Water quality
What is in that water that you just drank? Is it just hydrogen and oxygen atoms? Is it safe for drinking? All water is of a certain "quality" (and you can't tell by just looking), but what does "water quality" really mean?
General water quality • Groundwater quality • Wastewater and sewage water • Properties of water • Resources and activities
Water quality can be thought of as a measure of the suitability of water for a particular use based on selected physical, chemical, and biological characteristics.
General water quality
-
Acid Rain and Water
Depending on where you live, maybe you've heard of acid rain. Now, acid rain is not pure acid falling from the sky, but rather it is rainfall or atmospheric moisture that has been mixed with elements and gases that have caused the moisture to become more acidic than normal. Pure water has a pH of 7, and, generally, rainfall is somewhat on the acidic side (a bit less than 6). But, acid rain can...Bacteria and E. Coli in Water
Water, like everything else on Earth, including you, is full of bacteria. Some bacteria are beneficial and some are not. Escherichia coli ( E. coli) bacteria, found in the digestive tract of animals, can get into the environment, and if contacted by people, can cause health problems and sickness. Find out the details here.Desalination
Humans cannot drink saline water but saline water can be made into freshwater, for which there are many uses. The process is called "desalination", and it is being used more and more around the world to provide people with needed freshwater.Environmental DNA (eDNA)
Environmental DNA (eDNA) is organismal DNA that can be found in the environment. eDNA originates from cellular material shed by organisms (e.g., skin, hair, saliva, or feces) into aquatic and terrestrial environments. Researchers sample the air, soil, water or other areas to track or detect invasive, endangered, or rare species.Shocking Fish to Collect Ecologic Data
Collecting samples of water isn't the only way to test water quality. The USGS actually collects fish to see if and how they were affected by local pollution and chemicals in the water, such as pesticides. Read on to find out more.Mercury Contamination of Aquatic Environments
Mercury has got to be one of the most fascinating elements around. In looking at the bubbles of bright silver sitting on a flat surface, it is easy to see why mercury is also called "quicksilver." Mercury is the only metal that exists in liquid form. It may act somewhat like water, but it is nothing at all like water, especially in the potential harmful effects it can have on humans and ecosystems...Mining and Water Quality
Mine drainage is metal-rich water formed from a chemical reaction between water and rocks containing sulfur-bearing minerals. Problems that can be associated with mine drainage include contaminated drinking water, disrupted growth and reproduction of aquatic plants and animals, and the corroding effects of the acid on parts of infrastructures such as bridges.Pharmaceuticals in Water
There is a growing concern about the occurance of pharmaceuticals in water bodies and in drinking water. Pharmaceuticals get into the water supply via human excretion and by drugs being flushed down the toilet. You might think wastewater treatment plants would take care of the situation, but pharmaceuticals pass through water treatment.Water Quality Sampling Techniques
Checking the water quality of the Nation's streams, rivers, and lakes is one of the main responsibilities of the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Physical water measurements and streamflow are almost always taken, but often water samples are needed for chemical analyses, and sampling must follow strict guidelines to collect scientifically-viable samples.Saline Water and Salinity
In your everyday life you are not involved much with saline water. You are concerned with freshwater to serve your life's every need. But, most of Earth's water, and almost all of the water that people can access, is saline, or salty water. Just look at the oceans and remember that oceans comprise about 97% of all water on, in, and above the Earth.Sediment and Suspended Sediment
In nature, water is never totally clear, especially in surface water (like rivers & lakes). It may have dissolved & suspended materials that impart color or affect transparency (aka turbidity). Suspended sediment is an important factor in determining water quality & appearance.Urbanization and Water Quality
There's no end to the effects that urbanization can have on water bodies. Millions of people; landscape manipulation; waste material; dumping of chemicals and fertilizers; withdrawing water for peoples' uses. As you expect, urbanization rarely improves water quality, but in order to prevent problems, one needs to understand how urbanization affects the local waters.
