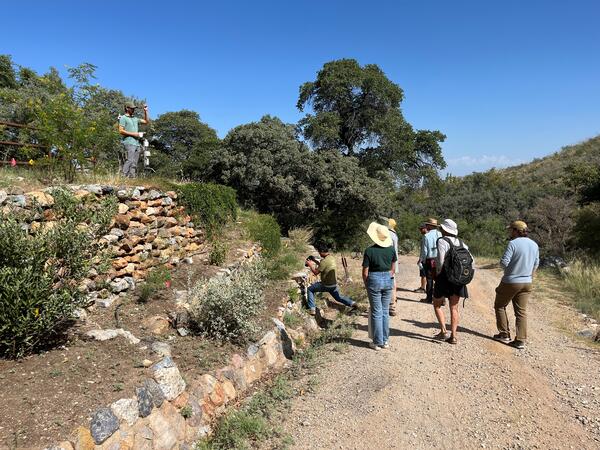
Albert Klein (University of Arizona) shows the pollinator garden designed and installed by University of Arizona students at the Santa Rita Experimental Range. Photo by Laura Shriver (USGS).
Images
See more about our science.
Albert Klein (University of Arizona) shows the pollinator garden designed and installed by University of Arizona students at the Santa Rita Experimental Range. Photo by Laura Shriver (USGS).

Long camelthorn rhizomes exposed in a wash at Wupatki National Monument
Long camelthorn rhizomes exposed in a wash at Wupatki National MonumentUSGS Biological Science Technician Claudia Dimartini poses with a long camelthorn (Alhagi maurorum) rhizome (underground root structure from which new plants can propagate that was exposed in a wash at the Deadman Wash Confluence Area. Photo by Laura Shriver (USGS).
Long camelthorn rhizomes exposed in a wash at Wupatki National Monument
Long camelthorn rhizomes exposed in a wash at Wupatki National MonumentUSGS Biological Science Technician Claudia Dimartini poses with a long camelthorn (Alhagi maurorum) rhizome (underground root structure from which new plants can propagate that was exposed in a wash at the Deadman Wash Confluence Area. Photo by Laura Shriver (USGS).
Sarah Costanzo (USGS) collects soil stability data prior to installing RestoreNet version 2.0 treatments at Canyonlands Research Center near Moab, UT. Photo by Laura Shriver (USGS).
Sarah Costanzo (USGS) collects soil stability data prior to installing RestoreNet version 2.0 treatments at Canyonlands Research Center near Moab, UT. Photo by Laura Shriver (USGS).

Soil and restoration science booth at USGS Flagstaff Science Center Open House
Soil and restoration science booth at USGS Flagstaff Science Center Open HouseLaura Shriver at the soil and restoration science booth at the USGS Flagstaff Science Center Open House. The booth included native seeds, biocrusts, a soil texturing activity, and science brief handouts.
Soil and restoration science booth at USGS Flagstaff Science Center Open House
Soil and restoration science booth at USGS Flagstaff Science Center Open HouseLaura Shriver at the soil and restoration science booth at the USGS Flagstaff Science Center Open House. The booth included native seeds, biocrusts, a soil texturing activity, and science brief handouts.

