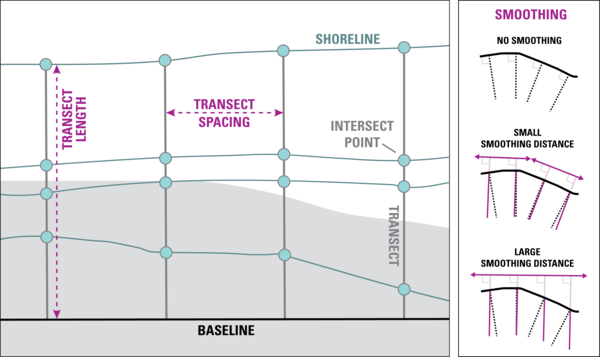
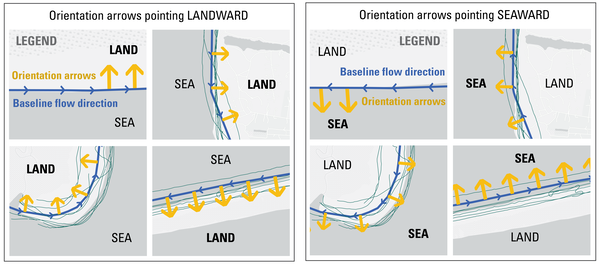
DSAS generates transects that are cast perpendicular to the reference baseline to intersect shorelines at a user-specified spacing alongshore.
Images
Woods Hole Coastal and Marine Science Center images
DSAS generates transects that are cast perpendicular to the reference baseline to intersect shorelines at a user-specified spacing alongshore.
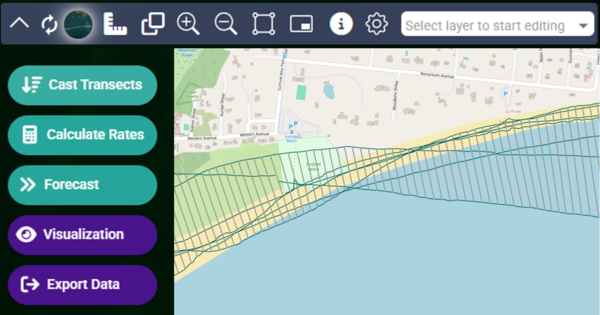
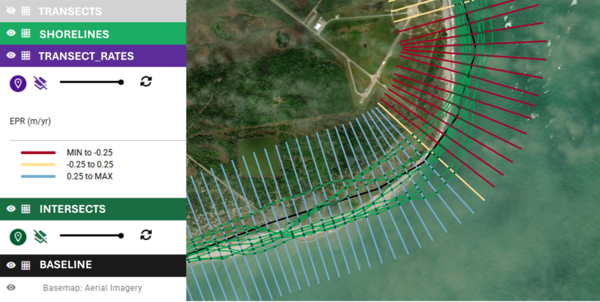
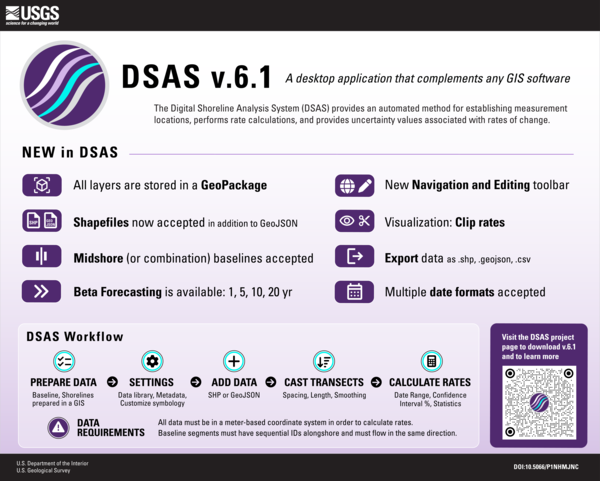
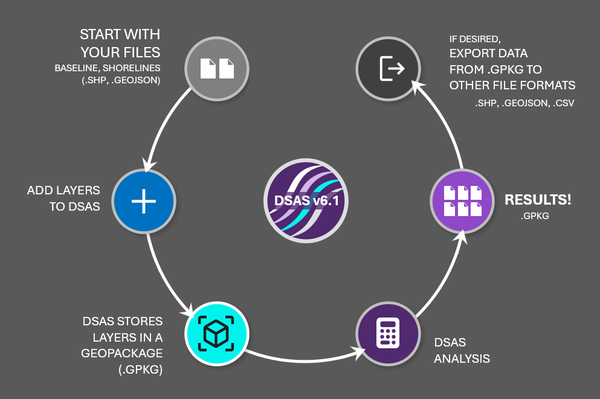
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
The Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) version 6 is a standalone application that calculates shoreline or boundary change over time. The GIS of a user’s choice is used to prepare the data for DSAS. Like previous versions, DSAS v.6 enables a user to calculate rate-of-change statistics from multiple historical shoreline positions.
