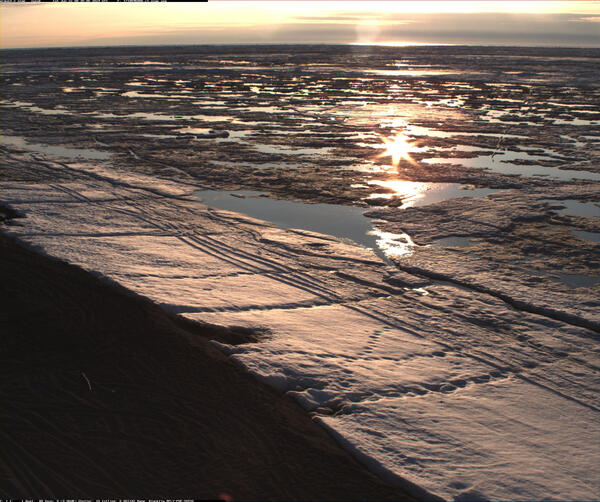
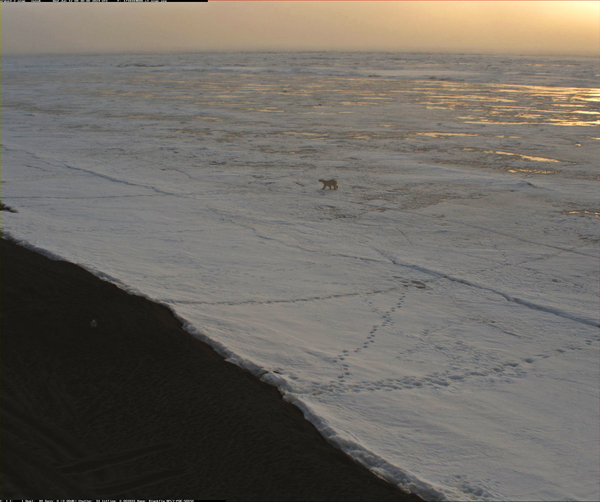
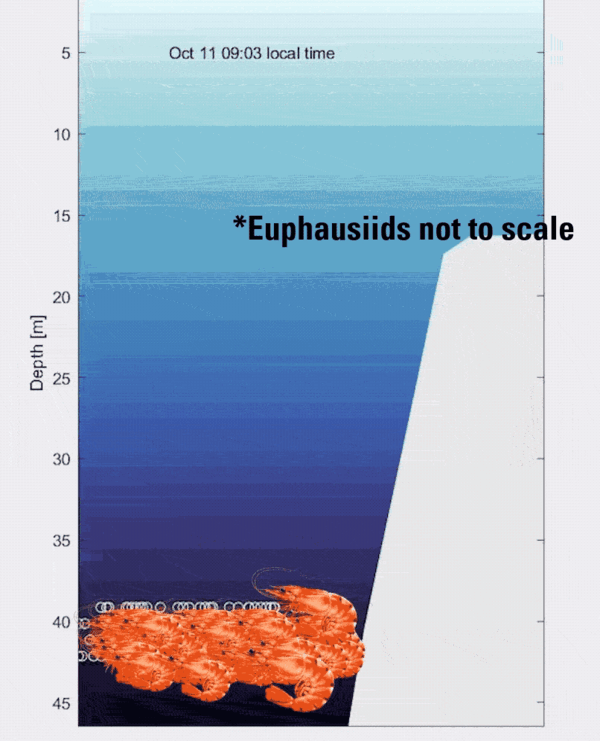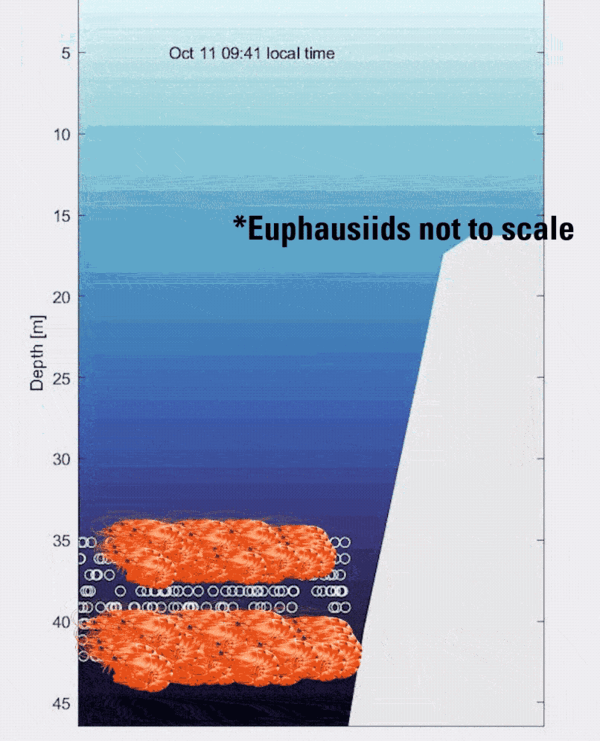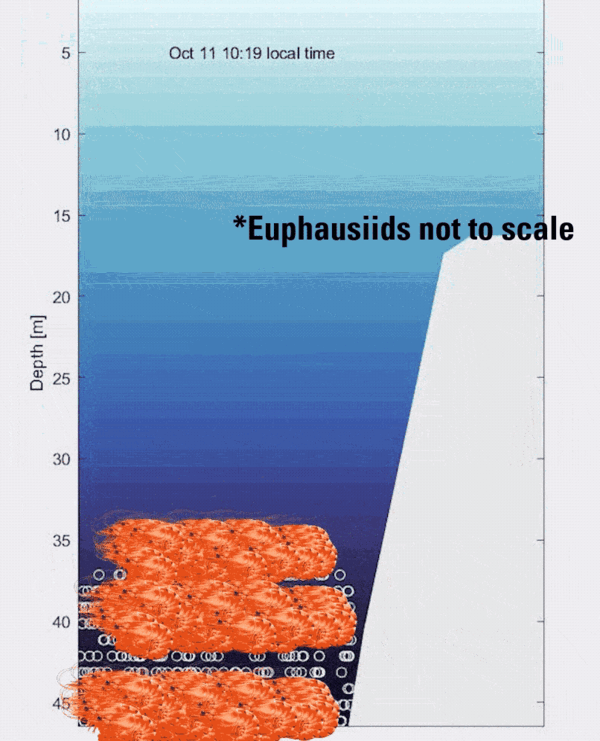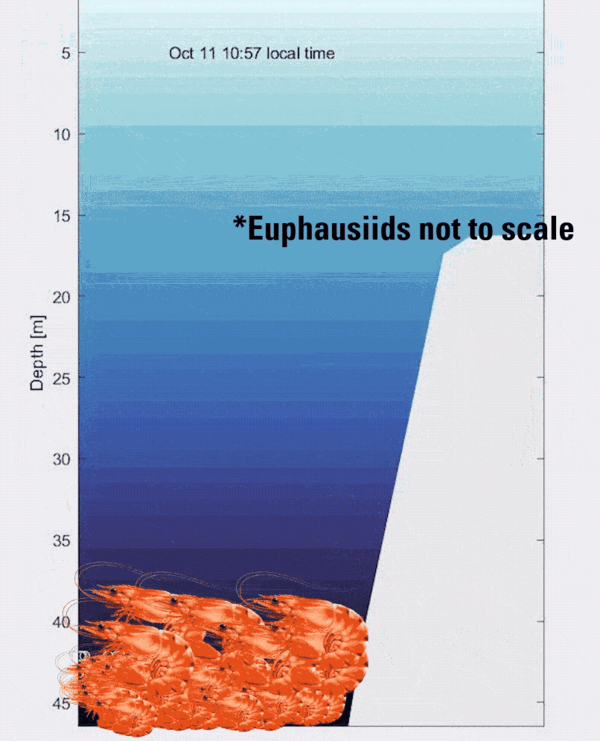
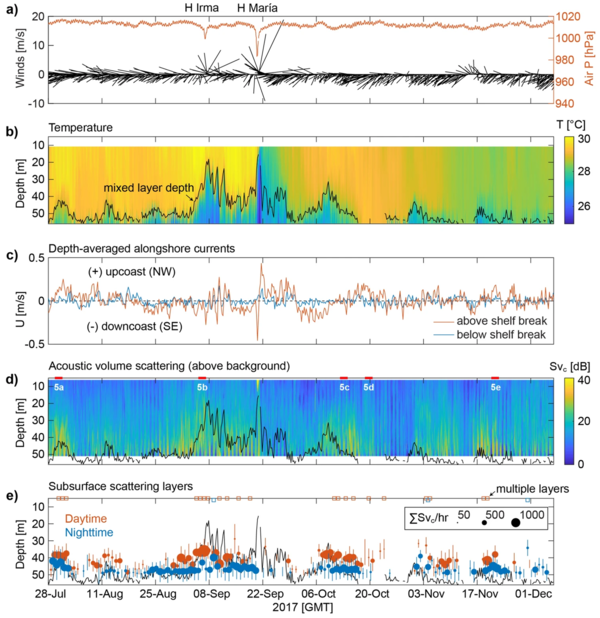
Animated GIF showing an illustration of zooplankton layers moving up and down the water column over a mesophotic reef
Animated GIF showing an illustration of zooplankton layers moving up and down the water column over a mesophotic reefAnimated GIF showing an illustration of zooplankton layers moving up and down the water column over a mesophotic reef.