Pennsylvania and the Potomac River Basin
Active
By Pennsylvania Water Science Center
January 9, 1999
USGS provides monitoring, analysis, modeling and research on streamflow and water quality in the Potomac river basin.
Media

Sources/Usage: Public Domain. View Media Details
New study highlights the role of wastewater and landscape sources contributing to pesticide contamination in the Potomac River watershed
Wastewater treatment plant discharges can be a source of organic contaminants, including pesticides, to rivers. Pesticide concentrations were predicted based on wastewater percentages in stream water using a modeling tool, and verified with measured concentrations to identify other potential landscape sources.
Changing Freshwater Flows Affect Fish Populations in the Potomac River
Issue: Millions of people rely on the Potomac River for drinking water and recreational opportunities. The Potomac is Maryland’s most popular freshwater fishing destination, and the second largest river that enters the Chesapeake Bay. Restoring fisheries is also an important goal for the Chesapeake Bay Partnership restoration efforts.
Mycobacteriosis among northern snakehead fish in the Potomac River
Mycobacteriosis among northern snakehead fish in the Potomac River
Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plant effluent contributions to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Potomac River: A basin-scale measuring and modeling approach Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plant effluent contributions to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Potomac River: A basin-scale measuring and modeling approach
Managing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water resources requires a basin-scale approach. Predicted environmental concentrations (PEC) and stream-vulnerability scores for PFAS were determined for the Potomac River watershed in the eastern United States. Approximately 15% of stream reaches contained municipal and/or industrial wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) discharges...
Authors
Larry B. Barber, Samuel Adam Miller, Lee Blaney, Paul M. Bradley, Kaycee E. Faunce, Jacob Fleck, Malinda Frick, Ke He, Ryan D. Hollins, Conor J. Lewellyn, Emily H. Majcher, Mitchell A. McAdoo, Kelly Smalling
Factors contributing to pesticide contamination in riverine systems: The role of wastewater and landscape sources Factors contributing to pesticide contamination in riverine systems: The role of wastewater and landscape sources
Wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) discharges can be a source of organic contaminants, including pesticides, to rivers. An integrated model was developed for the Potomac River watershed (PRW) to determine the amount of accumulated wastewater percentage of streamflow (ACCWW) and calculate predicted environmental concentrations (PECs) for 14 pesticides in non-tidal National Hydrography...
Authors
Samuel Adam Miller, Kaycee E. Faunce, Larry B. Barber, Jacob Fleck, Daniel Walter Burns, Jeramy Roland Jasmann, Michelle L. Hladik
Wastewater reuse and predicted ecological risk posed by contaminant mixtures in Potomac River watershed streams Wastewater reuse and predicted ecological risk posed by contaminant mixtures in Potomac River watershed streams
A wastewater model was applied to the Potomac River watershed to provide (i) a means to identify streams with a high likelihood of carrying elevated effluent-derived contaminants and (ii) risk assessments to aquatic life and drinking water. The model linked effluent discharges along stream networks, accumulated wastewater, and predicted contaminant loads of municipal wastewater...
Authors
Kaycee E. Faunce, Larry B. Barber, Steffanie H. Keefe, Jeramy Roland Jasmann, Jennifer L. Krstolic
Perfluoroalkyl substances in plasma of smallmouth bass from the Chesapeake Bay Watershed Perfluoroalkyl substances in plasma of smallmouth bass from the Chesapeake Bay Watershed
Smallmouth bass Micropterus dolomieu is an economically important sportfish and within the Chesapeake Bay watershed has experienced a high prevalence of external lesions, infectious disease, mortality events, reproductive endocrine disruption and population declines. To date, no clear or consistent associations with contaminants measured in fish tissue or surface water have been found...
Authors
Vicki S. Blazer, Stephanie E. Gordon, Heather L. Walsh, Cheyenne R. Smith
Modeling estrogenic activity in streams throughout the Potomac and Chesapeake Bay watersheds Modeling estrogenic activity in streams throughout the Potomac and Chesapeake Bay watersheds
Endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs), specifically estrogenic endocrine-disrupting compounds, vary in concentration and composition in surface waters under the influence of different landscape sources and landcover gradients. Estrogenic activity in surface waters may lead to adverse effects in aquatic species at both individual and population levels, often observed through the presence...
Authors
Stephanie E. Gordon, Daniel K. Jones, Vicki S. Blazer, Luke R. Iwanowicz, Brianna Williams, Kelly Smalling
Water resources data, Pennsylvania, water year 2004—Volume 2. Susquehanna and Potomac River basins Water resources data, Pennsylvania, water year 2004—Volume 2. Susquehanna and Potomac River basins
Water resources data for the 2004 water year for Pennsylvania consist of records of discharge and water quality of streams; contents and elevations of lakes and reservoirs; and water levels and water quality of ground-water wells. This report, Volume 2 contains (1) discharge records for 85 continuous-record streamflow-gaging stations, 13 partial-record stations, 18 special study and...