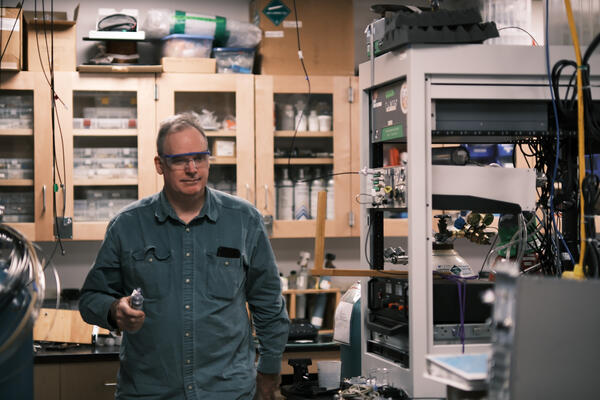
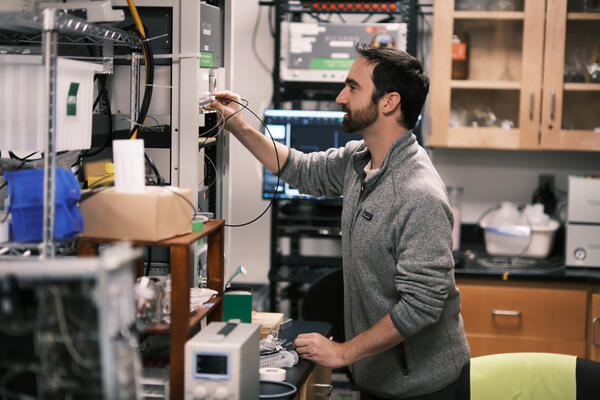
Testing a USGS patented device (DSIM) and measuring it's performance with a new analytical upgrade recently designed and installed. The DSIM allows for gas samples to be put into a spectrometer and measured in a closed loop, which increased the data signal fidelity, repeatability, and amount an analyte used.
Testing a USGS patented device (DSIM) and measuring it's performance with a new analytical upgrade recently designed and installed. The DSIM allows for gas samples to be put into a spectrometer and measured in a closed loop, which increased the data signal fidelity, repeatability, and amount an analyte used.
Testing a USGS patented device (DSIM) and measuring it's performance with a new analytical upgrade recently designed and installed. The DSIM allows for gas samples to be put into a spectrometer and measured in a closed loop, which increased the data signal fidelity, repeatability, and amount an analyte used.
Testing a USGS patented device (DSIM) and measuring it's performance with a new analytical upgrade recently designed and installed. The DSIM allows for gas samples to be put into a spectrometer and measured in a closed loop, which increased the data signal fidelity, repeatability, and amount an analyte used.
