USGS scientists evaluating the nebulizer assembly in a mixed mode ionization source of a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer used to measure individual cyanotoxins
Images
Images
USGS scientists evaluating the nebulizer assembly in a mixed mode ionization source of a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer used to measure individual cyanotoxins
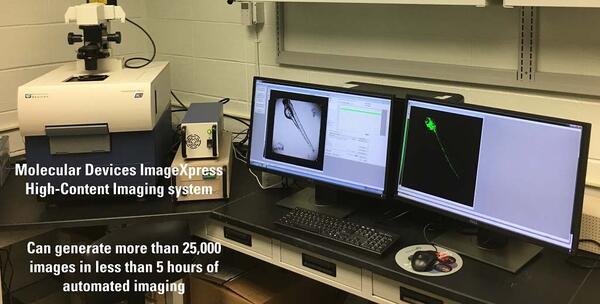
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging SystemMolecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System that can generate more than 25,000 images in less than 5 hours of automated image acquisition.
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging SystemMolecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System that can generate more than 25,000 images in less than 5 hours of automated image acquisition.

Keith A. Loftin is the lead scientist for algal and cyanobacteria
Keith A. Loftin is the lead scientist for algal and cyanobacteriaKeith A. Loftin, USGS, is the lead scientist for algal and cyanobacterial toxins
Keith A. Loftin is the lead scientist for algal and cyanobacteria
Keith A. Loftin is the lead scientist for algal and cyanobacteriaKeith A. Loftin, USGS, is the lead scientist for algal and cyanobacterial toxins
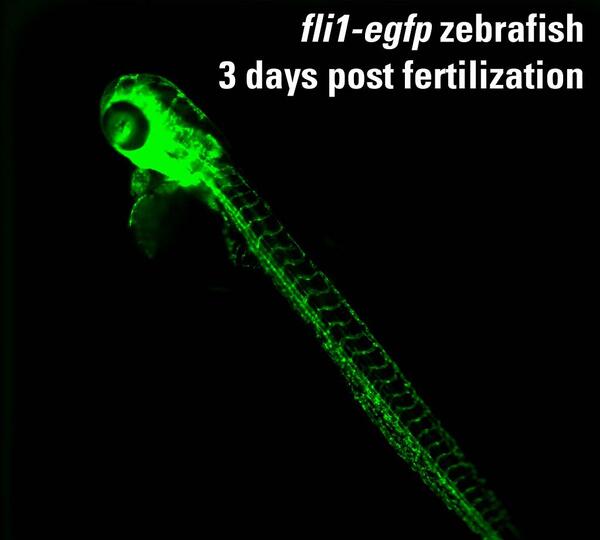
Using the 384-well plate format, a single zebrafish embryo is tested
Using the 384-well plate format, a single zebrafish embryo is testedUsing the 384-well plate format, a single zebrafish embryo is tested in each well. This is an example of a 72 hour post fertilization fli1:egfp zebrafish (3 millimeters long) imaged under a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) filter.
Using the 384-well plate format, a single zebrafish embryo is tested
Using the 384-well plate format, a single zebrafish embryo is testedUsing the 384-well plate format, a single zebrafish embryo is tested in each well. This is an example of a 72 hour post fertilization fli1:egfp zebrafish (3 millimeters long) imaged under a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) filter.

(USGS scientist working on data analysis of cyanotoxins in water
(USGS scientist working on data analysis of cyanotoxins in waterU.S. Geological Survey (USGS) scientist working on data analysis of cyanotoxins in water samples
(USGS scientist working on data analysis of cyanotoxins in water
(USGS scientist working on data analysis of cyanotoxins in waterU.S. Geological Survey (USGS) scientist working on data analysis of cyanotoxins in water samples

Microscopic video imaging for computerized analysis of sperm motility
Microscopic video imaging for computerized analysis of sperm motilityMicroscopic video imaging is used for computerized analysis of sperm motility parameters
Microscopic video imaging for computerized analysis of sperm motility
Microscopic video imaging for computerized analysis of sperm motilityMicroscopic video imaging is used for computerized analysis of sperm motility parameters

Native birds resting on marker buoys in Brownlee Reservoir, Idaho
Native birds resting on marker buoys in Brownlee Reservoir, IdahoNative birds resting on marker buoys in Brownlee Reservoir, Idaho.
Native birds resting on marker buoys in Brownlee Reservoir, Idaho
Native birds resting on marker buoys in Brownlee Reservoir, IdahoNative birds resting on marker buoys in Brownlee Reservoir, Idaho.

