Terrestrial Wildlife Diseases
Terrestrial Wildlife Diseases
Filter Total Items: 104
Harmful Algal Bloom Toxins in Alaska Seabirds
Elevated ocean temperatures are linked to the development of harmful algal blooms (HABs). Toxins from these blooms may pose health threats to marine organisms, including seabirds. Since 2015, the USGS has worked with a variety of stakeholders to develop testing methods and research projects to better understand the geographic extent, timing and impacts of algal toxins in Alaska marine ecosystems...
The Strain and Genetic Online Tissue Repository for Chronic Wasting Disease
The Strain and Genetic Online Tissue Repository (SAGOTR) is being developed by the USGS Fort Collins Science Center to document, track, discover, and request physical samples of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD). SAGOTR connects natural resource managers, tissue repositories, and researchers in one online platform, making it easier to locate and share samples and support research and management of CWD...
Avian Influenza Research
Since 2006, the USGS Alaska Science Center has been part of the State and Federal interagency team for the detection and response to highly pathogenic (HPAI) viruses in North America. Avian influenza or "bird flu" is a viral disease that primarily infects domestic poultry and wild birds. Avian influenza viruses are naturally occurring in wild birds such as ducks, geese, swans, and gulls. These...
A Matter of Scales: USGS Science to Reduce Invasive Snake Impacts
The U.S. Geological Survey Ecosystem Mission Area plays a major role in invasive snake science across the country and the globe, ranging from research on improving snake detection to projects that enhance eradication. Our extensive science ultimately scales up to benefiting public health, energy transmission, tourism, and other key aspects of American prosperity.
EESC Makes an Impact: Empowering State-led Wildlife Management
Management of state natural resources is a collaborative effort between state governments, federal agencies, tribal governments, and local stakeholders. USGS Eastern Ecological Science Center (EESC) supports state-led wildlife management with research that clarifies complex issues, enhances scientific quality and communication, broadens solution options, and enables cost-sharing and mutual...
White-nose syndrome vaccine updates
Since its emergence in 2006, white-nose syndrome (WNS) continues to spread in North America and has substantially impacted hibernating bat populations, contributing to declines of over 90% in northern long-eared ( Myotis septentrionalis), little brown ( Myotis lucifugus), and tri-colored bat ( Perimyotis subflavus) populations. We are developing tools and management strategies to protect bat...
Assessing the Ability of Incineration to Inactivate CWD Prions from Carcasses
Chronic wasting disease (CWD), a fatal neurologic disease of cervids, presents a monumental management challenge, in part because the etiologic agent, an infectious prion, can be transmitted directly or indirectly and is extremely difficult to inactivate. As CWD expands geographically and increases in prevalence, additional disposal options are desired to safely dispose of CWD-contaminated tissues...
Application of a systems approach for management of chronic wasting disease
The USGS National Wildlife Health Center, Montana Cooperative Wildlife Research Unit, Ventana Systems, Inc., and the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WIDNR) are applying a systems approach to map and model the complex relationships among ecological, epidemiological, social, and political processes affecting CWD. Through a participatory modeling process, we gathered subject matter...
Understanding and Containing Chronic Wasting Disease
Chronic wasting disease (CWD) is a contagious and fatal neurodegenerative disease affecting cervids (deer, elk, caribou, and moose) that is threatening the health and sustainability of cervid populations across North America. CWD is caused by misfolded proteins known as prions, which can be transmitted by direct contact or environmental exposure.
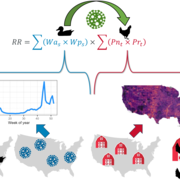
Advancing Risk Modeling for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
Ongoing global outbreaks demonstrate the capacity of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) to impact poultry, wild birds, and even human health. USGS research is advancing the understanding of the spatial and temporal interface between wild and domestic bird populations from which these viruses emerge to aid biosecurity planning and outbreak response.
Key Values of a Century of EESC Science
The USGS Eastern Ecological Science Center (EESC) is rooted in a proud tradition of service to the nation—advancing science that informs the conservation and management of fish, wildlife, and habitats across the eastern United States and beyond. Our mission is clear: deliver reliable, partner-driven science that supports natural resource decisions today, while ensuring these resources remain...
Avian Influenza Research at EESC
Emergence of avian influenza viruses with the potential to be highly pathogenic to poultry, wild birds, and humans cause serious concern for the global economic and public health sectors. Researchers at the USGS Eastern Ecological Science Center study multiple aspects of avian influenza viruses in wild birds as well as their implications for commercial agriculture with a special emphasis on...