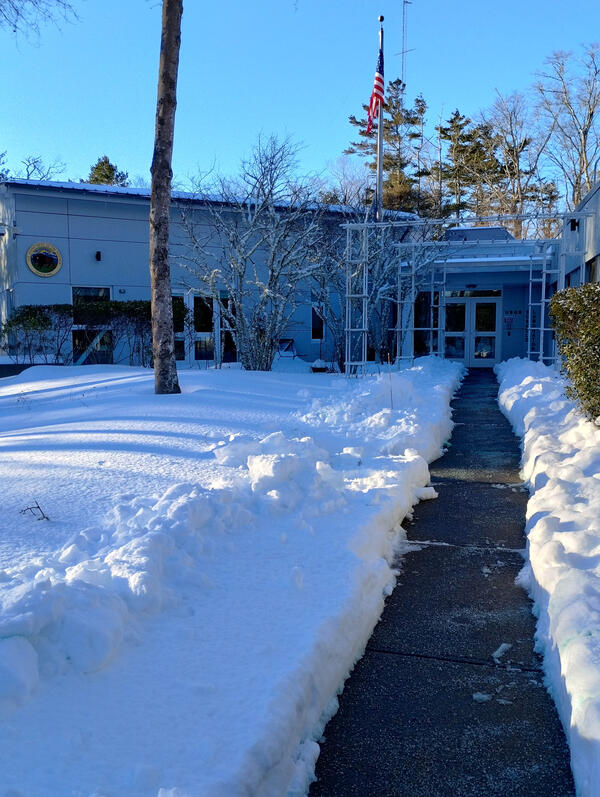
A snow covered science center in Woods Hole, Massachusetts after a powerful nor'easter hit the Cape Cod on January 25, 2026.
A snow covered science center in Woods Hole, Massachusetts after a powerful nor'easter hit the Cape Cod on January 25, 2026.
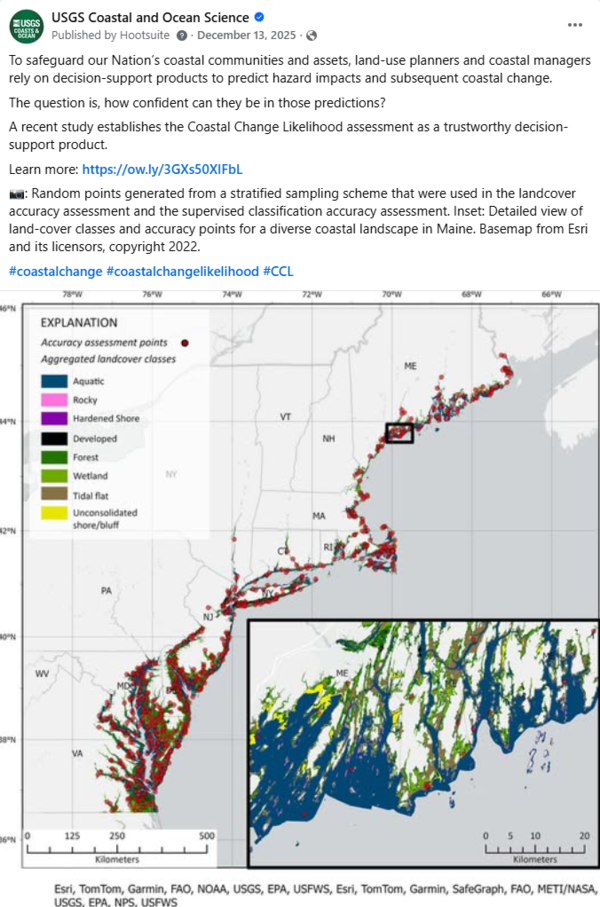
To safeguard our Nation’s coastal communities and assets, land-use planners and coastal managers rely on decision-support products to predict hazard impacts and subsequent coastal change. The question is, how confident can they be in those predictions?
To safeguard our Nation’s coastal communities and assets, land-use planners and coastal managers rely on decision-support products to predict hazard impacts and subsequent coastal change. The question is, how confident can they be in those predictions?
The USGS collected remote sensing data at Marconi Beach on Cape Cod National Seashore in Wellfleet, Massachusetts after fall storms in 2024 caused erosion and the loss of National Park Service beach access stairs.
