Avian Influenza
Explore our science related to: Avian Influenza
-
Advancing Risk Modeling for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
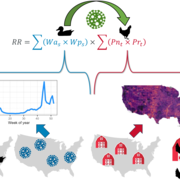
Ongoing global outbreaks demonstrate the capacity of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) to impact poultry, wild birds, and even human health. USGS research is advancing the understanding of the spatial and temporal interface between wild and domestic bird populations from which these viruses emerge to aid biosecurity planning and outbreak response.Deriving Spatial and Temporal Waterfowl Inputs for Disease Risk Modeling
USGS is creating spatially and temporally explicit inputs to improve avian influenza transmission risk modeling. This project places special emphasis on wild bird distribution and abundance models as well as avian influenza prevalence models.
Related
Filter Total Items: 15
The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America
Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) H5N1 was introduced in North America in late 2021 through trans-Atlantic pathways via migratory birds. These introductions have resulted in an unprecedented epizootic, a widespread disease event in animals, heavily affecting poultry, wild birds, and recently mammals. The North American incursions occurred during the largest epidemic season...
Authors
Johanna Harvey, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Michael C. Runge, Diann Prosser
The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America
Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) H5N1 was introduced in North America in late 2021 through trans-Atlantic pathways via migratory birds. These introductions have resulted in an unprecedented epizootic, a widespread disease event in animals, heavily affecting poultry, wild birds, and recently mammals. The North American incursions occurred during the largest epidemic season...
Authors
Johanna Harvey, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Michael C. Runge, Diann Prosser
Avian influenza antibody prevalence increases with mercury contamination in wild waterfowl Avian influenza antibody prevalence increases with mercury contamination in wild waterfowl
Environmental contamination is widespread and can negatively impact wildlife health. Some contaminants, including heavy metals, have immunosuppressive effects, but prior studies have rarely measured contamination and disease simultaneously, which limits our understanding of how contaminants and pathogens interact to influence wildlife health. Here, we measured mercury concentrations...
Authors
Claire Stewart Teitelbaum, Joshua T. Ackerman, Mason A. Hill, Jaqueline M. Satter, Michael L. Casazza, Susan E.W. De La Cruz, Walter M. Boyce, Evan James Buck, John M. Eadie, Mark P. Herzog, Elliott Matchett, Cory T. Overton, Sarah H. Peterson, Magdalena Plancarte, Andrew M. Ramey, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Diann Prosser
Spatiotemporal changes in influenza A virus prevalence among wild waterfowl inhabiting the continental United States throughout the annual cycle Spatiotemporal changes in influenza A virus prevalence among wild waterfowl inhabiting the continental United States throughout the annual cycle
Avian influenza viruses can pose serious risks to agricultural production, human health, and wildlife. An understanding of viruses in wild reservoir species across time and space is important to informing surveillance programs, risk models, and potential population impacts for vulnerable species. Although it is recognized that influenza A virus prevalence peaks in reservoir waterfowl in...
Authors
Cody M. Kent, Andrew M. Ramey, Joshua T. Ackerman, Justin Bahl, Sarah N. Bevins, Andrew S. Bowman, Walter Boyce, Carol Cardona, Michael L. Casazza, Troy D. Cline, Susan E.W. De La Cruz, Jeffrey S. Hall, Nichola J. Hill, Hon S. Ip, Scott Krauss, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Jacqueline M. Nolting, Magdalena Plancarte, Rebecca L. Poulson, Jonathan A. Runstadler, Richard D. Slemons, David E. Stallknecht, Jeffery D. Sullivan, John Y. Takekawa, Richard J. Webby, Robert G. Webster, Diann J. Prosser
A lesser scaup (Aythya affinis ) naturally infected with Eurasian 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus – Movement ecology and host factors A lesser scaup (Aythya affinis ) naturally infected with Eurasian 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus – Movement ecology and host factors
Despite the recognized role of wild waterfowl in the potential dispersal and transmission of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus, little is known about how infection affects these birds. This lack of information limits our ability to estimate viral spread in the event of an HPAI outbreak, thereby limiting our abilities to estimate and communicate risk. Here we present...
