In a September 21, 1966 press release, Secretary of the Interior Stewart Udall announced that the DOI was launching "Project EROS (Earth Resources Observation Satellites)." Udall's vision was to observe the Earth for the benefit of all.
When was the Landsat 9 satellite launched?
Landsat 9—a partnership between the USGS and NASA—was launched from Space Launch Complex 3E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California upon a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 launch vehicle on September 27, 2021.
Learn more: Landsat 9 Mission
Related
What sensors does the Landsat 9 satellite carry? What sensors does the Landsat 9 satellite carry?
Landsat 9 carries the same instruments that are on the Landsat 8 satellite but with some improvements: Operational Land Imager (OLI) for reflective band data. Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) for the thermal infrared bands. OLI has a slightly improved signal-to-noise ratio over Landsat 8's OLI. Landsat 9’s TIRS is a Class-B instrument with a five-year design life and a key improvement of stray light...
What is the Landsat satellite program and why is it important? What is the Landsat satellite program and why is it important?
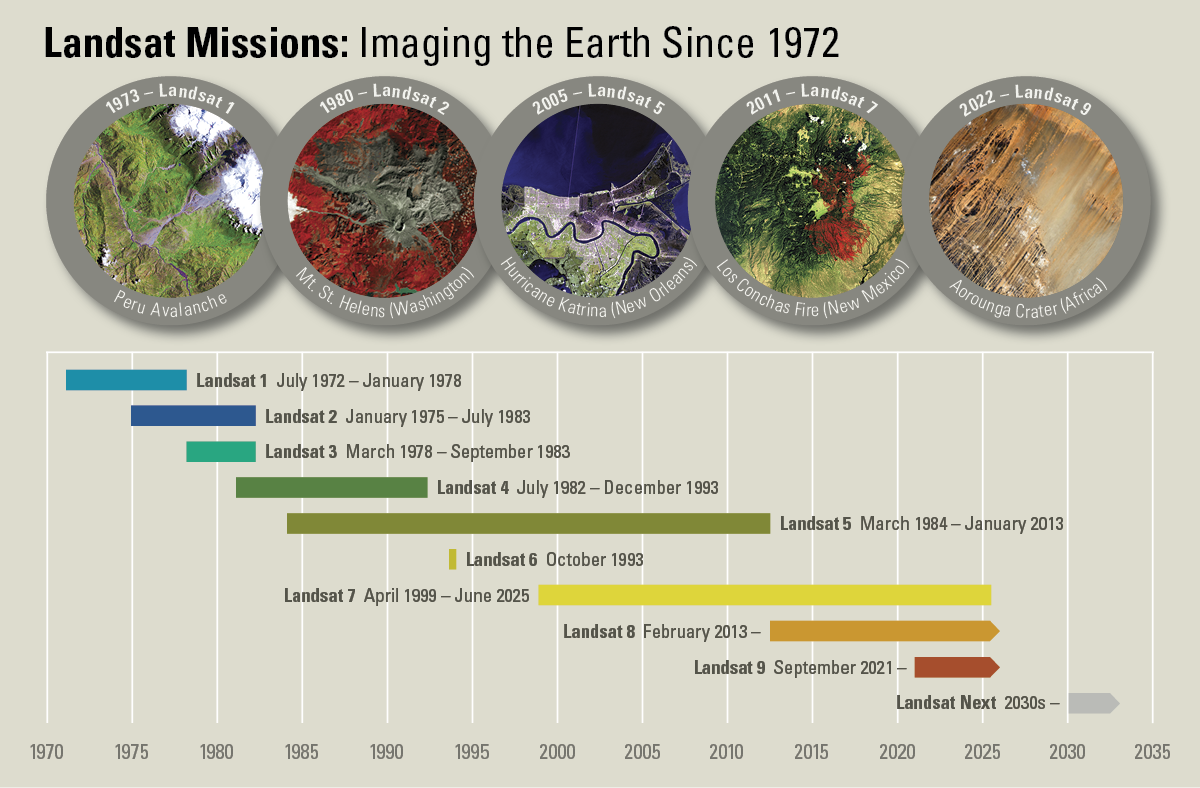
The Landsat Program is a series of Earth-observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. On July 23, 1972, in cooperation with NASA, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite (ERTS-1) was launched. It was later renamed Landsat 1. Additional Landsat satellites have launched to bring the world an archive of remote sensing data. Currently orbiting and active...
