Small Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) collecting digital photos to create digital elevation models. UAS are an increasingly important tool for monitoring, assessing, and conducting targeted scientific research for the nation.
Images
Below are images associated with the Arizona Water Science Center.
Small Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) collecting digital photos to create digital elevation models. UAS are an increasingly important tool for monitoring, assessing, and conducting targeted scientific research for the nation.
Chart showing changes in vegetation density in the Mississippi River delta in Louisiana, May 2015-May 2016. From a USGS Open File Report published in July 2017 by co-authors Elijah Ramsey III and Amina Rangoonwala,
Chart showing changes in vegetation density in the Mississippi River delta in Louisiana, May 2015-May 2016. From a USGS Open File Report published in July 2017 by co-authors Elijah Ramsey III and Amina Rangoonwala,
Havasu Creek spilling over Havasu Falls, downstream from Supai Village on the Havasupai Nation.
Havasu Creek spilling over Havasu Falls, downstream from Supai Village on the Havasupai Nation.
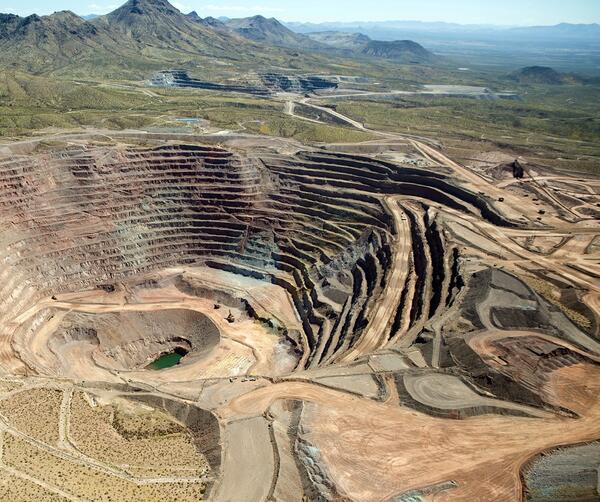
Photograph of Freeport McMoRan-Safford Copper Mine in Arizona. Photograph taken by Thomas J. Porter (USGS) on September 19, 2016, Latitude 32.85992 deg N, Longitude -109.622
Photograph of Freeport McMoRan-Safford Copper Mine in Arizona. Photograph taken by Thomas J. Porter (USGS) on September 19, 2016, Latitude 32.85992 deg N, Longitude -109.622
Colorado River at Imperial Dam northeast of Yuma, Arizona. Gates in the foreground supply Colorado River water to desilting ponds before being diverted to the All American Canal.
Colorado River at Imperial Dam northeast of Yuma, Arizona. Gates in the foreground supply Colorado River water to desilting ponds before being diverted to the All American Canal.

Trail head to Lower Jumpup Spring, north of Grand Canyon.
Trail head to Lower Jumpup Spring, north of Grand Canyon.Trail head sign to Lower Jumpup Spring, north of Grand Canyon.
Trail head to Lower Jumpup Spring, north of Grand Canyon.
Trail head to Lower Jumpup Spring, north of Grand Canyon.Trail head sign to Lower Jumpup Spring, north of Grand Canyon.
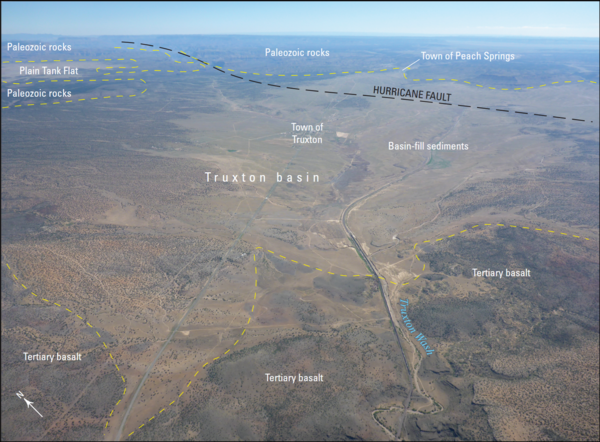
Aerial photograph of the Truxton Basin, northwestern Arizona, showing boundaries and geologic features
Aerial photograph of the Truxton Basin, northwestern Arizona, showing boundaries and geologic featuresAerial photograph of the Truxton basin, Arizona (view to northeast). Yellow dashed lines are approximate boundaries between labeled geologic features and units. From figure 2 in chapter B of Mason 2020
Aerial photograph of the Truxton Basin, northwestern Arizona, showing boundaries and geologic features
Aerial photograph of the Truxton Basin, northwestern Arizona, showing boundaries and geologic featuresAerial photograph of the Truxton basin, Arizona (view to northeast). Yellow dashed lines are approximate boundaries between labeled geologic features and units. From figure 2 in chapter B of Mason 2020
Photograph showing San Pedro Riparian National Conservation Area, residential development southeast of Sierra Vista, Arizona, and the Huachuca Mountains from Hereford Road, Cochise County, Arizona.
Photograph showing San Pedro Riparian National Conservation Area, residential development southeast of Sierra Vista, Arizona, and the Huachuca Mountains from Hereford Road, Cochise County, Arizona.
Former Kanab North uranium mine on the edge of Kanab Creek, north of Grand Canyon.
Former Kanab North uranium mine on the edge of Kanab Creek, north of Grand Canyon.

Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, Washington
Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, WashingtonThe turbid waters of the Elwha River and the coastal waters of the Strait of Juan de Fuca mix directly offshore of the river mouth, forming a large coastal plume. This plume is easily identified by the cloudiness of the water (or "turbidity") resulting from sediment discharged by the river. Two large dams on the Elwha River are being incrementally r
Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, Washington
Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, WashingtonThe turbid waters of the Elwha River and the coastal waters of the Strait of Juan de Fuca mix directly offshore of the river mouth, forming a large coastal plume. This plume is easily identified by the cloudiness of the water (or "turbidity") resulting from sediment discharged by the river. Two large dams on the Elwha River are being incrementally r

Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, Washington
Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, WashingtonThe turbid waters of the Elwha River and the coastal waters of the Strait of Juan de Fuca mix directly offshore of the river mouth, forming a large coastal plume. This plume is easily identified by the cloudiness of the water (or "turbidity") resulting from sediment discharged by the river. Two large dams on the Elwha River were incrementally r
Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, Washington
Turbid Coastal Plume of the Elwha River, WashingtonThe turbid waters of the Elwha River and the coastal waters of the Strait of Juan de Fuca mix directly offshore of the river mouth, forming a large coastal plume. This plume is easily identified by the cloudiness of the water (or "turbidity") resulting from sediment discharged by the river. Two large dams on the Elwha River were incrementally r
Remote rain gage affixed to the roof line of a building at the top of Montezuma Pass, Arizona.
Remote rain gage affixed to the roof line of a building at the top of Montezuma Pass, Arizona.
Flood-alert instrument tower with electronics shelter and precipitation gage at top of tower.
Flood-alert instrument tower with electronics shelter and precipitation gage at top of tower.

Electronics shelter on Flood-Alert Instrument Tower
Electronics shelter on Flood-Alert Instrument TowerElectronics inside the instrument shelter, which includes a high-data-rate transmitter (upper right) and line-of-sight receiver (middle left). The line-of-sight receiver picks up transmissions from the remote rain gage at the look-out area at the top of the Montezuma Pass, Arizona.
Electronics shelter on Flood-Alert Instrument Tower
Electronics shelter on Flood-Alert Instrument TowerElectronics inside the instrument shelter, which includes a high-data-rate transmitter (upper right) and line-of-sight receiver (middle left). The line-of-sight receiver picks up transmissions from the remote rain gage at the look-out area at the top of the Montezuma Pass, Arizona.
USGS divers Steve Rubin and Reg Reisenbichler laying out a survey transect in the Elwha River in northern Washington.
USGS divers Steve Rubin and Reg Reisenbichler laying out a survey transect in the Elwha River in northern Washington.
The Colorado River Basin showing the location of Lees Ferry, Glen Canyon Dam, and the Lees Ferry and other U.S. Geological Survey gaging stations (with station numbers) used in this study. Modified from Topping and others, 2003.
The Colorado River Basin showing the location of Lees Ferry, Glen Canyon Dam, and the Lees Ferry and other U.S. Geological Survey gaging stations (with station numbers) used in this study. Modified from Topping and others, 2003.
September 21, 1923, 9:00 a.m. --- Colorado River at Lees Ferry. From right bank on line with Klohr's house and gage house. Old "Dugway" or inclined gage shows to left of gage house. Gage height 11.05', discharge 27,000 cfs. Lens 16, time =1/25, camera supported. Photo by G.C. Stevens of the USGS. Source: 1921-1937 Surface Water Records File, Colorado R.
September 21, 1923, 9:00 a.m. --- Colorado River at Lees Ferry. From right bank on line with Klohr's house and gage house. Old "Dugway" or inclined gage shows to left of gage house. Gage height 11.05', discharge 27,000 cfs. Lens 16, time =1/25, camera supported. Photo by G.C. Stevens of the USGS. Source: 1921-1937 Surface Water Records File, Colorado R.













