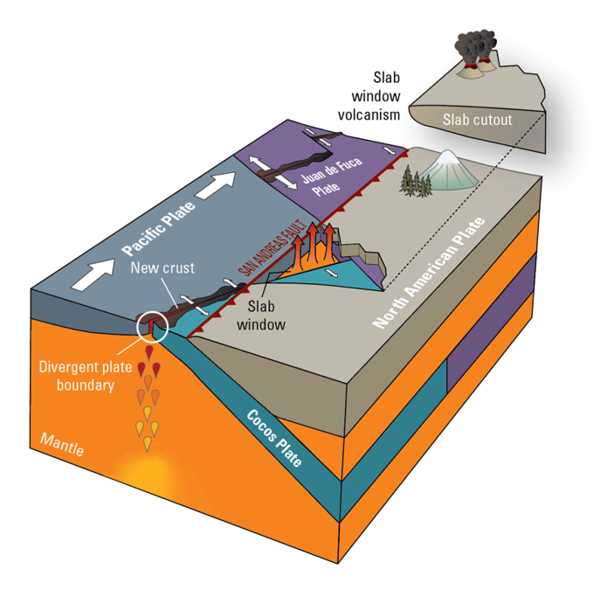
This figure shows an approximation of the tectonic plate geometry of western California as it existed roughly 20 million years ago. A piece of the North American tectonic plate has been cut out to show how a slab window is formed when a spreading ridge is subducted.
Images
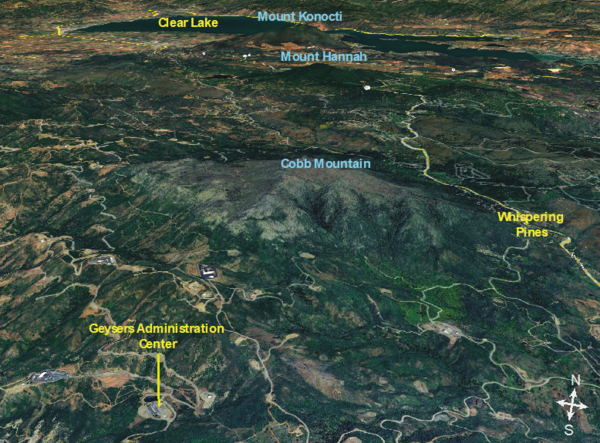
Images of Clear Lake Volcanic Field.
This figure shows an approximation of the tectonic plate geometry of western California as it existed roughly 20 million years ago. A piece of the North American tectonic plate has been cut out to show how a slab window is formed when a spreading ridge is subducted.
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic FieldRoughly a third of the total erupted volume of the Clear Lake volcanic field is represented by the ~ 35 km3 of rocks comprising Mt. Konocti and nearby hills. The mountain itself is over 1200 m (~4000 ft) high and is comprised primarily of a series of dacitic lava domes – Buckingham Peak, Wright Peak, and South Peak, and Howard Peak are all dacites.
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field
The lava dome complex of Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic FieldRoughly a third of the total erupted volume of the Clear Lake volcanic field is represented by the ~ 35 km3 of rocks comprising Mt. Konocti and nearby hills. The mountain itself is over 1200 m (~4000 ft) high and is comprised primarily of a series of dacitic lava domes – Buckingham Peak, Wright Peak, and South Peak, and Howard Peak are all dacites.
Just as the Bartlett Springs and Maacama faults are the major bounding faults of the Clear Lake volcanic field, the Collayami (purple) and Maacama (green) faults bound the Geysers Geothermal Field.
Just as the Bartlett Springs and Maacama faults are the major bounding faults of the Clear Lake volcanic field, the Collayami (purple) and Maacama (green) faults bound the Geysers Geothermal Field.
The Clear Lake volcanic field erupted in association with and within the San Andreas Fault Zone. Although the San Andreas fault is the hallmark fault associated with the transform tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American plates, the “boundary” between plates is more accurately described by a zone of faulting than by a single fault.
The Clear Lake volcanic field erupted in association with and within the San Andreas Fault Zone. Although the San Andreas fault is the hallmark fault associated with the transform tectonic boundary between the Pacific and North American plates, the “boundary” between plates is more accurately described by a zone of faulting than by a single fault.
At over 4700ft (1440 m), Cobb Mountain is the tallest peak in the Mayacamas Mountains. Cobb Mountain is comprised entirely of ~ 1 million-year-old silica-rich volcanic rocks related to the Clear Lake volcanic field.
At over 4700ft (1440 m), Cobb Mountain is the tallest peak in the Mayacamas Mountains. Cobb Mountain is comprised entirely of ~ 1 million-year-old silica-rich volcanic rocks related to the Clear Lake volcanic field.

Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth Burgess
Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth BurgessCalVO geologist Seth Burgess looking across Clear Lake at Mount Konocti, a prominent volcanic dome complex within the Clear Lake volcanic field. Photo courtesy of Alexander Rubin.
Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth Burgess
Mount Konocti, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and CalVO geologist Seth BurgessCalVO geologist Seth Burgess looking across Clear Lake at Mount Konocti, a prominent volcanic dome complex within the Clear Lake volcanic field. Photo courtesy of Alexander Rubin.
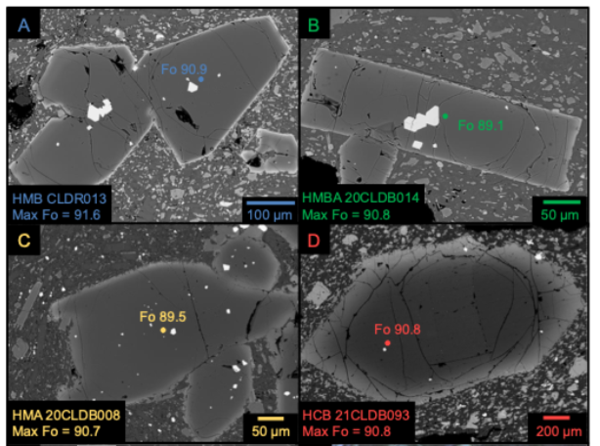
Back-scattered electron images of olivine and chromium spinel crystals
Back-scattered electron images of olivine and chromium spinel crystalsBack-scattered electron images of olivine and chromium spinel crystals from primitive Clear Lake Volcanic Field samples. The labeled colored dots on the crystals show the locations where they were analyzed with an electron microprobe for geochemical information. Figure by Dawnika Blatter.
Back-scattered electron images of olivine and chromium spinel crystals
Back-scattered electron images of olivine and chromium spinel crystalsBack-scattered electron images of olivine and chromium spinel crystals from primitive Clear Lake Volcanic Field samples. The labeled colored dots on the crystals show the locations where they were analyzed with an electron microprobe for geochemical information. Figure by Dawnika Blatter.
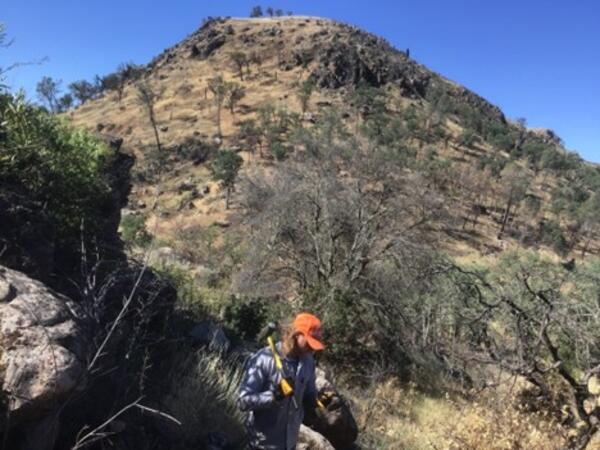