Authors
Diann Prosser, Hannah Schley, Nathan Simmons, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Josh Homyack, Matthew M. Weegman, Glenn H. Olsen, Alicia Berlin, Rebecca L. Poulson, David E. Stallknecht, Christopher K. Williams
Maintenance and dissemination of avian-origin influenza A virus within the northern Atlantic Flyway of North America Maintenance and dissemination of avian-origin influenza A virus within the northern Atlantic Flyway of North America
Wild waterbirds, the natural reservoirs for avian influenza viruses, undergo migratory movements each year, connecting breeding and wintering grounds within broad corridors known as flyways. In a continental or global view, the study of virus movements within and across flyways is important to understanding virus diversity, evolution, and movement. From 2015 to 2017, we sampled waterfowl...
Authors
Diann Prosser, Jiani Chen, Christina Ahlstrom, Andrew B. Reeves, Rebecca L. Poulson, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Daniel McAuley, Carl R. Callahan, Peter C. McGowan, Justin Bahl, David E. Stallknecht, Andrew M. Ramey
Highly pathogenic avian influenza is an emerging disease threat to wild birds in North America Highly pathogenic avian influenza is an emerging disease threat to wild birds in North America
Prior to the emergence of the A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996 (Gs/GD) H5N1 influenza A virus, the long-held and well-supported paradigm was that highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) outbreaks were restricted to poultry, the result of cross-species transmission of precursor viruses from wild aquatic birds that subsequently gained pathogenicity in domestic birds. Therefore, management...
Authors
Andrew M. Ramey, Nichola J. Hill, Thomas J. DeLiberto, Samantha E. J. Gibbs, M. Camille Hopkins, Andrew S. Lang, Rebecca L. Poulson, Diann Prosser, Jonathan M. Sleeman, David E. Stallknecht, Xiu-Feng Wan
Pathways for avian influenza virus spread: GPS reveals wild waterfowl in commercial livestock facilities and connectivity with the natural wetland landscape Pathways for avian influenza virus spread: GPS reveals wild waterfowl in commercial livestock facilities and connectivity with the natural wetland landscape
Zoonotic diseases are of considerable concern to the human population and viruses such as avian influenza (AIV) threaten food security, wildlife conservation and human health. Wild waterfowl and the natural wetlands they use are known AIV reservoirs, with birds capable of virus transmission to domestic poultry populations. While infection risk models have linked migration routes and AIV...
Authors
Fiona McDuie, Elliott Matchett, Diann Prosser, John Y. Takekawa, Maurice E. Pitesky, Austen Lorenz, Madeline M McCuen, Cory T. Overton, Joshua T. Ackerman, Susan E.W. De La Cruz, Michael L. Casazza
The spatial-temporal relationship of blue-winged teal to domestic poultry: Movement state modeling of a highly mobile avian influenza host The spatial-temporal relationship of blue-winged teal to domestic poultry: Movement state modeling of a highly mobile avian influenza host
1. Migratory waterfowl facilitate long distance dispersal of zoonotic pathogens and are increasingly recognized as contributing to the geographic spread of avian influenza viruses (AIV). AIV are globally distributed and have the potential to produce highly contagious poultry disease, economically impact both large-scale and backyard poultry producers, and raise the specter of epidemics...
Authors
John M. Humphreys, David C. Douglas, Andrew M. Ramey, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Catherine Soos, Paul T. Link, Patrick Walther, Diann Prosser
Do contrasting patterns of migration movements and disease outbreaks between congeneric waterfowl species reflect differing immunity? Do contrasting patterns of migration movements and disease outbreaks between congeneric waterfowl species reflect differing immunity?
Long-distance migrations influence the dynamics of hostpathogen interactions and understanding the role of migratory waterfowl in the spread of the highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses (HPAIV) is important. While wild geese have been associated with outbreak events, disease ecology of closely related species has not been studied to the same extent. The swan goose (Anser cygnoides)...
