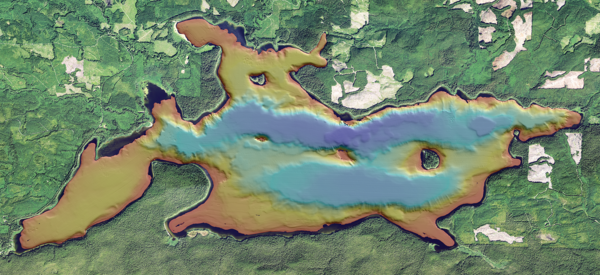
Ozette Lake is located above the locked portion of the northern Cascadia megathrust and is relatively isolated from other active faults.
Videos
Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center videos.
Ozette Lake is located above the locked portion of the northern Cascadia megathrust and is relatively isolated from other active faults.
Ozette Lake is located above the locked portion of the northern Cascadia megathrust and is relatively isolated from other active faults.
Ozette Lake is located above the locked portion of the northern Cascadia megathrust and is relatively isolated from other active faults.
In Fall 2025 the Hawaiʻi Abyssal Nodules and Associated Ecosystems Expedition, led by USGS scientists, will investigate the geology, minerals, and environmental setting of the deep seabed offshore Moku o Keawe (Hawaiʻi Island) in the U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone. This work is part of ongoing collaborative efforts with BOEM and NOAA.
In Fall 2025 the Hawaiʻi Abyssal Nodules and Associated Ecosystems Expedition, led by USGS scientists, will investigate the geology, minerals, and environmental setting of the deep seabed offshore Moku o Keawe (Hawaiʻi Island) in the U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone. This work is part of ongoing collaborative efforts with BOEM and NOAA.
In Fall 2025 the Hawaiʻi Abyssal Nodules and Associated Ecosystems Expedition, led by USGS scientists, will investigate the geology, minerals, and environmental setting of the deep seabed offshore Moku o Keawe (Hawaiʻi Island) in the U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone. This work is part of ongoing collaborative efforts with BOEM and NOAA.
In Fall 2025 the Hawaiʻi Abyssal Nodules and Associated Ecosystems Expedition, led by USGS scientists, will investigate the geology, minerals, and environmental setting of the deep seabed offshore Moku o Keawe (Hawaiʻi Island) in the U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone. This work is part of ongoing collaborative efforts with BOEM and NOAA.
 Cover image for the video "USGS Coastal and Marine Field Operations" showing montage of fieldwork
Cover image for the video "USGS Coastal and Marine Field Operations" showing montage of fieldwork
To conduct the science needed to understand coastal and marine geohazards, support habitat and resource management, and monitor how these environments change over time, the USGS Coastal and Marine Hazards and Resources Program relies on engineering, mechanical, and electronics expertise for field operations along the coast, in the nearshore environment, and in the d
To conduct the science needed to understand coastal and marine geohazards, support habitat and resource management, and monitor how these environments change over time, the USGS Coastal and Marine Hazards and Resources Program relies on engineering, mechanical, and electronics expertise for field operations along the coast, in the nearshore environment, and in the d
 Image of a deep-sea sulfide mound at Escanaba Trough with the text "Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough"
Image of a deep-sea sulfide mound at Escanaba Trough with the text "Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough"
Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough (AD)
Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough (AD)The global ocean is a significant carbon sink, absorbing about a third of all atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions (Gruber et al., 2019).
Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough (AD)
Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough (AD)The global ocean is a significant carbon sink, absorbing about a third of all atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions (Gruber et al., 2019).
 Image of a deep-sea sulfide mound at Escanaba Trough with the text "Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough"
Image of a deep-sea sulfide mound at Escanaba Trough with the text "Characterizing organic carbon at Escanaba Trough"
The global ocean is a significant carbon sink, absorbing about a third of all atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions (Gruber et al., 2019).
The global ocean is a significant carbon sink, absorbing about a third of all atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions (Gruber et al., 2019).
 Aerial image of a California beach with text reading "Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches"
Aerial image of a California beach with text reading "Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches"
Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches (AD)
Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches (AD)Most of the world’s beaches have regular cycles of erosion and recovery, but new USGS research is showing that these cycles may be considerably different from common perceptions.
Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches (AD)
Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches (AD)Most of the world’s beaches have regular cycles of erosion and recovery, but new USGS research is showing that these cycles may be considerably different from common perceptions.