Sampling primitive older lavas in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Sampling primitive older lavas in the Clear Lake Volcanic FieldUSGS CalVO Research Geologist Seth Burgess collecting a sample of old, primitive lava in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field for geochemical analysis. USGS photo by Dawnika Blatter.
Sampling primitive older lavas in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Sampling primitive older lavas in the Clear Lake Volcanic FieldUSGS CalVO Research Geologist Seth Burgess collecting a sample of old, primitive lava in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field for geochemical analysis. USGS photo by Dawnika Blatter.
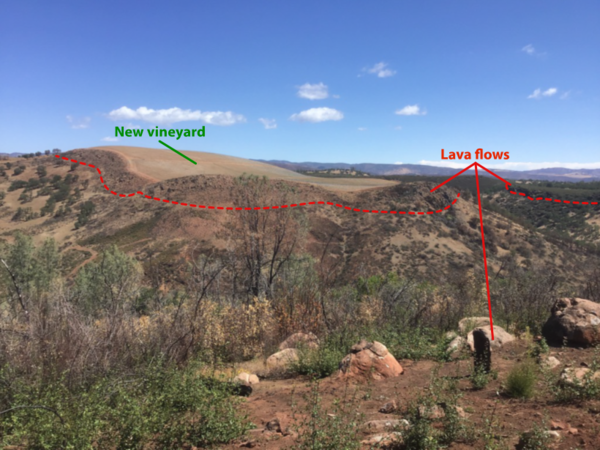
Inverted topography in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Inverted topography in the Clear Lake Volcanic FieldFrom this vantage point, the remnants of a Clear Lake volcanic field lava flow can be seen forming the prominent ridge across Highway 20. They are iron-rich and a popular location for vineyard cultivation.
Inverted topography in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Inverted topography in the Clear Lake Volcanic FieldFrom this vantage point, the remnants of a Clear Lake volcanic field lava flow can be seen forming the prominent ridge across Highway 20. They are iron-rich and a popular location for vineyard cultivation.
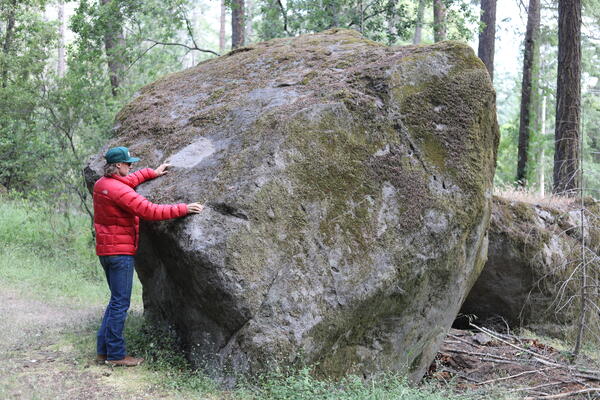