Collecting larval fish for the Dragonfly Mercury Project
Collecting larval fish for the Dragonfly Mercury ProjectBetween 2009 and 2018, scientists conducted a national scale assessment of mercury accumulation in the National Park System using dragonfly larvae as biosentinels (species that accumulate a pollutant in their tissues as an index of exposure to other organisms without significant adverse effects to the biosentinel) through a citizen science network called the Dragonf
Collecting larval fish for the Dragonfly Mercury Project
Collecting larval fish for the Dragonfly Mercury ProjectBetween 2009 and 2018, scientists conducted a national scale assessment of mercury accumulation in the National Park System using dragonfly larvae as biosentinels (species that accumulate a pollutant in their tissues as an index of exposure to other organisms without significant adverse effects to the biosentinel) through a citizen science network called the Dragonf

Photograph of the entrance to Grand Traverse Bay Harbor
Photograph of the entrance to Grand Traverse Bay HarborPhotograph of the entrance to Grand Traverse Bay Harbor, located 8 kilometers downdrift of the spoils pile. Migration of the dark-colored stamp sands (moving from left to right) has buried the original beach, overtopped the wall, and partially blocked the channel.
Photograph of the entrance to Grand Traverse Bay Harbor
Photograph of the entrance to Grand Traverse Bay HarborPhotograph of the entrance to Grand Traverse Bay Harbor, located 8 kilometers downdrift of the spoils pile. Migration of the dark-colored stamp sands (moving from left to right) has buried the original beach, overtopped the wall, and partially blocked the channel.

Cover of California's Fourth Climate Change Assessment Report
Cover of California's Fourth Climate Change Assessment ReportCover of the 2018 publication, "California’s Fourth Climate Change Assessment: Statewide Summary Report."
Cover of California's Fourth Climate Change Assessment Report
Cover of California's Fourth Climate Change Assessment ReportCover of the 2018 publication, "California’s Fourth Climate Change Assessment: Statewide Summary Report."

Yellowstone National Park Dragonfly Mercury Project Sampling
Yellowstone National Park Dragonfly Mercury Project SamplingThis image shows citizen scientists along with National Park Service personnel identifying invertebrates as part of the Dragonfly Mercury Project.
Yellowstone National Park Dragonfly Mercury Project Sampling
Yellowstone National Park Dragonfly Mercury Project SamplingThis image shows citizen scientists along with National Park Service personnel identifying invertebrates as part of the Dragonfly Mercury Project.
After 100 years of restricted tidal activity to support agricultural use and salt harvesting, the tidal marshes around San Francisco Bay, like this one at Bair Island, are steadily rebuilding, returning to a stunning mosaic of marsh, mudflat, and channels.
After 100 years of restricted tidal activity to support agricultural use and salt harvesting, the tidal marshes around San Francisco Bay, like this one at Bair Island, are steadily rebuilding, returning to a stunning mosaic of marsh, mudflat, and channels.

Rocky Mountain NP Dragonfly Mercury Project sampling
Rocky Mountain NP Dragonfly Mercury Project samplingCitizen scientists after a day of collecting dragonfly larvae for the Dragonfly Mercury Project.
Rocky Mountain NP Dragonfly Mercury Project sampling
Rocky Mountain NP Dragonfly Mercury Project samplingCitizen scientists after a day of collecting dragonfly larvae for the Dragonfly Mercury Project.