Authors
R.R. Durlin, W.P. Schaffstall
Ground-water quality and data on wells and springs in Pennsylvania: Volume II, Susquehanna and Potomac River basins Ground-water quality and data on wells and springs in Pennsylvania: Volume II, Susquehanna and Potomac River basins
Volume II of the Ground-Water Quality and Data on Wells and Springs in Pennsylvania presents ground-water quality and physical data on about 1,400 wells and springs in the Susquehanna and Potomac River basins in Pennsylvania. Locations are shown on site-location maps derived from the hydrologic unit map. Codes showing the geologic age and aquifer are provided. (USGS)
Authors
Harry E. Koester, Denise R. Miller
USGS Potomac River Watershed Accumulated Wastewater Viewer USGS Potomac River Watershed Accumulated Wastewater Viewer
These data and application are provided as part of USGS research on contaminants in surface waters across the United States and supported by the USGS Water Mission Area Proxies Project and the USGS Ecosystem Mission Area Environmental Health Program (Toxic Substances Hydrology).
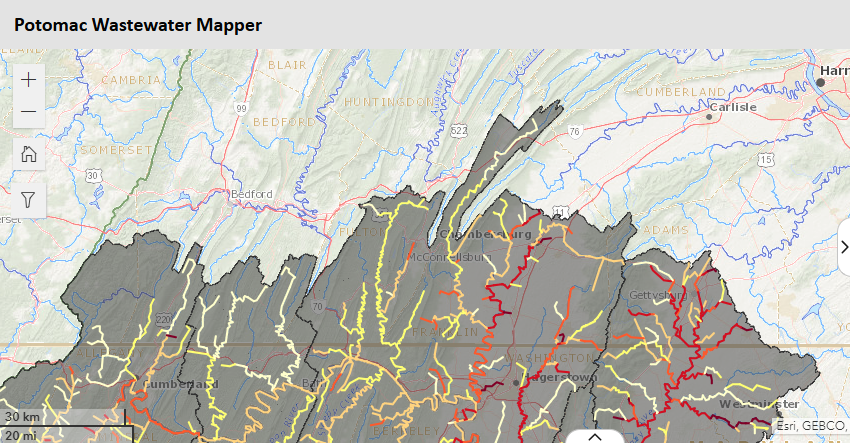
Interactive Map: Potomac Wastewater Mapper Interactive Map: Potomac Wastewater Mapper
The Potomac Wastewater Mapper is intended to help identify streams with elevated wastewater conditions or predicted ecological risk posed by municipal effluent-derived wastewater mixtures that may require further attention by resource managers, either through targeted contaminant monitoring and sampling or wastewater treatment plant upgrades to improve contaminant removal.
USGS provides monitoring, analysis, modeling and research on streamflow and water quality in the Potomac river basin.
Media


Sources/Usage: Public Domain. View Media Details
New study highlights the role of wastewater and landscape sources contributing to pesticide contamination in the Potomac River watershed
Wastewater treatment plant discharges can be a source of organic contaminants, including pesticides, to rivers. Pesticide concentrations were predicted based on wastewater percentages in stream water using a modeling tool, and verified with measured concentrations to identify other potential landscape sources.
Changing Freshwater Flows Affect Fish Populations in the Potomac River
Issue: Millions of people rely on the Potomac River for drinking water and recreational opportunities. The Potomac is Maryland’s most popular freshwater fishing destination, and the second largest river that enters the Chesapeake Bay. Restoring fisheries is also an important goal for the Chesapeake Bay Partnership restoration efforts.
Mycobacteriosis among northern snakehead fish in the Potomac River
Mycobacteriosis among northern snakehead fish in the Potomac River
Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plant effluent contributions to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Potomac River: A basin-scale measuring and modeling approach Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plant effluent contributions to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Potomac River: A basin-scale measuring and modeling approach
Managing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water resources requires a basin-scale approach. Predicted environmental concentrations (PEC) and stream-vulnerability scores for PFAS were determined for the Potomac River watershed in the eastern United States. Approximately 15% of stream reaches contained municipal and/or industrial wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) discharges...
