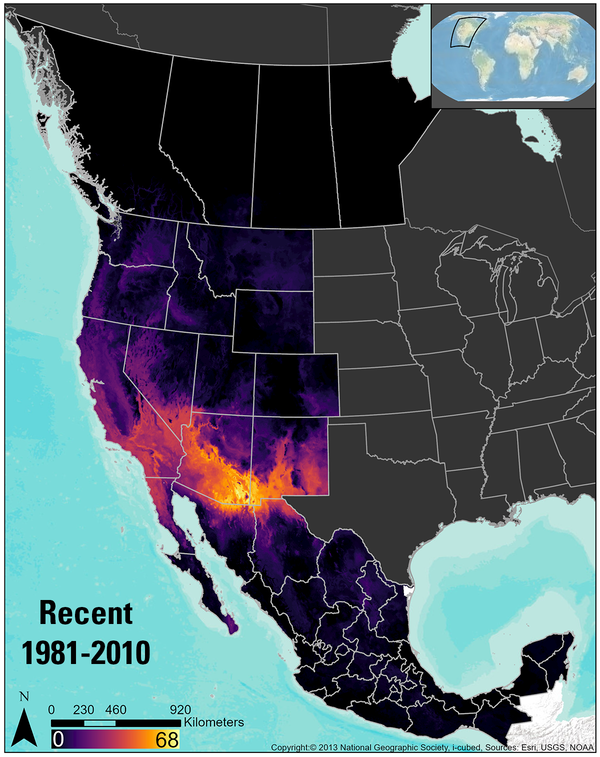
Reptile species richness and its predicted geographic change
Reptile species richness and its predicted geographic changeThe climate-niche distribution--or the areas with suitable climate for survival--were mapped 130 reptile species in the recent time period and predicted for the late-century time period under the RCP 8.5 climate scenario. The RCP 8.5 scenario assumes carbon emissions continue at their current levels.