Terrestrial Wildlife Diseases
Terrestrial Wildlife Diseases
Filter Total Items: 104
EESC Makes an Impact: Protecting Ecosystems to Safeguard Food and Water
Research at the USGS Eastern Ecological Science Center (EESC) supports understanding of the connection between ecosystem health and the quality and availability of America's food and water. USGS studies help monitor and assess the health of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, species populations, water quality, and contaminants affecting health and habitats. Information gained through this...
EESC Makes an Impact: Preserving our Hunting Resources
Hunting is an economic engine for the U.S. and responsible management of these resources directly supports 45.2 billion dollars spent by hunters annually. Conservation and management of hunting resources also contributes substantially to the 394.8 billion dollars spent on all wildlife-related recreation. Hunting traditions are an integral component of our American heritage, with 14.4 million...
Avian Influenza Host Movement Ecology
Understanding disease systems requires an understanding of the basic ecology of host species. USGS is involved in global efforts to explore the movements of bird species that are hosts of avian influenza as well as the potential impacts of changing landscapes on avian influenza.
Using Global Telemetry to Understand Avian Movement and Migration
USGS researchers are collaborating with partners around the globe to leverage new and existing telemetry data to answer broad scale questions about factors influencing avian movement and migration.
Avian Influenza Spread, Prevalence and Persistence
USGS researchers seek to understand the factors influencing the spread and persistence of avian influenza viruses on the landscape. This research also addresses how novel strains of highly pathogenic avian influenza are impacting a larger number and diversity of host species, including waterfowl, shorebirds, raptors and other birds.
Identifying Spatial and Temporal Trends in Avian Influenza Prevalence in Wild Waterfowl Across the United States
USGS researchers are at the forefront of building and maintaining datasets that represent the spatial and temporal patterns in avian influenza virus prevalence in wild birds, which is critical information used to estimate transmission risk to domestic poultry.
Deriving Spatial and Temporal Waterfowl Inputs for Disease Risk Modeling
USGS is creating spatially and temporally explicit inputs to improve avian influenza transmission risk modeling. This project places special emphasis on wild bird distribution and abundance models as well as avian influenza prevalence models.
Developing Waterfowl Distribution and Abundance Models to Inform Avian Influenza Transmission Risk
USGS researchers are developing novel methods to improve our understanding of waterfowl distributions and abundance across the United States to inform a variety of ongoing disease studies. Understanding the distribution of wild waterfowl is a critical component to assessing avian influenza transmission risks across the landscape.
North American Bat Monitoring Program (NABat)
Bats are essential contributing members of healthy, functioning ecosystems. They perform numerous ecosystem services like insect pest control and plant pollination, and provide enormous economic benefits through ecotourism, medical research, and novel biotechnologies. North American bats face unprecedented threats including habitat loss and fragmentation, white-nose syndrome, and wind energy...
USGS Chronic Wasting Disease Research at NOROCK
Chronic wasting disease (CWD) is a growing management issue in the U.S. and has been detected in 36 states as of April 2025, including many western states. There is no cure or vaccine for CWD, and the disease threatens economically important animals like elk and deer. NOROCK scientists have taken a multi-pronged approach to develop actionable science including 1) evaluating CWD management options...
USGS Chronic Wasting Disease Research at the National Elk Refuge
Over the past 20 years, chronic wasting disease (CWD) in Wyoming has been spreading slowly outward from the southeastern corner of the state into the Greater Yellowstone Area and Wyoming's elk feed grounds. CWD detections have been getting closer to the National Elk Refuge, which provides supplemental feeding to approximately 8,000 elk and 500 bison each winter. NOROCK scientists have been...
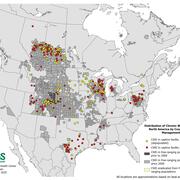
Expanding Distribution of Chronic Wasting Disease
Chronic wasting disease (CWD) has been detected in 36 US states and five Canadian provinces in free-ranging cervids and/or captive cervid facilities.