A map of the United States including Hawaii, Alaska, and Puerto Rico shows landslide susceptibility from yellow (low) to red (high), where the areas without shading represent negligible potential for landslides.
Images
Browse our photos of landslide research and post-landslide investigations.
A map of the United States including Hawaii, Alaska, and Puerto Rico shows landslide susceptibility from yellow (low) to red (high), where the areas without shading represent negligible potential for landslides.
¿Dónde Ocurren los Deslizamientos de Tierra?
(Mapa Nacional de Susceptibilidad a Deslizamientos de Tierra, 2024)
¿Dónde Ocurren los Deslizamientos de Tierra?
(Mapa Nacional de Susceptibilidad a Deslizamientos de Tierra, 2024)
Damaged trees and debris deposited from the tsunami caused by the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide in Alaska.
Damaged trees and debris deposited from the tsunami caused by the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide in Alaska.
Photo looking towards the landslide source, with debris from the subsequent tsunami in the foreground.
Photo looking towards the landslide source, with debris from the subsequent tsunami in the foreground.

2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Flattened Vegetation
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Flattened VegetationFlattened vegetation due to the tsunami caused by the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide in Alaska.
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Flattened Vegetation
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Flattened VegetationFlattened vegetation due to the tsunami caused by the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide in Alaska.

2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Tsunami Damage Surveying
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Tsunami Damage SurveyingGeologist conducts a survey of the tsunami damage following the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide in Alaska.
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Tsunami Damage Surveying
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Tsunami Damage SurveyingGeologist conducts a survey of the tsunami damage following the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide in Alaska.

2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Source Area and Runout
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Source Area and RunoutLandslide source area and upper portion of the landslide runout. The upper reaches of the landslide source material of the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon landslide in Alaska.
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Source Area and Runout
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Source Area and RunoutLandslide source area and upper portion of the landslide runout. The upper reaches of the landslide source material of the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon landslide in Alaska.
Lower portion of the landslide runout along the Pedersen Glacier from the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon landslide in Alaska.
Lower portion of the landslide runout along the Pedersen Glacier from the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon landslide in Alaska.
Tsunami damage between the upper and lower portions of the lagoon from the landslide-generated tsunami from the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon landslide in Alaska. It moved toward the east at the western shore and uplands of the landform between the lagoons.
Tsunami damage between the upper and lower portions of the lagoon from the landslide-generated tsunami from the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon landslide in Alaska. It moved toward the east at the western shore and uplands of the landform between the lagoons.

2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Before/After Imagery Gif
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Before/After Imagery GifAnimation of satellite images from the 4 August and 9 August, 2024, showing the extent of vegetation damage due to the landslide-generated tsunami.
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Before/After Imagery Gif
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Before/After Imagery GifAnimation of satellite images from the 4 August and 9 August, 2024, showing the extent of vegetation damage due to the landslide-generated tsunami.
Map showing location of landslide initiation for the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide (yellow circle), approximate travel path to water (black dotted line with arrow), and preliminary estimates of tsunami height.
Map showing location of landslide initiation for the 2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide (yellow circle), approximate travel path to water (black dotted line with arrow), and preliminary estimates of tsunami height.
Seismic signals from the August 7, 2024 Pedersen Lagoon (Alaska) tsunamigenic landslide recorded on seismic station AK.SWD, located approximately 30 km from the landslide location. Three directions of ground motion are shown. The landslide signal is followed by a long-duration, resonating signal characteristic of a seiche in the lagoon.
Seismic signals from the August 7, 2024 Pedersen Lagoon (Alaska) tsunamigenic landslide recorded on seismic station AK.SWD, located approximately 30 km from the landslide location. Three directions of ground motion are shown. The landslide signal is followed by a long-duration, resonating signal characteristic of a seiche in the lagoon.
Overview map and location of the landslide-generated tsunami event within Alaska (inset) and Kenai Fjords National Park.
Overview map and location of the landslide-generated tsunami event within Alaska (inset) and Kenai Fjords National Park.

2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Sentinel 2 NIR Time-Lapse GIF
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Sentinel 2 NIR Time-Lapse GIFAnimation of Sentinel-2 near-infrared (NIR) satellite images from 19 July, 27 July, and 9 August 2024, showing landslide-generated tsunami. Increase in dark/black areas on the land on 9 August show the extent of damage from the tsunami.
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Sentinel 2 NIR Time-Lapse GIF
2024 Pedersen Lagoon Landslide Sentinel 2 NIR Time-Lapse GIFAnimation of Sentinel-2 near-infrared (NIR) satellite images from 19 July, 27 July, and 9 August 2024, showing landslide-generated tsunami. Increase in dark/black areas on the land on 9 August show the extent of damage from the tsunami.
USGS scientists Bill Schulz and Mason Einbund collaborate with University of Puerto Rico-Mayagüez professor Stephen Hughes at Yabucoa, Puerto Rico landslide monitoring station.
USGS scientists Bill Schulz and Mason Einbund collaborate with University of Puerto Rico-Mayagüez professor Stephen Hughes at Yabucoa, Puerto Rico landslide monitoring station.
This is a cover photo for the Landslide Basics node with the title next to an illustration of a landslide.
This is a cover photo for the Landslide Basics node with the title next to an illustration of a landslide.
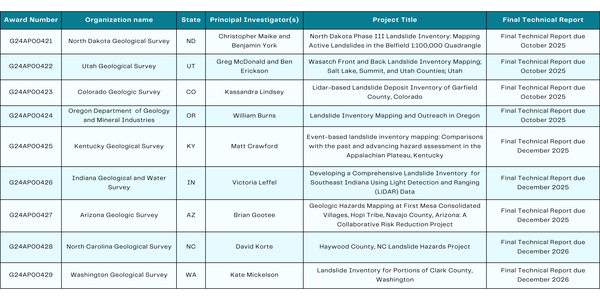
Table displaying the USGS Landslide external grant recipients. The information for each recipient organization, project title, and principal investigators is included.
Table displaying the USGS Landslide external grant recipients. The information for each recipient organization, project title, and principal investigators is included.
Text "Landslide Basics" on green background, infographic made for landslide basics page
Text "Landslide Basics" on green background, infographic made for landslide basics page
Flooding and debris flows during rain events following the 2024 South Fork Fire near Ruidoso, New Mexico.
Flooding and debris flows during rain events following the 2024 South Fork Fire near Ruidoso, New Mexico.
A road sign in the 2024 South Fork Fire, Lincoln National Forest, New Mexico warns of flooding and debris flow hazards. Partially burned trees are visible on the hillslope in the image background. Mud and other debris moved down the slope and were deposited along the road, near the base of the sign.
A road sign in the 2024 South Fork Fire, Lincoln National Forest, New Mexico warns of flooding and debris flow hazards. Partially burned trees are visible on the hillslope in the image background. Mud and other debris moved down the slope and were deposited along the road, near the base of the sign.
Fast-moving, highly destructive debris flows triggered by intense rainfall are one of the most dangerous post-fire hazards. The risk of floods and debris flows after fires increases due to vegetation loss and soil exposure. Cases of sudden and deadly debris flow are well documented along the western United States, particularly in Southern California.
Fast-moving, highly destructive debris flows triggered by intense rainfall are one of the most dangerous post-fire hazards. The risk of floods and debris flows after fires increases due to vegetation loss and soil exposure. Cases of sudden and deadly debris flow are well documented along the western United States, particularly in Southern California.