Authors
Shenlai Yin, Yanjie Xu, Nyambyar Batbayar, John Y. Takekawa, Yali Si, Diann Prosser, Scott H. Newman, Herbert H.T. Prins, Willem F. de Boer
Crossroads of highly pathogenic H5N1: overlap between wild and domestic birds in the Black Sea-Mediterranean impacts global transmission Crossroads of highly pathogenic H5N1: overlap between wild and domestic birds in the Black Sea-Mediterranean impacts global transmission
Understanding transmission dynamics that link wild and domestic animals is a key element of predicting the emergence of infectious disease, an event that has highest likelihood of occurring wherever human livelihoods depend on agriculture and animal trade. Contact between poultry and wild birds is a key driver of the emergence of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI), a process that...
Authors
Nichola J. Hill, Lacy M. Smith, Sabir B. Muzaffar, Jessica L. Nagel, Diann Prosser, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Kyle A. Spragens, Carlos A. DeMattos, Cecilia C. Demattos, Lu’ay El Sayed, Kiraz Erciyas-Yavuz, C. Todd Davis, Joyce Jones, Zoltan Kis, Ruben O. Donis, Scott H. Newman, John Y. Takekawa
The pathogenesis of a North American H5N2 clade 2.3.4.4 group A highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in surf scoters (Melanitta perspicillata) The pathogenesis of a North American H5N2 clade 2.3.4.4 group A highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in surf scoters (Melanitta perspicillata)
Background Aquatic waterfowl, particularly those in the order Anseriformes and Charadriiformes, are the ecological reservoir of avian influenza viruses (AIVs). Dabbling ducks play a recognized role in the maintenance and transmission of AIVs. Furthermore, the pathogenesis of highly pathogenic AIV (HPAIV) in dabbling ducks is well characterized. In contrast, the role of diving ducks in...
Authors
Jasmine M. Luczo, Diann Prosser, Mary J. Pantin-Jackwood, Alicia Berlin, Erica Spackman
Visualizing Models for Avian Influenza Viruses Visualizing Models for Avian Influenza Viruses
Emergence of avian influenza viruses with the potential to be highly pathogenic to poultry, wild birds, & humans, such as the highly pathogenic H5N1 and H7N9 cause serious concern for the global economic & public health sectors. Visual representations of model data can be effective in helping to discover how the spread of the virus is influenced by environmental & human
Related
Filter Total Items: 15
The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America
Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) H5N1 was introduced in North America in late 2021 through trans-Atlantic pathways via migratory birds. These introductions have resulted in an unprecedented epizootic, a widespread disease event in animals, heavily affecting poultry, wild birds, and recently mammals. The North American incursions occurred during the largest epidemic season...
Authors
Johanna Harvey, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Michael C. Runge, Diann Prosser
The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America The changing dynamics of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: Next steps for management & science in North America
Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) H5N1 was introduced in North America in late 2021 through trans-Atlantic pathways via migratory birds. These introductions have resulted in an unprecedented epizootic, a widespread disease event in animals, heavily affecting poultry, wild birds, and recently mammals. The North American incursions occurred during the largest epidemic season...
Authors
Johanna Harvey, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Michael C. Runge, Diann Prosser
Avian influenza antibody prevalence increases with mercury contamination in wild waterfowl Avian influenza antibody prevalence increases with mercury contamination in wild waterfowl
Environmental contamination is widespread and can negatively impact wildlife health. Some contaminants, including heavy metals, have immunosuppressive effects, but prior studies have rarely measured contamination and disease simultaneously, which limits our understanding of how contaminants and pathogens interact to influence wildlife health. Here, we measured mercury concentrations...