 Aerial image of a California beach with text reading "Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches"
Aerial image of a California beach with text reading "Shoreline Seasonality of California's Beaches"
Most of the world’s beaches have regular cycles of erosion and recovery, but new USGS research is showing that these cycles may be considerably different from common perceptions.
Most of the world’s beaches have regular cycles of erosion and recovery, but new USGS research is showing that these cycles may be considerably different from common perceptions.
 Coral on a cinderblock and a scuba diver on a coral reef
Coral on a cinderblock and a scuba diver on a coral reef
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and propertyCoral reef restoration can protect hundreds of millions of dollars of coastal property and business activity annually from storm-driven flooding.
It can protect thousands of people, especially children, the elderly, minorities, and those below the poverty line. Thus, coral reef restoration is a mechanism to provide environmental equity.
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and propertyCoral reef restoration can protect hundreds of millions of dollars of coastal property and business activity annually from storm-driven flooding.
It can protect thousands of people, especially children, the elderly, minorities, and those below the poverty line. Thus, coral reef restoration is a mechanism to provide environmental equity.
 Coral on a cinderblock and a scuba diver on a coral reef
Coral on a cinderblock and a scuba diver on a coral reef
(Spanish captions) Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property
(Spanish captions) Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and propertyCoral reef restoration can protect hundreds of millions of dollars of coastal property and business activity annually from storm-driven flooding.
It can protect thousands of people, especially children, the elderly, minorities, and those below the poverty line. Thus, coral reef restoration is a mechanism to provide environmental equity.
(Spanish captions) Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property
(Spanish captions) Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and propertyCoral reef restoration can protect hundreds of millions of dollars of coastal property and business activity annually from storm-driven flooding.
It can protect thousands of people, especially children, the elderly, minorities, and those below the poverty line. Thus, coral reef restoration is a mechanism to provide environmental equity.
 Coral on a cinderblock and a scuba diver on a coral reef
Coral on a cinderblock and a scuba diver on a coral reef
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property (AD)
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property (AD)Coral reef restoration can protect hundreds of millions of dollars of coastal property and business activity annually from storm-driven flooding.
It can protect thousands of people, especially children, the elderly, minorities, and those below the poverty line. Thus, coral reef restoration is a mechanism to provide environmental equity.
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property (AD)
Hybrid coral reef restoration: A cost-effective, nature-based solution to protect people and property (AD)Coral reef restoration can protect hundreds of millions of dollars of coastal property and business activity annually from storm-driven flooding.
It can protect thousands of people, especially children, the elderly, minorities, and those below the poverty line. Thus, coral reef restoration is a mechanism to provide environmental equity.
 Cover image for timelapse at the Elwha River Mouth on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Cover image for timelapse at the Elwha River Mouth on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
This PlaneCam video was produced by developing animation tracklines in ArcGlobe, using imagery from PlaneCam flights.
This PlaneCam video was produced by developing animation tracklines in ArcGlobe, using imagery from PlaneCam flights.
This PlaneCam video was produced by developing animation tracklines in ArcGlobe, using imagery from PlaneCam flights.
This PlaneCam video was produced by developing animation tracklines in ArcGlobe, using imagery from PlaneCam flights.
 Cover image for timelapse at Lake Aldwell Delta, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Cover image for timelapse at Lake Aldwell Delta, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
 Cover image for timelapse at Glines Canyon Dam, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Cover image for timelapse at Glines Canyon Dam, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
 Cover image for timelapse at Former Lake Mills, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Cover image for timelapse at Former Lake Mills, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
 Cover image for timelapse at Lower Lake Aldwell, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Cover image for timelapse at Lower Lake Aldwell, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
 Cover image for timelapse at Lake Mills Delta, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Cover image for timelapse at Lake Mills Delta, Elwha River, on the Olympic Peninsula in Washington
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
Timelapsed photo data is sequenced at about 1 pixel-averaged frame per day, meaning that all of the images from a given day are combined, and the RGB values for a given x/y location on the image are the average of every RGB value for that location for that day.
 Cover image for sediment core lab video, showing core-lab walk-in refrigerator
Cover image for sediment core lab video, showing core-lab walk-in refrigerator
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
 Cover image for sediment core lab video, showing core-lab walk-in refrigerator
Cover image for sediment core lab video, showing core-lab walk-in refrigerator
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.
USGS scientists collect core samples from estuaries, lakes, coasts, and marine environments to study a range of physical and chemical properties preserved in sediment or coral over time. They process and analyze these core samples at the Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center’s Sediment Core Lab.