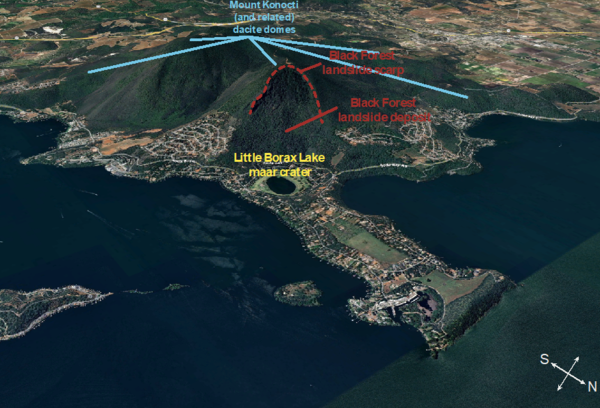
Black Forest landslide boulder, Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Black Forest landslide boulder, Clear Lake Volcanic FieldA prominent feature carved out of the side of Mount Konocti is the Black Forest landslide, which occurred on the eastern side of Buckingham Peak and deposited massive boulders down near the shore of Clear Lake. Determining when the landslide occurred is difficult, but two broad age constraints do exist.
Black Forest landslide boulder, Clear Lake Volcanic Field
Black Forest landslide boulder, Clear Lake Volcanic FieldA prominent feature carved out of the side of Mount Konocti is the Black Forest landslide, which occurred on the eastern side of Buckingham Peak and deposited massive boulders down near the shore of Clear Lake. Determining when the landslide occurred is difficult, but two broad age constraints do exist.
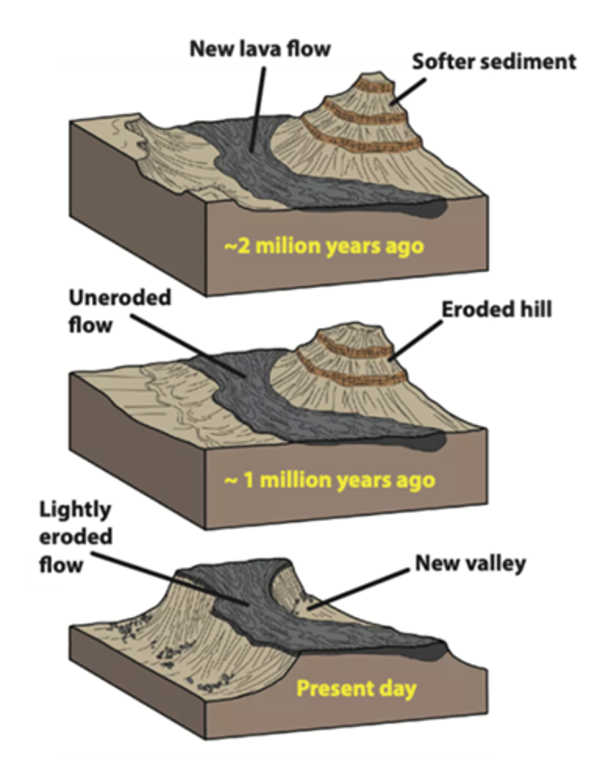
Schematic illustration of inverted topography (NPS)
Schematic illustration of inverted topography (NPS)Schematic illustrations of the formation of inverted topography. Top graphic: Lava flows travel in topographic lows and valleys below surrounding topographic highs. Middle graphic: The hard volcanic rock protects the underlying country rock from erosion, eroding more slowly than the surrounding topography.
Schematic illustration of inverted topography (NPS)
Schematic illustration of inverted topography (NPS)Schematic illustrations of the formation of inverted topography. Top graphic: Lava flows travel in topographic lows and valleys below surrounding topographic highs. Middle graphic: The hard volcanic rock protects the underlying country rock from erosion, eroding more slowly than the surrounding topography.

Kelsey Creek rhyodacite lava, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Kelsey Creek rhyodacite lava, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaRhyodacite has more silica than dacite and less than rhyolite. This flow-banded rhyodacite is gorgeous in outcrop and is around a half million years old.
Kelsey Creek rhyodacite lava, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Kelsey Creek rhyodacite lava, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaRhyodacite has more silica than dacite and less than rhyolite. This flow-banded rhyodacite is gorgeous in outcrop and is around a half million years old.

Andesite on Highway 175, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Andesite on Highway 175, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThis outcrop is along Highway 175, near Hobergs, and is comprised of andesite. Andesite contains more silica than basalt, but less than dacite.
Andesite on Highway 175, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Andesite on Highway 175, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThis outcrop is along Highway 175, near Hobergs, and is comprised of andesite. Andesite contains more silica than basalt, but less than dacite.

Eruption Episode 4 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Eruption Episode 4 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThe cinder cone in the distance is Round Mountain, which is being actively quarried for road rock. Eruption episode 4 is the most recent in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and is characterized primarily by lava flows, cinder cones (like the one pictured), and maar deposits.
Eruption Episode 4 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Eruption Episode 4 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThe cinder cone in the distance is Round Mountain, which is being actively quarried for road rock. Eruption episode 4 is the most recent in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field, and is characterized primarily by lava flows, cinder cones (like the one pictured), and maar deposits.
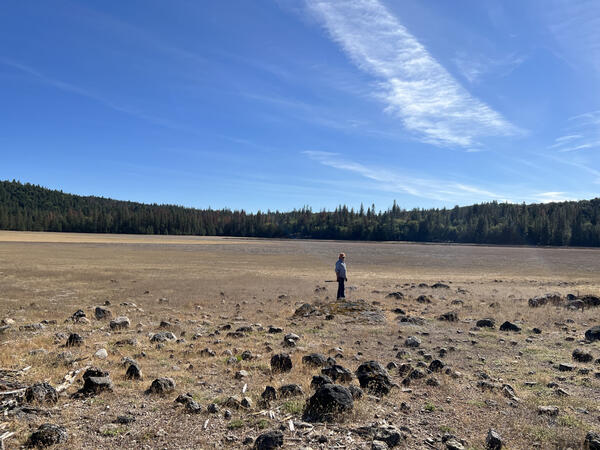

