Many Americans may be drinking groundwater with high strontium levels
Concentrations highest in wells that tap limestone aquifers
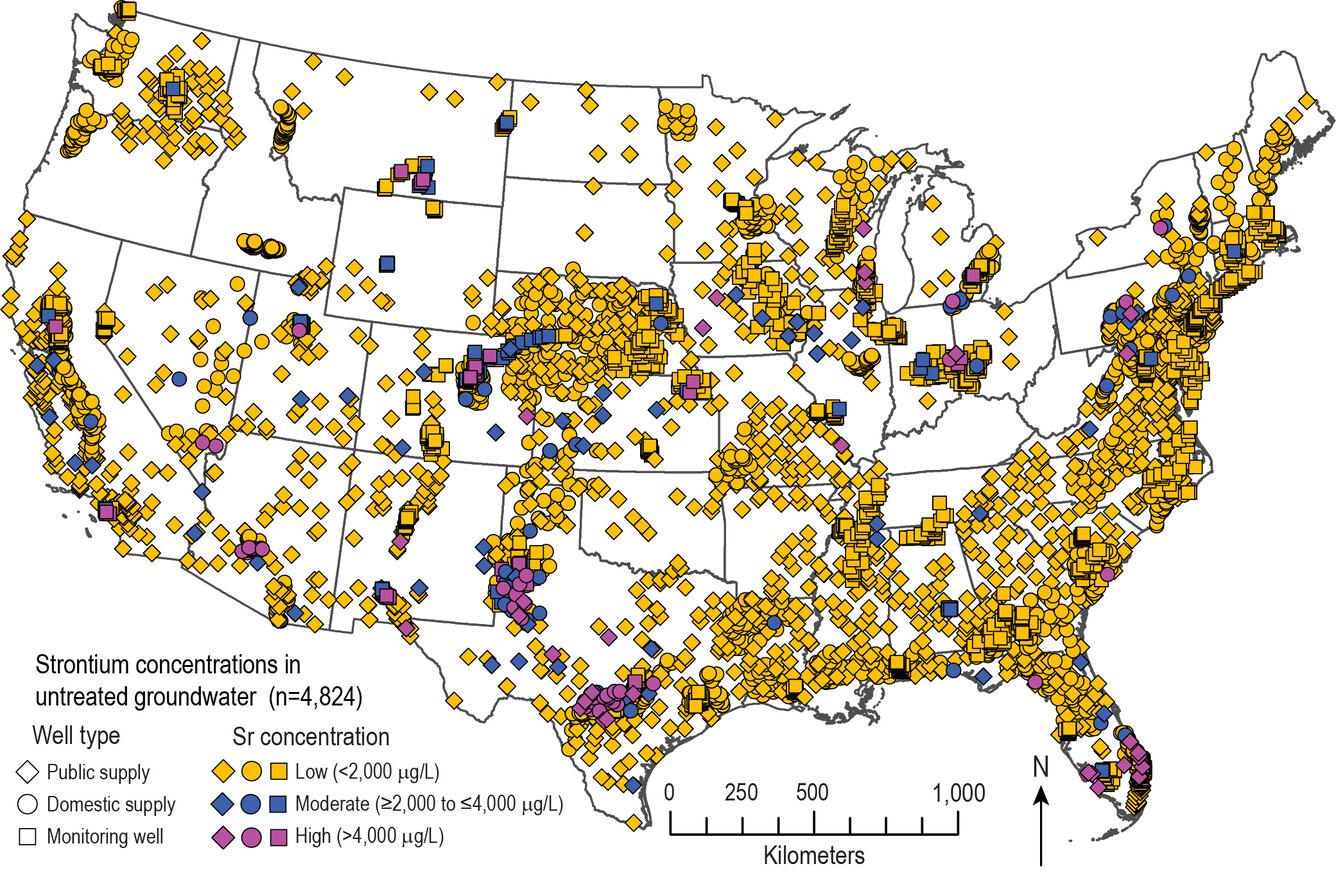
A new USGS study reports that about 2.3 percent of drinking-water wells in the U.S. have concentrations of strontium at levels that present a potential human health risk. These wells provide water for an estimated 2.3 million people.
Strontium occurs naturally in some minerals, including calcium carbonate. If strontium-containing minerals are present in soils, sediments, and rocks, strontium is released to groundwater as those minerals dissolve.
Elevated levels of strontium in groundwater were found primarily in samples of untreated groundwater from drinking-water wells that tap carbonate-rock aquifers, such as in southern Florida and central Texas. Elevated concentrations also were measured in drinking-water wells in areas of naturally upwelling brine that mixes with potable groundwater, such as in the southern High Plains aquifer in west Texas. Additionally, elevated concentrations occurred in shallow monitoring wells in unconsolidated sand and gravel aquifers in the western U.S., for example in Colorado.
Strontium is under consideration by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for regulation; currently it has a non-regulatory health-based screening level of 4,000 micrograms per liter. Elevated strontium concentrations can adversely affect bone development and mineralization. Conventional water treatment processes, such as coagulation/filtration, are largely ineffective at removing strontium from drinking water. However, water-softening treatments such as lime-soda ash or cation-exchange water softeners designed to reduce calcium concentrations also can decrease strontium concentrations.