-
Groundwater Quality
Even though the ground is an excellent mechanism for filtering out particulate matter, such as leaves, soil, and bugs, dissolved chemicals and gases can still occur in large enough concentrations in groundwater to cause problems.Contamination of Groundwater
Groundwater will normally look clear and clean because the ground naturally filters out particulate matter. But did you know that natural and human-induced chemicals can be found in groundwater even if appears to be clean? Below is a list of some contaminants that can occur in groundwater.Contamination in U.S. Private Wells
Groundwater is crucial to millions of Americans as well as many more worldwide. Groundwater provides drinking water to many. Thus, having reliably clean groundwater is of concern for many throughout the world. But, groundwater can become contaminated with chemicals, biologic organisms, and other possibly-harmful agents.Pesticides in Groundwater
Commercial pesticide applicators, farmers, and homeowners apply about 1 billion pounds of pesticides annually to agricultural land, non-crop land, and urban areas throughout the United States. The use of pesticides has helped to make the United States the largest producer of food in the world and has provided other benefits, but has also been accompanied by concerns about their potential adverse...
-
Urban Water Quality: Sewage Overflows
Wastewater and sewage treatment are important topics in any society, all throughout history and into today. Improperly disposed of or treated sewage can cause disease and harm the ecosystem. That is why when a sewage overflow occurs it garners negative news attention.Wastewater Treatment Water Use
Wastewater is used water. It includes substances such as human waste, food scraps, oils, soaps and chemicals. In homes, this includes water from sinks, showers, bathtubs, toilets, washing machines and dishwashers. Businesses and industries also contribute their share of used water that must be cleaned.Reclaimed Wastewater
Thirsty? How about a refreshing cup of reclaimed wastewater? No, we're kidding. You probably don't drink much reclaimed wastewater (although some people do - see below)! But reclaimed wastewater has many uses, with more promise of usage in the future.A Visit to a Wastewater Treatment Plant
Have you ever wondered what happens to that water and waste after you flush? How about after you pull the plug on your tub? The modern wastewater-treatment plant employs basic physics and high technology to purify the dirtiest of water so it can go back into the environment as a member in good standing of the water cycle.
-
Alkalinity and Water
Definition of alkalinity: "The buffering capacity of a water body; a measure of the ability of the water body to neutralize acids and bases and thus maintain a fairly stable pH level"Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Water
You don't often think that water bodies contain oxygen, but water does contain a small amount of dissolved oxygen. A small amount, but it is essential for life in the water. Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) generally represents how much oxygen is needed to break down organic matter in water.Water Color
Is pure water really clear? Not really—even pure water is not colorless, but has a slight blue tint to it. In the natural world you often see water that is definitely not clear. Sediment and organics color natural water shades of brown or green. And if too much iron in present, even your drinking water can have a brown hue. Read on to investigate water color in the environment.Dissolved Oxygen and Water
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is a measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in the water - the amount of oxygen available to living aquatic organisms. The amount of dissolved oxygen in a stream or lake can tell us a lot about its water quality.Conductivity (Electrical Conductance) and Water
Water and electricity don't mix, right? Well actually, pure water is an excellent insulator and does not conduct electricity. The thing is, you won't find any pure water in nature, so don't mix electricity and water. Our Water Science School page will give you all the details.Hardness of Water
In scientific terms, water hardness is generally the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in water. But in layman's terms, you may notice water hardness when your hands still feel slimy after washing with soap and water, or when your drinking glasses at home become less than crystal clear. Learn a lot more about water hardness on the Water Science School site.Nitrogen and Water
Nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are essential for plant and animal growth and nourishment, but the overabundance of certain nutrients in water can cause several adverse health and ecological effects.pH and Water
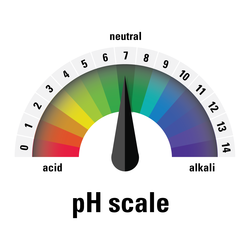
pH is a measure of how acidic/basic water is. The range goes from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. pHs of less than 7 indicate acidity, whereas a pH of greater than 7 indicates a base. The pH of water is a very important measurement concerning water quality.Phosphorus and Water
Nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are essential for plant and animal growth and nourishment, but the overabundance of certain nutrients in water can cause a number of adverse health and ecological effects.Turbidity and Water
Lucky for us all, our drinking water is almost always clear (very low turbidity). Other water, such as the creek behind your house after a rainstorm, is likely to be highly turbid—brown with floating sediment. Turbidity is the clarity of water and it is an important factor in water quality.
-
Water Quality Questions & Answers
What is in that water that you just drank? Is it just hydrogen and oxygen atoms? Is it safe for drinking? All water is of a certain "quality" (and you can't tell by just looking), but what does "water quality" really mean? It can be thought of as a measure of the suitability of water for a particular use based on selected physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. Here at the Water...