; view to the west.
Oblique aerial view of San Andreas Fault (between white arrows) in southeastern Coachella Valley, near Red Canyon; view to the west.