The USGS collected remote sensing data at Marconi Beach on Cape Cod National Seashore in Wellfleet, Massachusetts after fall storms in 2024 caused erosion and the loss of National Park Service beach access stairs.
The #USGS deployed a nanopod off Marconi Beach, Wellfleet, MA, to measure winter wave conditions. They also collected sediment samples to characterize sediment grain size.
The #USGS deployed a nanopod off Marconi Beach, Wellfleet, MA, to measure winter wave conditions. They also collected sediment samples to characterize sediment grain size.
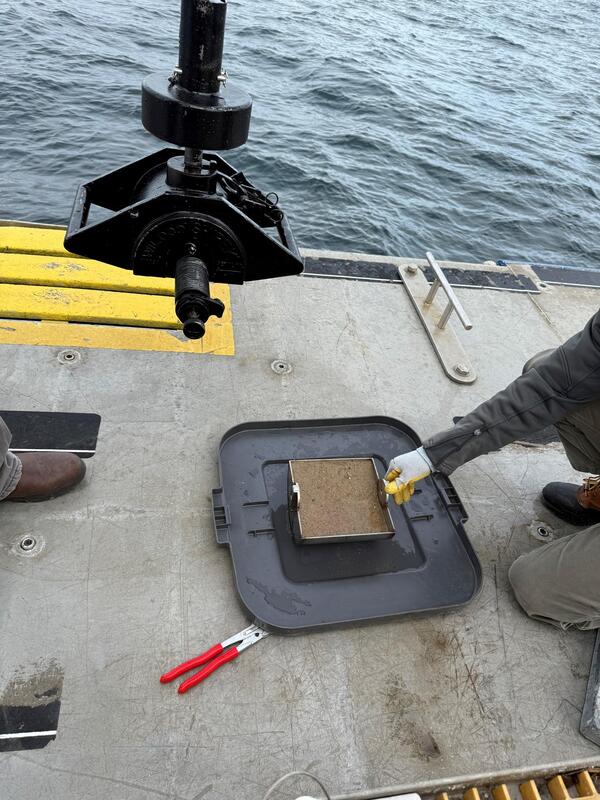
Shipek grab sampler and sediment sample. Image is included in USGS data release, "Grain-size analysis of sediment samples collected in the nearshore zone offshore of Marconi Beach, Wellfleet, MA, December 9, 2024."
Shipek grab sampler and sediment sample. Image is included in USGS data release, "Grain-size analysis of sediment samples collected in the nearshore zone offshore of Marconi Beach, Wellfleet, MA, December 9, 2024."
To assess our #sedimenttransport prediction techniques, #USGS scientists deployed a high-tech instrument off #SandyNeckBeach in Barnstable, Massachusetts from March-April 2021 to measure water velocity, temperature, and salinity, wave pressure, tidal force, seabed changes, and sediment characteristics.
To assess our #sedimenttransport prediction techniques, #USGS scientists deployed a high-tech instrument off #SandyNeckBeach in Barnstable, Massachusetts from March-April 2021 to measure water velocity, temperature, and salinity, wave pressure, tidal force, seabed changes, and sediment characteristics.
The USGS uses a nationwide network of coastal observing cameras (CoastCams) to monitor coastal conditions in near real-time and support research on a variety of coastal processes and hazards.
The USGS uses a nationwide network of coastal observing cameras (CoastCams) to monitor coastal conditions in near real-time and support research on a variety of coastal processes and hazards.
A new study introduces a cutting-edge biogeomorphic model (UBMorph) to help predict how #ChesapeakeBay #saltmarshes will change over time. Using UBMorph, researchers found that 404 square kilometers (37%) of vegetated #marsh area in Chesapeake Bay could be lost by 2110.
A new study introduces a cutting-edge biogeomorphic model (UBMorph) to help predict how #ChesapeakeBay #saltmarshes will change over time. Using UBMorph, researchers found that 404 square kilometers (37%) of vegetated #marsh area in Chesapeake Bay could be lost by 2110.