Authors
Claire Stewart Teitelbaum, Joshua T. Ackerman, Mason A. Hill, Jaqueline M. Satter, Michael L. Casazza, Susan E.W. De La Cruz, Walter M. Boyce, Evan James Buck, John M. Eadie, Mark P. Herzog, Elliott Matchett, Cory T. Overton, Sarah H. Peterson, Magdalena Plancarte, Andrew M. Ramey, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Diann Prosser
Spatiotemporal changes in influenza A virus prevalence among wild waterfowl inhabiting the continental United States throughout the annual cycle Spatiotemporal changes in influenza A virus prevalence among wild waterfowl inhabiting the continental United States throughout the annual cycle
Avian influenza viruses can pose serious risks to agricultural production, human health, and wildlife. An understanding of viruses in wild reservoir species across time and space is important to informing surveillance programs, risk models, and potential population impacts for vulnerable species. Although it is recognized that influenza A virus prevalence peaks in reservoir waterfowl in...
Authors
Cody M. Kent, Andrew M. Ramey, Joshua T. Ackerman, Justin Bahl, Sarah N. Bevins, Andrew S. Bowman, Walter Boyce, Carol Cardona, Michael L. Casazza, Troy D. Cline, Susan E.W. De La Cruz, Jeffrey S. Hall, Nichola J. Hill, Hon S. Ip, Scott Krauss, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Jacqueline M. Nolting, Magdalena Plancarte, Rebecca L. Poulson, Jonathan A. Runstadler, Richard D. Slemons, David E. Stallknecht, Jeffery D. Sullivan, John Y. Takekawa, Richard J. Webby, Robert G. Webster, Diann J. Prosser
A lesser scaup (Aythya affinis ) naturally infected with Eurasian 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus – Movement ecology and host factors A lesser scaup (Aythya affinis ) naturally infected with Eurasian 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus – Movement ecology and host factors
Despite the recognized role of wild waterfowl in the potential dispersal and transmission of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus, little is known about how infection affects these birds. This lack of information limits our ability to estimate viral spread in the event of an HPAI outbreak, thereby limiting our abilities to estimate and communicate risk. Here we present...
Authors
Diann Prosser, Hannah Schley, Nathan Simmons, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Josh Homyack, Matthew M. Weegman, Glenn H. Olsen, Alicia Berlin, Rebecca L. Poulson, David E. Stallknecht, Christopher K. Williams
Maintenance and dissemination of avian-origin influenza A virus within the northern Atlantic Flyway of North America Maintenance and dissemination of avian-origin influenza A virus within the northern Atlantic Flyway of North America
Wild waterbirds, the natural reservoirs for avian influenza viruses, undergo migratory movements each year, connecting breeding and wintering grounds within broad corridors known as flyways. In a continental or global view, the study of virus movements within and across flyways is important to understanding virus diversity, evolution, and movement. From 2015 to 2017, we sampled waterfowl...
Authors
Diann Prosser, Jiani Chen, Christina Ahlstrom, Andrew B. Reeves, Rebecca L. Poulson, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Daniel McAuley, Carl R. Callahan, Peter C. McGowan, Justin Bahl, David E. Stallknecht, Andrew M. Ramey
Highly pathogenic avian influenza is an emerging disease threat to wild birds in North America Highly pathogenic avian influenza is an emerging disease threat to wild birds in North America
Prior to the emergence of the A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996 (Gs/GD) H5N1 influenza A virus, the long-held and well-supported paradigm was that highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) outbreaks were restricted to poultry, the result of cross-species transmission of precursor viruses from wild aquatic birds that subsequently gained pathogenicity in domestic birds. Therefore, management...
Authors
Andrew M. Ramey, Nichola J. Hill, Thomas J. DeLiberto, Samantha E. J. Gibbs, M. Camille Hopkins, Andrew S. Lang, Rebecca L. Poulson, Diann Prosser, Jonathan M. Sleeman, David E. Stallknecht, Xiu-Feng Wan
Pathways for avian influenza virus spread: GPS reveals wild waterfowl in commercial livestock facilities and connectivity with the natural wetland landscape Pathways for avian influenza virus spread: GPS reveals wild waterfowl in commercial livestock facilities and connectivity with the natural wetland landscape
Zoonotic diseases are of considerable concern to the human population and viruses such as avian influenza (AIV) threaten food security, wildlife conservation and human health. Wild waterfowl and the natural wetlands they use are known AIV reservoirs, with birds capable of virus transmission to domestic poultry populations. While infection risk models have linked migration routes and AIV...
