Toxins and Harmful Algal Blooms Science Team
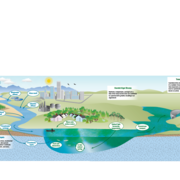
The team develops advanced methods to study factors driving algal toxin production, how and where wildlife or humans are exposed to toxins, and ecotoxicology. That information is used to develop decision tools to understand if toxin exposure leads to adverse health effects in order to protect human and wildlife health.