Celebrating a successful restoration experiment installation
Celebrating a successful restoration experiment installationFrom left to right, Ember Bradbury (Colorado State University), Sarah Costanzo (USGS), Sonoma Brill (USGS), and Laura Shriver (USGS) celebrate installing a RestoreNet site at Canyonlands Research Center near Moab, UT.
Celebrating a successful restoration experiment installation
Celebrating a successful restoration experiment installationFrom left to right, Ember Bradbury (Colorado State University), Sarah Costanzo (USGS), Sonoma Brill (USGS), and Laura Shriver (USGS) celebrate installing a RestoreNet site at Canyonlands Research Center near Moab, UT.
A landscape of sagebrush (Artemisia tridentada) and yellow sweet clover (Melilotus officinalis) on the Charles M. Russell National Wildlife Refuge in Montana.
A landscape of sagebrush (Artemisia tridentada) and yellow sweet clover (Melilotus officinalis) on the Charles M. Russell National Wildlife Refuge in Montana.
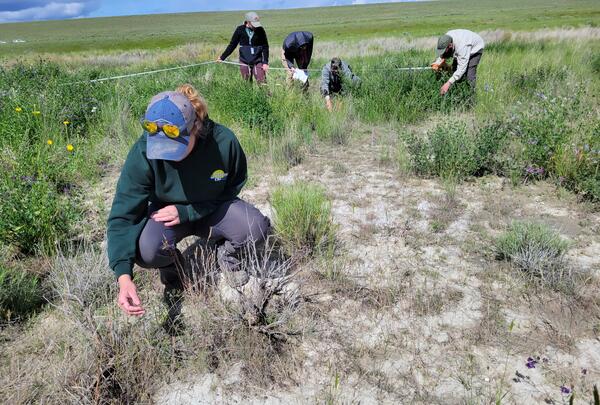
A storm rolls in during field work at the Charles M. Russell National Wildlife Refuge in Montana. Crews were measuring plant cover and other site characteristics. Sagebrush and yellow sweet clover are visible.
A storm rolls in during field work at the Charles M. Russell National Wildlife Refuge in Montana. Crews were measuring plant cover and other site characteristics. Sagebrush and yellow sweet clover are visible.
A five-person USGS crew collecting Rapid and Other Assessment and Monitoring (ROAM) density data in southwest Idaho. One person is inspecting a plant in the foreground, while the rest of the team are identifying and counting individual plants during a radial density belt.
A five-person USGS crew collecting Rapid and Other Assessment and Monitoring (ROAM) density data in southwest Idaho. One person is inspecting a plant in the foreground, while the rest of the team are identifying and counting individual plants during a radial density belt.
A downward-facing photo taken on a Rapid and Other Methods for Assessment and Monitoring (ROAM) plot that is within a fuel break. The photo includes a lot of gravel and bare ground, with intermixed small grasses, forbs, and shrubs.
A downward-facing photo taken on a Rapid and Other Methods for Assessment and Monitoring (ROAM) plot that is within a fuel break. The photo includes a lot of gravel and bare ground, with intermixed small grasses, forbs, and shrubs.
Many new big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) plants that have just sprouted from the ground in the Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area in Idaho.
Many new big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) plants that have just sprouted from the ground in the Morley Nelson Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area in Idaho.
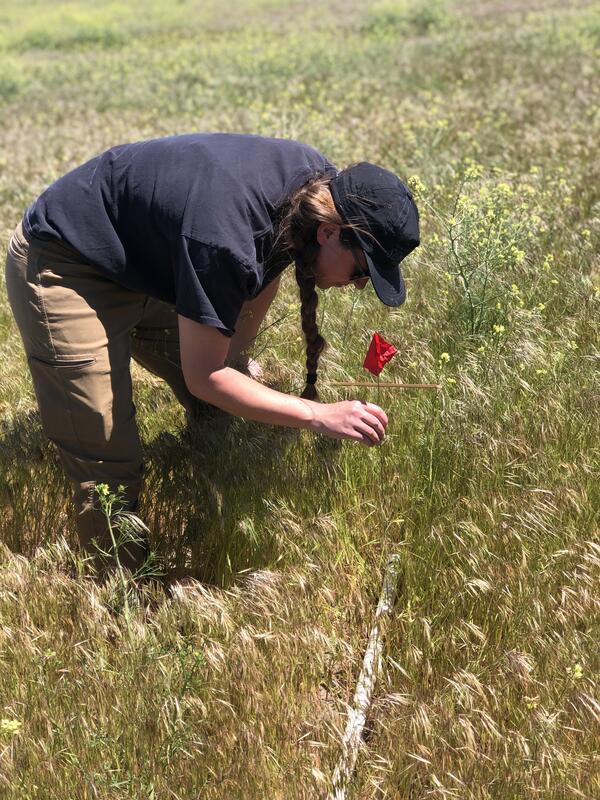
A field crew member collecting stick-point intercept data at a Project ROAM (Rapid and Other Methods for Assessment and Monitoring) plot. A meter-long 'stick' is dropped and five recordings of vegetation are collected by dropping a pin flag along the stick. The vegetation it comes into contact with is recorded to estimate cover.
A field crew member collecting stick-point intercept data at a Project ROAM (Rapid and Other Methods for Assessment and Monitoring) plot. A meter-long 'stick' is dropped and five recordings of vegetation are collected by dropping a pin flag along the stick. The vegetation it comes into contact with is recorded to estimate cover.

Cattle at a Northern Arizona RestoreNet experimental study site, Bar T Bar Ranch, AZ
Cattle at a Northern Arizona RestoreNet experimental study site, Bar T Bar Ranch, AZCattle inside a grazing enclosure at the Bar T Bar Ranch RestoreNet site in Northern Arizona.
Cattle at a Northern Arizona RestoreNet experimental study site, Bar T Bar Ranch, AZ
Cattle at a Northern Arizona RestoreNet experimental study site, Bar T Bar Ranch, AZCattle inside a grazing enclosure at the Bar T Bar Ranch RestoreNet site in Northern Arizona.

RAMPS employees and partners pose in front of a cattle grazing enclosure at a RestoreNet site
RAMPS employees and partners pose in front of a cattle grazing enclosure at a RestoreNet siteFrom left to right: RAMPS Ecologist Seth Munson, RAMPS Coordinator Laura Shriver, RAMPS Biologist Sarah Costanzo, NAU postdoctoral researcher Collin VanBuren, and Diablo Trust Program Manager Corinne LaViolette. Photo by Seth Munson (USGS).
RAMPS employees and partners pose in front of a cattle grazing enclosure at a RestoreNet site
RAMPS employees and partners pose in front of a cattle grazing enclosure at a RestoreNet siteFrom left to right: RAMPS Ecologist Seth Munson, RAMPS Coordinator Laura Shriver, RAMPS Biologist Sarah Costanzo, NAU postdoctoral researcher Collin VanBuren, and Diablo Trust Program Manager Corinne LaViolette. Photo by Seth Munson (USGS).

