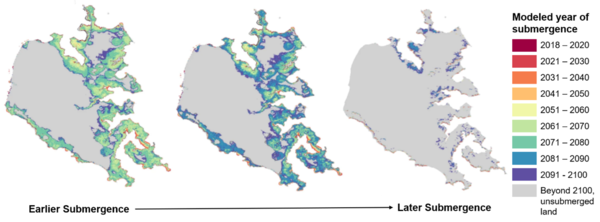
Maps showing the predicted year of submergence for parts of the Eastern Neck Island National Wildlife Refuge
Maps showing the predicted year of submergence for parts of the Eastern Neck Island National Wildlife RefugeMaps showing the predicted year of submergence for parts of the Eastern Neck Island National Wildlife Refuge, as predicted by three different models under the same RSLR scenario.