Scientist Sitting Next to a Biological Safety Cabinet in a Laboratory
Scientist Sitting Next to a Biological Safety Cabinet in a LaboratoryA U.S.
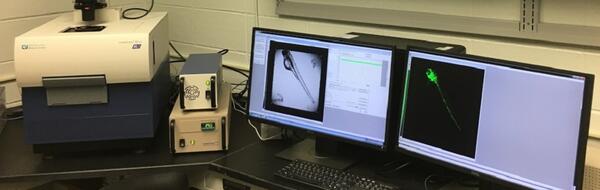
High-Content Screening Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri
High-Content Screening Laboratory -- Columbia, MissouriHigh-Content Screening Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri
High-Content Screening Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri
High-Content Screening Laboratory -- Columbia, MissouriHigh-Content Screening Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri
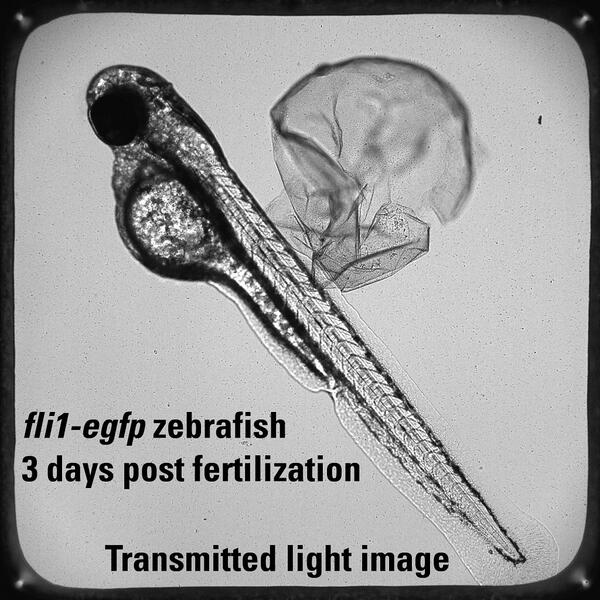
This is an example of a 72 hour post fertilization
This is an example of a 72 hour post fertilizationThis is an example of a 72 hour post fertilization fli1:egfp zebrafish (3 millimeters long) imaged under transmitted light. The same imaging system with was used.
This is an example of a 72 hour post fertilization
This is an example of a 72 hour post fertilizationThis is an example of a 72 hour post fertilization fli1:egfp zebrafish (3 millimeters long) imaged under transmitted light. The same imaging system with was used.
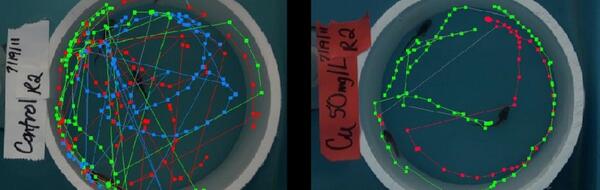
Behavioral Toxicology Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri
Behavioral Toxicology Laboratory -- Columbia, MissouriBehavioral Toxicology Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri. Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fish
Behavioral Toxicology Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri
Behavioral Toxicology Laboratory -- Columbia, MissouriBehavioral Toxicology Laboratory -- Columbia, Missouri. Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fish

Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fish
Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fishBehavioral Toxicology Laboratory — Columbia, Missouri. Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fish demonstrate changes in swimming behavior detected following exposure to metals. Such changes can impact ability of fish to survive.
Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fish
Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fishBehavioral Toxicology Laboratory — Columbia, Missouri. Swimming paths of control (left) and copper (right) exposed fish demonstrate changes in swimming behavior detected following exposure to metals. Such changes can impact ability of fish to survive.

TZebrafish developmental cardiovascular toxicity high-content screen
TZebrafish developmental cardiovascular toxicity high-content screenThe zebrafish developmental cardiovascular toxicity high-content screening assay uses a 384-well plate format to maximize number of treatments and replicates possible on each plate.
TZebrafish developmental cardiovascular toxicity high-content screen
TZebrafish developmental cardiovascular toxicity high-content screenThe zebrafish developmental cardiovascular toxicity high-content screening assay uses a 384-well plate format to maximize number of treatments and replicates possible on each plate.

Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging SystemHigh-Content Screening Laboratory — Columbia, Missouri. Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System
Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging SystemHigh-Content Screening Laboratory — Columbia, Missouri. Molecular Devices ImageXpress† High-Content Imaging System

Multimode, microplate reader used to measure optical density
Multimode, microplate reader used to measure optical densityMultimode, microplate reader