Are there any restrictions on the use or redistribution of Landsat data? Are there any restrictions on the use or redistribution of Landsat data?
There are no restrictions on Landsat data downloaded from the USGS; it can be used or redistributed as desired. We do request that you include a statement of the data source when citing, copying, or reprinting USGS Landsat data or images. Details are on the EROS Data Citation page. Learn more: USGS Copyrights and Credits statement
Can Landsat satellite acquisition requests be made for a specific date and location? Can Landsat satellite acquisition requests be made for a specific date and location?
The Landsat 8 and Landsat 9 satellites together acquire approximately 1,500 scenes daily. These scenes are available for download within 6 hours of acquisition. Landsat satellite acquisitions are managed as a system, known as a satellite constellation. Long-Term Acquisition Plans (LTAPs) direct and optimize the daily acquisitions of each active Landsat satellite. Special requests for future...
What are the acquisition schedules for the Landsat satellites? What are the acquisition schedules for the Landsat satellites?
The Landsat 8 and Landsat 9 satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of 705 kilometers (438 miles) in a 185 kilometer (115 miles) swath, moving from north to south over the sunlit side of the Earth in a sun synchronous orbit. Each satellite makes a complete orbit every 99 minutes, completes about 14 full orbits each day, and crosses every point on Earth once every 16 days. The satellite orbits...
How do I search for and download Landsat data? How do I search for and download Landsat data?
Landsat data products held in the USGS archives can be searched and downloaded at no charge from a variety of sources. Visit Landsat Data Access for information about how Landsat data products can be downloaded individually or in bulk. Landsat imagery not found in the USGS archive might have been collected by one of the USGS International Cooperator ground stations, each of which are the primary...
After a Landsat scene is collected, when will it become available for search and download? After a Landsat scene is collected, when will it become available for search and download?
Landsat scenes become available through EarthExplorer within 6 hours after acquisition and become visible in GloVis within 24 hours. See Landsat Acquisitions for acquisition calendars and information about daily schedules.
In a September 21, 1966 press release, Secretary of the Interior Stewart Udall announced that the DOI was launching "Project EROS (Earth Resources Observation Satellites)." Udall's vision was to observe the Earth for the benefit of all.
 Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt HansenMatt Hansen talks about the value of Landsat data as an infrastructure for research and innovation.
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt HansenMatt Hansen talks about the value of Landsat data as an infrastructure for research and innovation.
 Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis WoodcockBoston University Professor Curtis Woodcock talks about the significance Landsat was had in science and what he hopes to see as the mission continues.
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis WoodcockBoston University Professor Curtis Woodcock talks about the significance Landsat was had in science and what he hopes to see as the mission continues.
 Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted ScambosTed Scambos, Lead Scientist at the National Snow & Ice Data Center, talks about the roll of Landsat in his research studying polar regions.
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted ScambosTed Scambos, Lead Scientist at the National Snow & Ice Data Center, talks about the roll of Landsat in his research studying polar regions.
2019 Joint Agency Commercial Imagery Evaluation—Land remote sensing satellite compendium 2019 Joint Agency Commercial Imagery Evaluation—Land remote sensing satellite compendium
Landsat 9 Landsat 9
Earth as art 5 Earth as art 5
U.S. Landsat Analysis Ready Data U.S. Landsat Analysis Ready Data
Landsat Collections Landsat Collections
Landsat benefiting society for fifty years Landsat benefiting society for fifty years
Landsat eyes help guard the world's forests Landsat eyes help guard the world's forests
Landsat helps bolster food security Landsat helps bolster food security
Landsat plays a key role in reducing hunger on earth Landsat plays a key role in reducing hunger on earth
Landsat brings understanding to the impact of industrialization Landsat brings understanding to the impact of industrialization
When wildfire damage threatens humans, Landsat provides answers When wildfire damage threatens humans, Landsat provides answers
Landsat—The watchman that never sleeps Landsat—The watchman that never sleeps
Related
What sensors does the Landsat 9 satellite carry? What sensors does the Landsat 9 satellite carry?