Newly installed RestoreNet treatments including pits + seedballs + live topsoil and live topsoil + direct seeding
Newly installed RestoreNet treatments including pits + seedballs + live topsoil and live topsoil + direct seedingNewly installed RestoreNet Version 2.0 treatment plots at Bar T Bar Ranch in Northern Arizona. Left: a plot that received pitting + seedballs + live topsoil inoculum (in the seedballs), Right: a plot that received live topsoil inoculum (spread across the plot) and direct seeding.
Newly installed RestoreNet treatments including pits + seedballs + live topsoil and live topsoil + direct seeding
Newly installed RestoreNet treatments including pits + seedballs + live topsoil and live topsoil + direct seedingNewly installed RestoreNet Version 2.0 treatment plots at Bar T Bar Ranch in Northern Arizona. Left: a plot that received pitting + seedballs + live topsoil inoculum (in the seedballs), Right: a plot that received live topsoil inoculum (spread across the plot) and direct seeding.

Bike-produced seedballs before field implementation
Bike-produced seedballs before field implementationSeedballs produced by a seedball bike drying before field implementation. The seedball bike was constructed at USGS with help from the University of Arizona and Northern Arizona University for RestoreNet restoration experiments.
Bike-produced seedballs before field implementation
Bike-produced seedballs before field implementationSeedballs produced by a seedball bike drying before field implementation. The seedball bike was constructed at USGS with help from the University of Arizona and Northern Arizona University for RestoreNet restoration experiments.

Laura Norman with graduate students in Baja California Sur
Laura Norman with graduate students in Baja California SurNorman with graduate students from the Academic Department of Earth Sciences at the Autonomous University of Baja California Sur (UABCS) teaching high school students from El Sargento at the “Caminos Del Agua” Water Festival (photo by Alfredo Martinez, March 11, 2024).
Laura Norman with graduate students in Baja California Sur
Laura Norman with graduate students in Baja California SurNorman with graduate students from the Academic Department of Earth Sciences at the Autonomous University of Baja California Sur (UABCS) teaching high school students from El Sargento at the “Caminos Del Agua” Water Festival (photo by Alfredo Martinez, March 11, 2024).

RAMPS Biologist rides a seedball bike to make seedballs for RestoreNet restoration
RAMPS Biologist rides a seedball bike to make seedballs for RestoreNet restorationRAMPS Biologist Sarah Costanzo rides a seedball bike designed to create seedballs (mixes of seed, clay, and other materials) for RestoreNet restoration
RAMPS Biologist rides a seedball bike to make seedballs for RestoreNet restoration
RAMPS Biologist rides a seedball bike to make seedballs for RestoreNet restorationRAMPS Biologist Sarah Costanzo rides a seedball bike designed to create seedballs (mixes of seed, clay, and other materials) for RestoreNet restoration
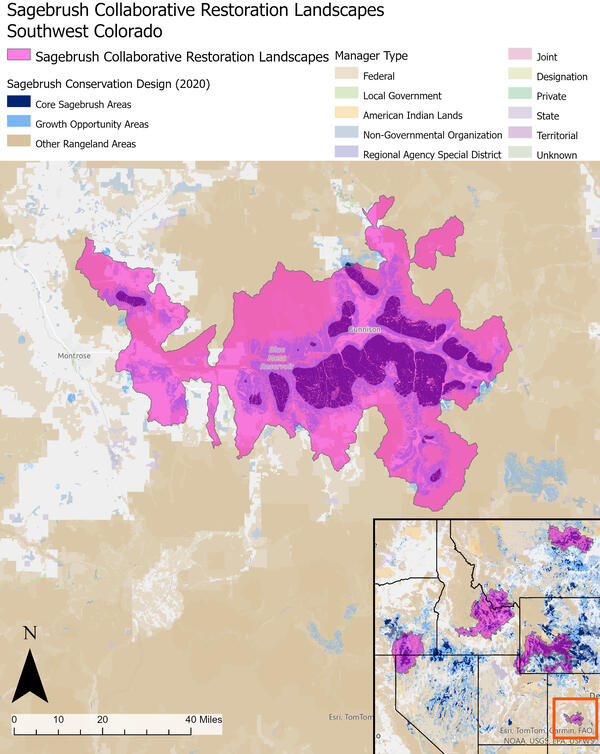
Southwest Colorado Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscape
Southwest Colorado Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration LandscapeSagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.
Southwest Colorado Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscape
Southwest Colorado Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration LandscapeSagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.

Northern Montana Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscape
Northern Montana Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration LandscapeSagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.
Northern Montana Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscape
Northern Montana Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration LandscapeSagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.

Wyoming and Northeast Utah Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscape
Wyoming and Northeast Utah Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration LandscapeSagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.
Wyoming and Northeast Utah Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscape
Wyoming and Northeast Utah Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration LandscapeSagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.
Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.
Layer Sources
Sagebrush Collaborative Restoration Landscapes capture over a third of the remaining intact Core Sagebrush Areas across the sagebrush biome.
Layer Sources