Eruption Episode 2 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Eruption Episode 2 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaEruption episode 2 rocks are higher in silica than those characterizing Episode 1, and instead of being primarily lava flows that filled existing valleys, Episode 2 rocks commonly erupted as volcanic domes. Cobb Mountain erupted during this episode, as did Boggs Mountain.
Eruption Episode 2 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Eruption Episode 2 rocks, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaEruption episode 2 rocks are higher in silica than those characterizing Episode 1, and instead of being primarily lava flows that filled existing valleys, Episode 2 rocks commonly erupted as volcanic domes. Cobb Mountain erupted during this episode, as did Boggs Mountain.

Maar eruption deposit, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Maar eruption deposit, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThe layered deposits shown in this picture were created by a maar eruption, when magma and volcanic gasses interact with groundwater to create an explosive eruption. Maar eruptions like these commonly generate craters, some of which can be seen along the western shore of Clear Lake. Soda Bay, near where this photo was taken, is a maar crater.
Maar eruption deposit, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Maar eruption deposit, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThe layered deposits shown in this picture were created by a maar eruption, when magma and volcanic gasses interact with groundwater to create an explosive eruption. Maar eruptions like these commonly generate craters, some of which can be seen along the western shore of Clear Lake. Soda Bay, near where this photo was taken, is a maar crater.

Mount Konocti lava dome complex, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Mount Konocti lava dome complex, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThis view of Mt. Konocti from within the Clearlake Riviera neighborhood shows the topographic outline of the many discrete volcanic domes that comprise the mountain. Volcanic domes ooze from the ground to form steep-sided domes which can coalesce, forming mountains with multiple peaks. Mt.
Mount Konocti lava dome complex, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
Mount Konocti lava dome complex, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThis view of Mt. Konocti from within the Clearlake Riviera neighborhood shows the topographic outline of the many discrete volcanic domes that comprise the mountain. Volcanic domes ooze from the ground to form steep-sided domes which can coalesce, forming mountains with multiple peaks. Mt.

High Valley basaltic andesite lava flow, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
High Valley basaltic andesite lava flow, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThis lava flow of basaltic andesite composition erupted in the High Valley area. The blocky appearance of this flow top is termed 'A'ā (pronounced "ah-ah"), which is a Hawaiian term for lava flows that have a rough rubbly surface composed of broken lava blocks called clinkers. USGS photo by Dawnika Blatter
High Valley basaltic andesite lava flow, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California
High Valley basaltic andesite lava flow, Clear Lake Volcanic Field, CaliforniaThis lava flow of basaltic andesite composition erupted in the High Valley area. The blocky appearance of this flow top is termed 'A'ā (pronounced "ah-ah"), which is a Hawaiian term for lava flows that have a rough rubbly surface composed of broken lava blocks called clinkers. USGS photo by Dawnika Blatter
This outcropping of rocks along Morgan Valley Road is comprised of dacite, the most common composition in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field. Dacite contains more silica than basalt but less than rhyolite, so it’s commonly referred to as an “intermediate” composition.
This outcropping of rocks along Morgan Valley Road is comprised of dacite, the most common composition in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field. Dacite contains more silica than basalt but less than rhyolite, so it’s commonly referred to as an “intermediate” composition.
A southwesterly view of Mount Konocti, which is one of the largest volcanic features in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field. Buckingham Peninsula can also be seen stretching from the base of Mount Konocti into the foreground toward the eastern shore of the lake. USGS photo by J.Ball
A southwesterly view of Mount Konocti, which is one of the largest volcanic features in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field. Buckingham Peninsula can also be seen stretching from the base of Mount Konocti into the foreground toward the eastern shore of the lake. USGS photo by J.Ball
These freshly excavated boulders along Spruce Grove Road are basalt, which is an iron and magnesium-rich rock that’s fairly uncommon in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field.
These freshly excavated boulders along Spruce Grove Road are basalt, which is an iron and magnesium-rich rock that’s fairly uncommon in the Clear Lake Volcanic Field.