Landsat 9 carries the same instruments that are on the Landsat 8 satellite but with some improvements: Operational Land Imager (OLI) for reflective band data. Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) for the thermal infrared bands. OLI has a slightly improved signal-to-noise ratio over Landsat 8's OLI. Landsat 9’s TIRS is a Class-B instrument with a five-year design life and a key improvement of stray light...
What is the Landsat satellite program and why is it important? What is the Landsat satellite program and why is it important?
The Landsat Program is a series of Earth-observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. On July 23, 1972, in cooperation with NASA, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite (ERTS-1) was launched. It was later renamed Landsat 1. Additional Landsat satellites have launched to bring the world an archive of remote sensing data. Currently orbiting and active...
Are there any restrictions on the use or redistribution of Landsat data? Are there any restrictions on the use or redistribution of Landsat data?
There are no restrictions on Landsat data downloaded from the USGS; it can be used or redistributed as desired. We do request that you include a statement of the data source when citing, copying, or reprinting USGS Landsat data or images. Details are on the EROS Data Citation page. Learn more: USGS Copyrights and Credits statement
Can Landsat satellite acquisition requests be made for a specific date and location? Can Landsat satellite acquisition requests be made for a specific date and location?
The Landsat 8 and Landsat 9 satellites together acquire approximately 1,500 scenes daily. These scenes are available for download within 6 hours of acquisition. Landsat satellite acquisitions are managed as a system, known as a satellite constellation. Long-Term Acquisition Plans (LTAPs) direct and optimize the daily acquisitions of each active Landsat satellite. Special requests for future...
What are the acquisition schedules for the Landsat satellites? What are the acquisition schedules for the Landsat satellites?
The Landsat 8 and Landsat 9 satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of 705 kilometers (438 miles) in a 185 kilometer (115 miles) swath, moving from north to south over the sunlit side of the Earth in a sun synchronous orbit. Each satellite makes a complete orbit every 99 minutes, completes about 14 full orbits each day, and crosses every point on Earth once every 16 days. The satellite orbits...
How do I search for and download Landsat data? How do I search for and download Landsat data?
Landsat data products held in the USGS archives can be searched and downloaded at no charge from a variety of sources. Visit Landsat Data Access for information about how Landsat data products can be downloaded individually or in bulk. Landsat imagery not found in the USGS archive might have been collected by one of the USGS International Cooperator ground stations, each of which are the primary...
After a Landsat scene is collected, when will it become available for search and download? After a Landsat scene is collected, when will it become available for search and download?
Landsat scenes become available through EarthExplorer within 6 hours after acquisition and become visible in GloVis within 24 hours. See Landsat Acquisitions for acquisition calendars and information about daily schedules.
In a September 21, 1966 press release, Secretary of the Interior Stewart Udall announced that the DOI was launching "Project EROS (Earth Resources Observation Satellites)." Udall's vision was to observe the Earth for the benefit of all.
In a September 21, 1966 press release, Secretary of the Interior Stewart Udall announced that the DOI was launching "Project EROS (Earth Resources Observation Satellites)." Udall's vision was to observe the Earth for the benefit of all.
 Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt HansenMatt Hansen talks about the value of Landsat data as an infrastructure for research and innovation.
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt Hansen
Landsat in Action - Infrastructure of Landsat Data with Matt HansenMatt Hansen talks about the value of Landsat data as an infrastructure for research and innovation.
 Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis WoodcockBoston University Professor Curtis Woodcock talks about the significance Landsat was had in science and what he hopes to see as the mission continues.
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis Woodcock
Landsat in Action - The Importance of Landsat with Curtis WoodcockBoston University Professor Curtis Woodcock talks about the significance Landsat was had in science and what he hopes to see as the mission continues.
 Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted ScambosTed Scambos, Lead Scientist at the National Snow & Ice Data Center, talks about the roll of Landsat in his research studying polar regions.
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted Scambos
Landsat In Action - Monitoring Polar Ice Caps with Ted ScambosTed Scambos, Lead Scientist at the National Snow & Ice Data Center, talks about the roll of Landsat in his research studying polar regions.