Social Media: Shoreline Change of Long Island Sound
Social Media: Shoreline Change of Long Island SoundA new #datarelease contains a GIS compilation of vector shorelines and associated #shorelinechange data from the 1800s to the 2010s for the coast of Long Island Sound, #NewYork and #Connecticut.
Social Media: Shoreline Change of Long Island Sound
Social Media: Shoreline Change of Long Island SoundA new #datarelease contains a GIS compilation of vector shorelines and associated #shorelinechange data from the 1800s to the 2010s for the coast of Long Island Sound, #NewYork and #Connecticut.
ROV pilots Raeylynn Heinz and Alex Wick (both from OSU OOI) celebrate as their ROV and the OBS surface in Skilak Lake.
ROV pilots Raeylynn Heinz and Alex Wick (both from OSU OOI) celebrate as their ROV and the OBS surface in Skilak Lake.
View from the remotely operated vehicle (ROV) after attaching a recovery line to the ocean bottom seismograph 190 meters deep in Skilak Lake, Alaska.
View from the remotely operated vehicle (ROV) after attaching a recovery line to the ocean bottom seismograph 190 meters deep in Skilak Lake, Alaska.
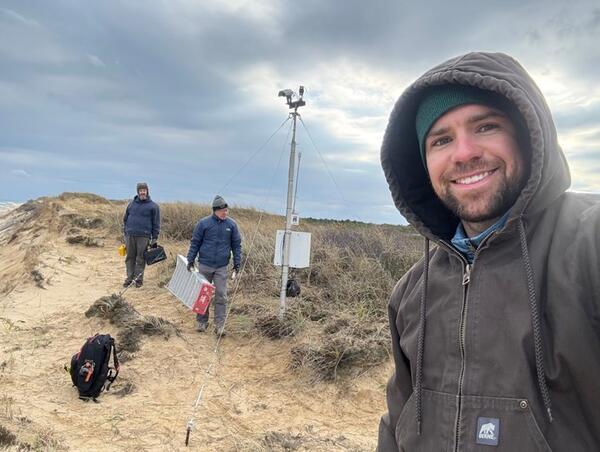
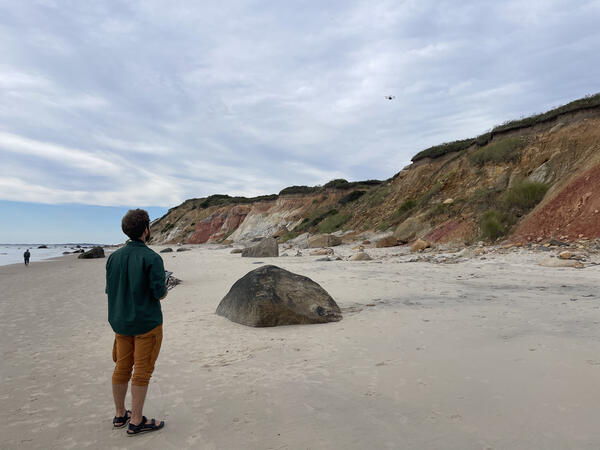
The USGS Aerial Imaging and Mapping Group (AIMG) collaborated with the Wampanoag Tribe of Gay Head (Aquinnah), the Town of Aquinnah, and the Aquinnah Police Department to collect high-resolution data of the Gay Head Cliffs.
The USGS Aerial Imaging and Mapping Group (AIMG) collaborated with the Wampanoag Tribe of Gay Head (Aquinnah), the Town of Aquinnah, and the Aquinnah Police Department to collect high-resolution data of the Gay Head Cliffs.
The USGS Aerial Imaging and Mapping Group (AIMG) collaborated with the Wampanoag Tribe of Gay Head (Aquinnah), the Town of Aquinnah, and the Aquinnah Police Department to collect high-resolution data of the Gay Head Cliffs.
The USGS Aerial Imaging and Mapping Group (AIMG) collaborated with the Wampanoag Tribe of Gay Head (Aquinnah), the Town of Aquinnah, and the Aquinnah Police Department to collect high-resolution data of the Gay Head Cliffs.