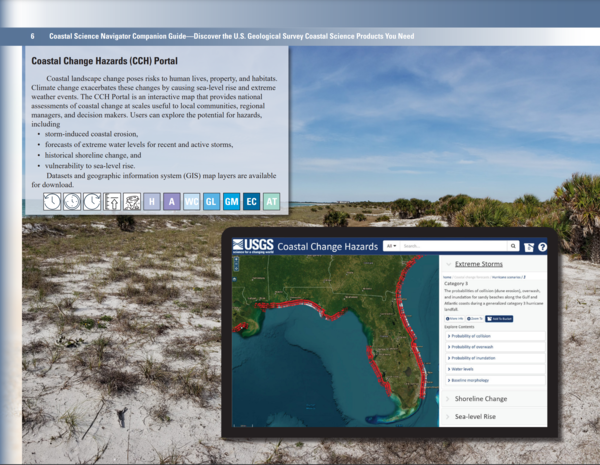
Coastal Change Hazards Portal page of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide.
Multimedia
The Coastal and Marine Hazards and Resources Program shares a wide range of resources to help explain and illustrate scientific concepts, our scientific activities, expertise, technology, tools, and other educational resources. Through newsletters, multimedia resources, special events, and other products, you can learn more about the many ways our science supports the Nation.
Images
Coastal Change Hazards Portal page of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide.
The Coastal Change Likelihood Website page of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide.
The Coastal Change Likelihood Website page of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide.
The U.S. Coastal Wetlands Synthesis page of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide.
The U.S. Coastal Wetlands Synthesis page of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide.
The Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide introduces you to USGS coastal change hazards-related products—including interactive data maps, downloadable software, geonarratives, and more. It's organized by timescale, highlighting products relevant to the present, past, and future, although many cover multiple timescales.
The Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide introduces you to USGS coastal change hazards-related products—including interactive data maps, downloadable software, geonarratives, and more. It's organized by timescale, highlighting products relevant to the present, past, and future, although many cover multiple timescales.
Screenshots from the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide overlaid on top of image of the Army Corps of Engineers Field Research Facility pier near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina.
Screenshots from the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide overlaid on top of image of the Army Corps of Engineers Field Research Facility pier near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina.
Cover of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide. The guide introduces some of the many coastal change hazards-related products available through the USGS. In it, we showcase the products included in the Coastal Science Navigator’s initial publication in July 2023.
Cover of the Coastal Science Navigator Companion Guide. The guide introduces some of the many coastal change hazards-related products available through the USGS. In it, we showcase the products included in the Coastal Science Navigator’s initial publication in July 2023.
Videos
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
Join USGS Research Geologist and lifelong surfer Jon Warrick at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center Santa Cruz as he discusses how coastal and ocean geoscience contributes to a better understanding of how waves form and behave as they approach the shore—critical information with a broad range of applications, not least of which is surfing!
Join USGS Research Geologist and lifelong surfer Jon Warrick at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center Santa Cruz as he discusses how coastal and ocean geoscience contributes to a better understanding of how waves form and behave as they approach the shore—critical information with a broad range of applications, not least of which is surfing!
Join USGS Research Geologist and lifelong surfer Jon Warrick at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center Santa Cruz as he discusses how coastal and ocean geoscience contribute to a better understanding of how waves form and behave as they approach the shore—critical information with a broad range of applications, not least of which is surfing!
Join USGS Research Geologist and lifelong surfer Jon Warrick at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center Santa Cruz as he discusses how coastal and ocean geoscience contribute to a better understanding of how waves form and behave as they approach the shore—critical information with a broad range of applications, not least of which is surfing!
 Introduction to the USGS Coastal Science Navigator
Introduction to the USGS Coastal Science Navigator
The Coastal Science Navigator is intended to help users discover USGS Coastal Change Hazards information, products, and tools relevant to their scientific or decision-making needs.
The Coastal Science Navigator is intended to help users discover USGS Coastal Change Hazards information, products, and tools relevant to their scientific or decision-making needs.
The USGS uses a variety of survey tools—including personal watercraft (jet skis) equipped with GPS and sonar—to measure how sandy coastlines change over time. Sandy coastlines are a valuable resource that protect human-made structures from waves, serve as habitat for important species, and provide a variety of recreational opportunities.
The USGS uses a variety of survey tools—including personal watercraft (jet skis) equipped with GPS and sonar—to measure how sandy coastlines change over time. Sandy coastlines are a valuable resource that protect human-made structures from waves, serve as habitat for important species, and provide a variety of recreational opportunities.
Webcams

Time-averaged images, which represent the time-mean of all the images collected during a video, are used to identify areas where waves are breaking, which show up as bright white bands in the image.
Time-averaged images, which represent the time-mean of all the images collected during a video, are used to identify areas where waves are breaking, which show up as bright white bands in the image.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.
Two video cameras are installed atop a utility pole near the northernmost point of land in the United States at Nuvuk (Point Barrow), Alaska. The cameras point northwest toward the Arctic Ocean and the boundary between the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Every half hour during daylight hours, the cameras collect snapshots and video for 10 minutes.