Authors
Larry B. Barber, Samuel Adam Miller, Lee Blaney, Paul M. Bradley, Kaycee E. Faunce, Jacob Fleck, Malinda Frick, Ke He, Ryan D. Hollins, Conor J. Lewellyn, Emily H. Majcher, Mitchell A. McAdoo, Kelly Smalling
Factors contributing to pesticide contamination in riverine systems: The role of wastewater and landscape sources Factors contributing to pesticide contamination in riverine systems: The role of wastewater and landscape sources
Wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) discharges can be a source of organic contaminants, including pesticides, to rivers. An integrated model was developed for the Potomac River watershed (PRW) to determine the amount of accumulated wastewater percentage of streamflow (ACCWW) and calculate predicted environmental concentrations (PECs) for 14 pesticides in non-tidal National Hydrography...
Authors
Samuel Adam Miller, Kaycee E. Faunce, Larry B. Barber, Jacob Fleck, Daniel Walter Burns, Jeramy Roland Jasmann, Michelle L. Hladik
Wastewater reuse and predicted ecological risk posed by contaminant mixtures in Potomac River watershed streams Wastewater reuse and predicted ecological risk posed by contaminant mixtures in Potomac River watershed streams
A wastewater model was applied to the Potomac River watershed to provide (i) a means to identify streams with a high likelihood of carrying elevated effluent-derived contaminants and (ii) risk assessments to aquatic life and drinking water. The model linked effluent discharges along stream networks, accumulated wastewater, and predicted contaminant loads of municipal wastewater...
Authors
Kaycee E. Faunce, Larry B. Barber, Steffanie H. Keefe, Jeramy Roland Jasmann, Jennifer L. Krstolic
Perfluoroalkyl substances in plasma of smallmouth bass from the Chesapeake Bay Watershed Perfluoroalkyl substances in plasma of smallmouth bass from the Chesapeake Bay Watershed
Smallmouth bass Micropterus dolomieu is an economically important sportfish and within the Chesapeake Bay watershed has experienced a high prevalence of external lesions, infectious disease, mortality events, reproductive endocrine disruption and population declines. To date, no clear or consistent associations with contaminants measured in fish tissue or surface water have been found...
Authors
Vicki S. Blazer, Stephanie E. Gordon, Heather L. Walsh, Cheyenne R. Smith
Modeling estrogenic activity in streams throughout the Potomac and Chesapeake Bay watersheds Modeling estrogenic activity in streams throughout the Potomac and Chesapeake Bay watersheds
Endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs), specifically estrogenic endocrine-disrupting compounds, vary in concentration and composition in surface waters under the influence of different landscape sources and landcover gradients. Estrogenic activity in surface waters may lead to adverse effects in aquatic species at both individual and population levels, often observed through the presence...
Authors
Stephanie E. Gordon, Daniel K. Jones, Vicki S. Blazer, Luke R. Iwanowicz, Brianna Williams, Kelly Smalling
Water resources data, Pennsylvania, water year 2004—Volume 2. Susquehanna and Potomac River basins Water resources data, Pennsylvania, water year 2004—Volume 2. Susquehanna and Potomac River basins
Water resources data for the 2004 water year for Pennsylvania consist of records of discharge and water quality of streams; contents and elevations of lakes and reservoirs; and water levels and water quality of ground-water wells. This report, Volume 2 contains (1) discharge records for 85 continuous-record streamflow-gaging stations, 13 partial-record stations, 18 special study and...
Authors
R.R. Durlin, W.P. Schaffstall
Ground-water quality and data on wells and springs in Pennsylvania: Volume II, Susquehanna and Potomac River basins Ground-water quality and data on wells and springs in Pennsylvania: Volume II, Susquehanna and Potomac River basins
Volume II of the Ground-Water Quality and Data on Wells and Springs in Pennsylvania presents ground-water quality and physical data on about 1,400 wells and springs in the Susquehanna and Potomac River basins in Pennsylvania. Locations are shown on site-location maps derived from the hydrologic unit map. Codes showing the geologic age and aquifer are provided. (USGS)
Authors
Harry E. Koester, Denise R. Miller
USGS Potomac River Watershed Accumulated Wastewater Viewer USGS Potomac River Watershed Accumulated Wastewater Viewer
These data and application are provided as part of USGS research on contaminants in surface waters across the United States and supported by the USGS Water Mission Area Proxies Project and the USGS Ecosystem Mission Area Environmental Health Program (Toxic Substances Hydrology).
Interactive Map: Potomac Wastewater Mapper Interactive Map: Potomac Wastewater Mapper
The Potomac Wastewater Mapper is intended to help identify streams with elevated wastewater conditions or predicted ecological risk posed by municipal effluent-derived wastewater mixtures that may require further attention by resource managers, either through targeted contaminant monitoring and sampling or wastewater treatment plant upgrades to improve contaminant removal.




