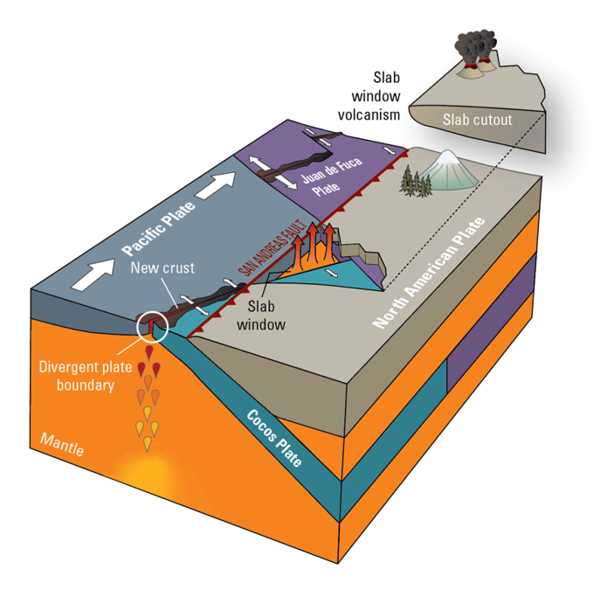
This figure shows an approximation of the tectonic plate geometry of western California as it existed roughly 20 million years ago. A piece of the North American tectonic plate has been cut out to show how a slab window is formed when a spreading ridge is subducted.
Multimedia
Images
This figure shows an approximation of the tectonic plate geometry of western California as it existed roughly 20 million years ago. A piece of the North American tectonic plate has been cut out to show how a slab window is formed when a spreading ridge is subducted.
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field
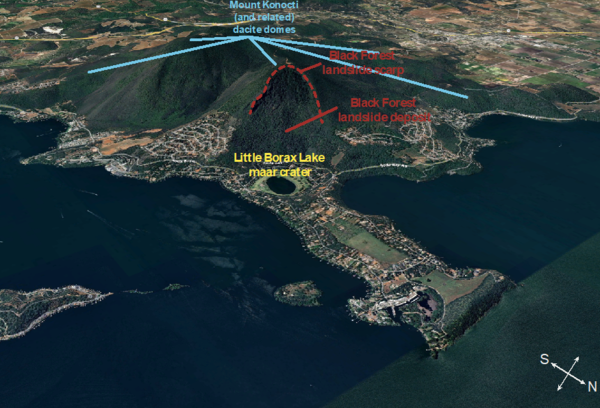
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic FieldRoughly a third of the total erupted volume of the Clear Lake volcanic field is represented by the ~ 35 km3 of rocks comprising Mt. Konocti and nearby hills. The mountain itself is over 1200 m (~4000 ft) high and is comprised primarily of a series of dacitic lava domes – Buckingham Peak, Wright Peak, and South Peak, and Howard Peak are all dacites.
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic FieldRoughly a third of the total erupted volume of the Clear Lake volcanic field is represented by the ~ 35 km3 of rocks comprising Mt. Konocti and nearby hills. The mountain itself is over 1200 m (~4000 ft) high and is comprised primarily of a series of dacitic lava domes – Buckingham Peak, Wright Peak, and South Peak, and Howard Peak are all dacites.
Just as the Bartlett Springs and Maacama faults are the major bounding faults of the Clear Lake volcanic field, the Collayami (purple) and Maacama (green) faults bound the Geysers Geothermal Field.
Just as the Bartlett Springs and Maacama faults are the major bounding faults of the Clear Lake volcanic field, the Collayami (purple) and Maacama (green) faults bound the Geysers Geothermal Field.
The Clear Lake volcanic field erupted in association with and within the San Andreas Fault Zone. Although the San Andreas fault is the hallmark fault associated with the transform tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American plates, the “boundary” between plates is more accurately described by a zone of faulting than by a single fault.
The Clear Lake volcanic field erupted in association with and within the San Andreas Fault Zone. Although the San Andreas fault is the hallmark fault associated with the transform tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American plates, the “boundary” between plates is more accurately described by a zone of faulting than by a single fault.
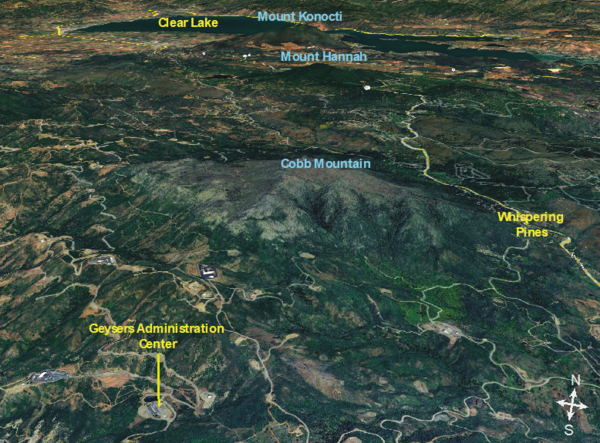
At over 4700ft (1440 m), Cobb Mountain is the tallest peak in the Mayacamas Mountains. Cobb Mountain is comprised entirely of ~ 1 million-year-old silica-rich volcanic rocks related to the Clear Lake volcanic field.
At over 4700ft (1440 m), Cobb Mountain is the tallest peak in the Mayacamas Mountains. Cobb Mountain is comprised entirely of ~ 1 million-year-old silica-rich volcanic rocks related to the Clear Lake volcanic field.

Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth Burgess
Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth BurgessCalVO geologist Seth Burgess looking across Clear Lake at Mount Konocti, a prominent volcanic dome complex within the Clear Lake volcanic field. Photo courtesy of Alexander Rubin.
Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth Burgess
Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth BurgessCalVO geologist Seth Burgess looking across Clear Lake at Mount Konocti, a prominent volcanic dome complex within the Clear Lake volcanic field. Photo courtesy of Alexander Rubin.