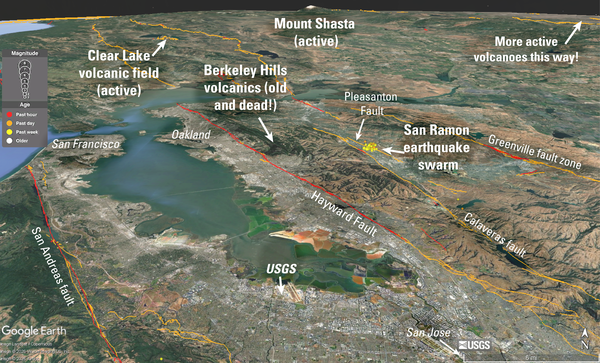
Map of the January-February 2026 San Ramon earthquake swarm, Bay area faults, and volcanic areas
Map of the January-February 2026 San Ramon earthquake swarm, Bay area faults, and volcanic areasThis oblique Google Earth map shows the location of the 2026 San Ramon earthquake swarm, along with notable faults in the San Francisco Bay area and the nearest volcanic areas to the swarm. Google Earth image modified by J. Ball, USGS.