Authors
Fiona McDuie, Elliott Matchett, Diann Prosser, John Y. Takekawa, Maurice E. Pitesky, Austen Lorenz, Madeline M McCuen, Cory T. Overton, Joshua T. Ackerman, Susan E.W. De La Cruz, Michael L. Casazza
The spatial-temporal relationship of blue-winged teal to domestic poultry: Movement state modeling of a highly mobile avian influenza host The spatial-temporal relationship of blue-winged teal to domestic poultry: Movement state modeling of a highly mobile avian influenza host
1. Migratory waterfowl facilitate long distance dispersal of zoonotic pathogens and are increasingly recognized as contributing to the geographic spread of avian influenza viruses (AIV). AIV are globally distributed and have the potential to produce highly contagious poultry disease, economically impact both large-scale and backyard poultry producers, and raise the specter of epidemics...
Authors
John M. Humphreys, David C. Douglas, Andrew M. Ramey, Jennifer M. Mullinax, Catherine Soos, Paul T. Link, Patrick Walther, Diann Prosser
Do contrasting patterns of migration movements and disease outbreaks between congeneric waterfowl species reflect differing immunity? Do contrasting patterns of migration movements and disease outbreaks between congeneric waterfowl species reflect differing immunity?
Long-distance migrations influence the dynamics of hostpathogen interactions and understanding the role of migratory waterfowl in the spread of the highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses (HPAIV) is important. While wild geese have been associated with outbreak events, disease ecology of closely related species has not been studied to the same extent. The swan goose (Anser cygnoides)...
Authors
Shenlai Yin, Yanjie Xu, Nyambyar Batbayar, John Y. Takekawa, Yali Si, Diann Prosser, Scott H. Newman, Herbert H.T. Prins, Willem F. de Boer
Crossroads of highly pathogenic H5N1: overlap between wild and domestic birds in the Black Sea-Mediterranean impacts global transmission Crossroads of highly pathogenic H5N1: overlap between wild and domestic birds in the Black Sea-Mediterranean impacts global transmission
Understanding transmission dynamics that link wild and domestic animals is a key element of predicting the emergence of infectious disease, an event that has highest likelihood of occurring wherever human livelihoods depend on agriculture and animal trade. Contact between poultry and wild birds is a key driver of the emergence of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI), a process that...
Authors
Nichola J. Hill, Lacy M. Smith, Sabir B. Muzaffar, Jessica L. Nagel, Diann Prosser, Jeffery D. Sullivan, Kyle A. Spragens, Carlos A. DeMattos, Cecilia C. Demattos, Lu’ay El Sayed, Kiraz Erciyas-Yavuz, C. Todd Davis, Joyce Jones, Zoltan Kis, Ruben O. Donis, Scott H. Newman, John Y. Takekawa
The pathogenesis of a North American H5N2 clade 2.3.4.4 group A highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in surf scoters (Melanitta perspicillata) The pathogenesis of a North American H5N2 clade 2.3.4.4 group A highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in surf scoters (Melanitta perspicillata)
Background Aquatic waterfowl, particularly those in the order Anseriformes and Charadriiformes, are the ecological reservoir of avian influenza viruses (AIVs). Dabbling ducks play a recognized role in the maintenance and transmission of AIVs. Furthermore, the pathogenesis of highly pathogenic AIV (HPAIV) in dabbling ducks is well characterized. In contrast, the role of diving ducks in...
Authors
Jasmine M. Luczo, Diann Prosser, Mary J. Pantin-Jackwood, Alicia Berlin, Erica Spackman
Visualizing Models for Avian Influenza Viruses Visualizing Models for Avian Influenza Viruses
Emergence of avian influenza viruses with the potential to be highly pathogenic to poultry, wild birds, & humans, such as the highly pathogenic H5N1 and H7N9 cause serious concern for the global economic & public health sectors. Visual representations of model data can be effective in helping to discover how the spread of the virus is influenced by environmental & human